This probe is available from Cayman Chemical, Sigma and Tocris
| Probe |
 |
IOX2 |
Biology of the hypoxia inducible factor (HIF) prolyl-hydroxylases
Levels of the Hypoxia Inducible Factor (HIF), a master regulator of the cellular-response to hypoxia, are regulated by the post-translational modification of prolyl-residues in oxygen-dependent degradation domains in the HIFα subunit. HIFα prolyl-hydroxylation signals for its degradation by the proteasome. The requirement of the HIF prolyl-hydroxylases (PHD or EGLN enzymes) for dioxygen as a co-substrate enables them to act as the hypoxia-sensing component of the HIF system. PHDs are members of the 2-oxoglutarate (2OG-dependent) oxygenase superfamily. Inhibition of the PHDs reduces HIFα prolyl-hydroxylation thereby elevating HIF levels and artificially inducing the hypoxic response. Because HIF-target genes include those encoding for biomedically important proteins such as erythropoietin (EPO) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), PHD inhibition is of considerable medical interest.
IOX2: A chemical probe for HIF prolyl-hydroxylases
IOX2, a chemical probe for HIF prolyl-hydroxylases is the result of collaborations with the University of Sevilla, Genome Institute of Singapore, University of Sheffield, University of Oxford, BioNanotechnology Research Center KRIBB and the SGC [1].
Potency Against Target Family
IOX2 displayed an AlphaScreen IC50 of 22nM for inhibition of PHD2
