 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
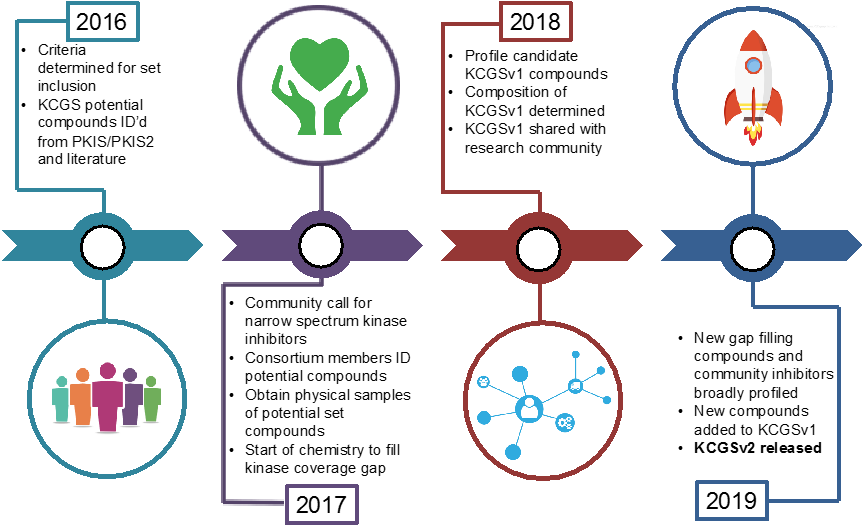
Kinases are important drug targets, yet industry and academia have focused on only a small subset of the kinome. To expedite kinome-wide target discovery, we have begun construction of a comprehensive kinase chemogenomic set (KCGS). Our goal is to create and distribute a set of well-annotated kinase inhibitors that can be screened in a broad range of disease relevant phenotypic assays. The set is designed in such a way that the results of phenotypic screening point to important kinases to study in more depth. The set will be comprised of kinase inhibitors that each individually only inhibit a small subset of kinases (we call this narrow profile), but together explore inhibition across the kinome. We call the methodology “kinase chemogenomics” since it seeks to use a set of small molecule kinase inhibitors to interrogate the biology of all kinase gene products in cells.
How to get involved:
We see the creation of this set as a collaborative project between industrial and academic scientists. By making this resource publically available the KCGS will accelerate basic research into the biological function and therapeutic potential of hundreds of understudied protein kinases. Our goal, with the help of the research community, is to complete this set by the end of 2019.
For additional information please see our recent publication.
Scientists with interest in joining the consortium should contact David Drewry by email at david.drewry@unc.edu.
We are currently building a kinase chemogenomic consortium open to any scientist who wishes to contribute to the creation of the comprehensive KCGS as a public resource. Membership in the consortium allows for access to pre-publication kinase screening data, medicinal chemistry collaboration with our team, broad kinome screening as required to ensure compound suitability, and a copy of the complete set, once finalized and created, for screening in phenotypic screens. We welcome contributions of existing kinase inhibitors and submission of ideas for synthesis of new inhibitors that address any of the gap kinases.