Selectivity Beyond Target Family
IOX2 was found to be inactive against a panel of 55 receptors and ion channels (CEREP panel) at 10µM.
Co-crystal structure
The co-crystal structure of IOX2 with PHD2 has NOT been solved, however, there is a crystal structure with a close analogue (pdb id: 4BQW). This analogue has a methyl rather than benzyl group on the isoquinoline nitrogen. Please click on the 'Co-Crystal structures' tab above for more details.
Cellular Activity
IOX2 showed selective inhibition (by Western blot) of PHD catalysed HIF-1α prolyl-hydroxylation in a variety of human cell lines including renal carcinoma (RCC4) cell line lacking VHL, embryonic kidney (293T), bone osteosarcoma (U2OS) and RCC4 reexpressing VHL (RCC4/VHL) cells.
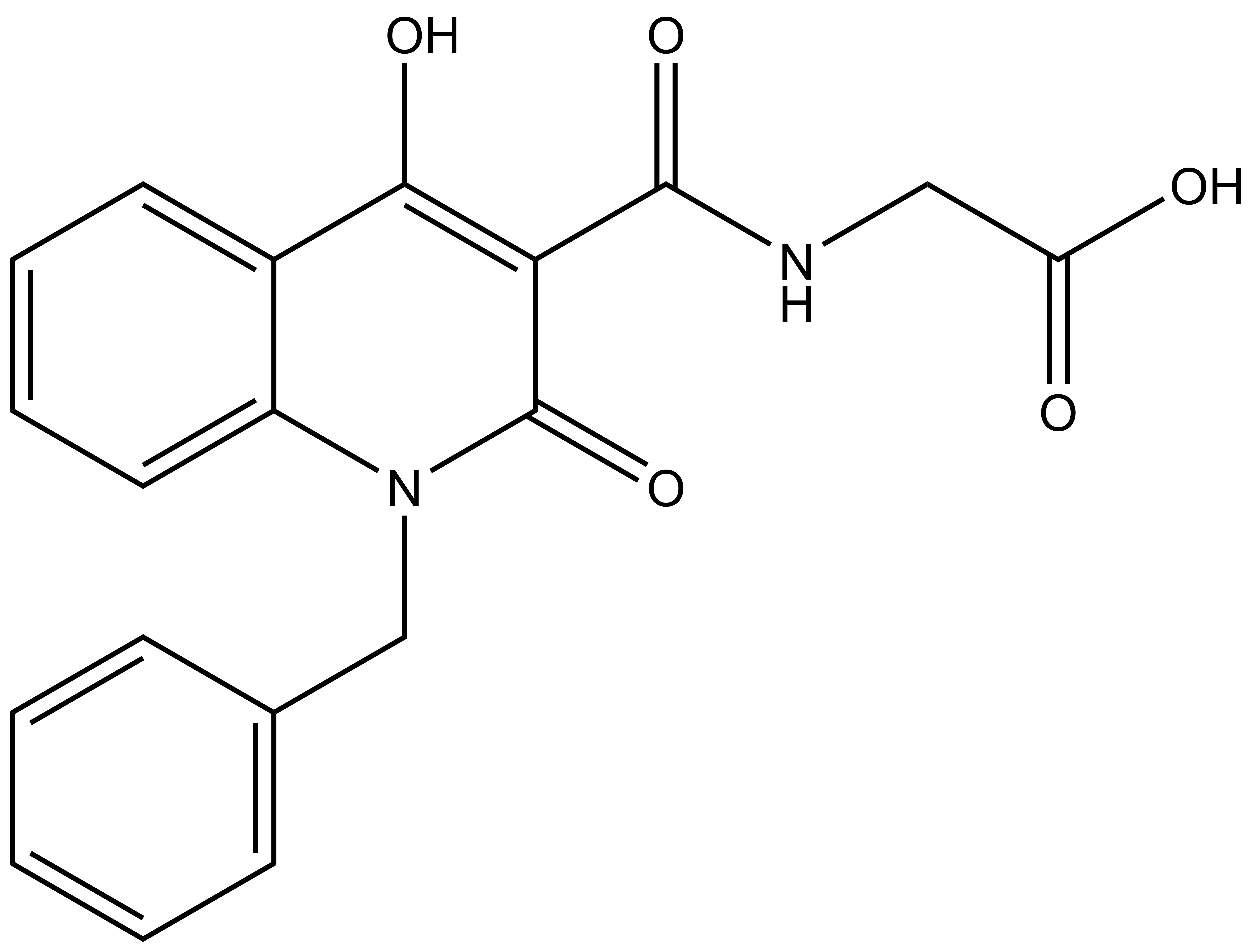 |
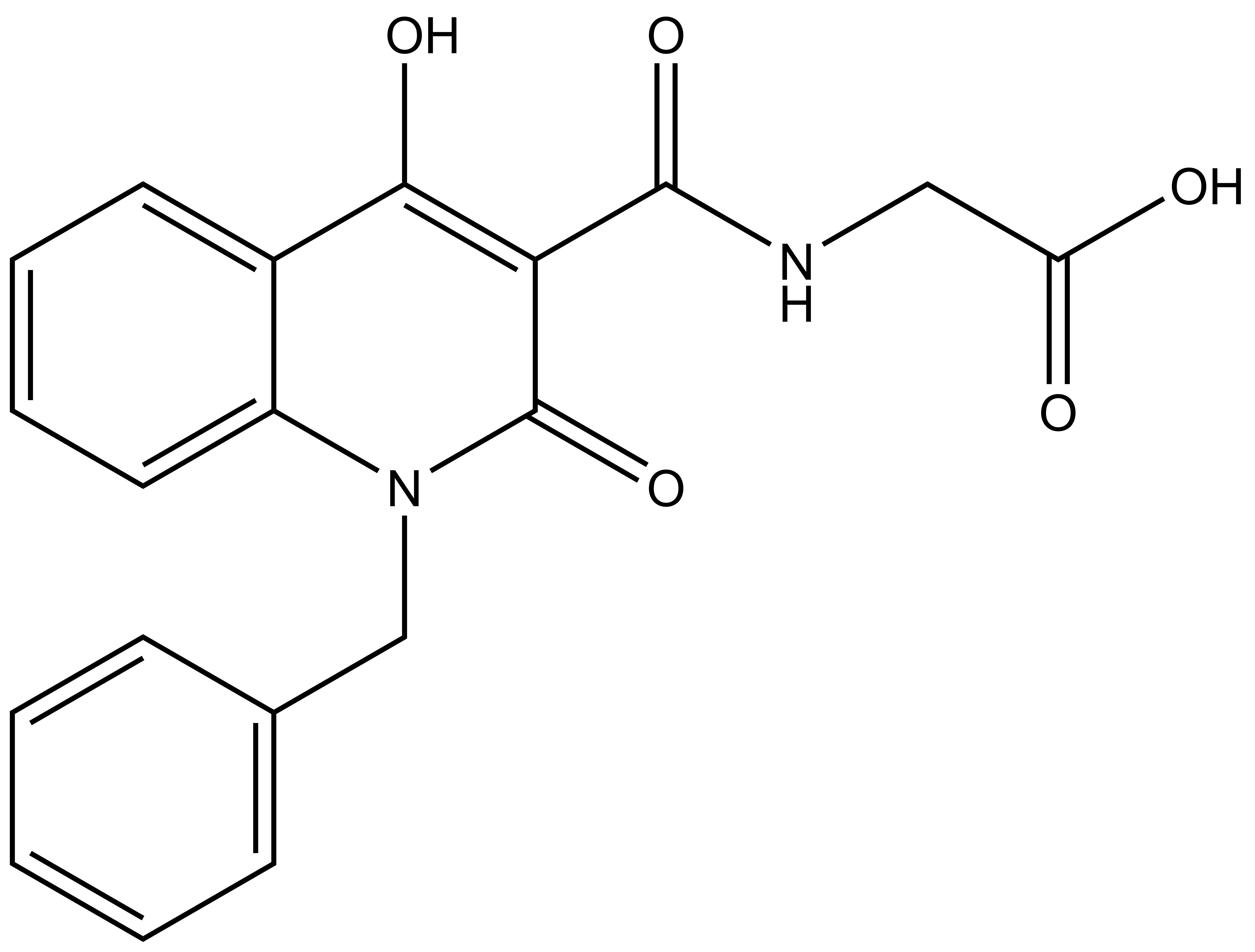
(1-benzyl-4-hydroxy-2-oxo-1, 2-dihydroquinoline-3-carbonyl)glycine |
| Physical and chemical properties | |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | 352.35 |
| Molecular formula | C19H16N2O5 |
| IUPAC name | (1-benzyl-4-hydroxy-2-oxo-1,2-dihydroquinoline-3-carbonyl)glycine |
| logP | -3.99 |
| PSA | |
| No. of chiral centres | 0 |
| No. of rotatable bonds | 5 |
| No. of hydrogen bond acceptors | 7 |
| No. of hydrogen bond donors | 3 |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| Dissolution | Soluble to 100 uM in DMSO |
An inactive, negative control for IOX2 has not yet been identified
IOX2 displayed an AlphaScreen IC50 of 22nM for inhibition of PHD2; values for each data point are averages ± standard deviation (n≥3).
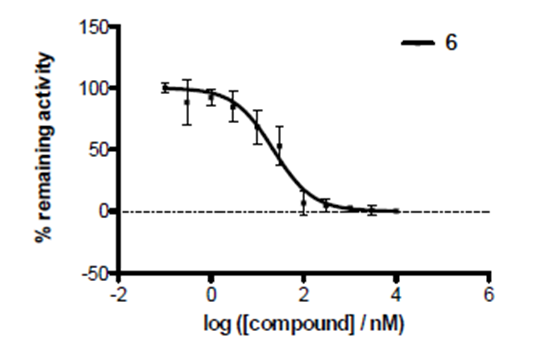
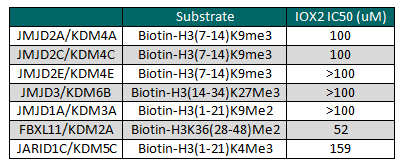
IOX2 was profiled against a panel of human histone Nε-methyl lysine demethylase 2OG-oxygenases in an AlphaScreen assay to determine selectivity.
IOX2 was found to be inactive against a panel of 55 receptors and ion channels (CEREP panel) at 10µM.
Engagement of IOX2 in an in vitro cell assay
Efficacy of IOX2 in a human renal carcinoma (RCC4) cell line lacking VHL (required for the degradation of hydroxylated HIF-α) was established, using antibodies selective for hydroxylated form(s) of a peptide corresponding to the HIF-1α C-terminal oxygen-dependent degradation domain to probe for PHD catalysed inhibition of HIF prolyl-hydroxylation in comparison to FIH catalysed asparaginyl-hydroxylation. IOX2 was further tested in VHL-competent cell lines, including human embryonic kidney (293T), human bone osteosarcoma (U2OS) and RCC4 reexpressing VHL (RCC4/VHL) cells, where increased HIF-1α levels were used as an indicator for PHD inhibition. IOX2 effectively increased HIF-1α levels in all tested VHL-competent cell lines showing that the inhibitory effects are independent of cell type. These results establish that IOX2 is a potent and selective cellular PHD inhibitor.
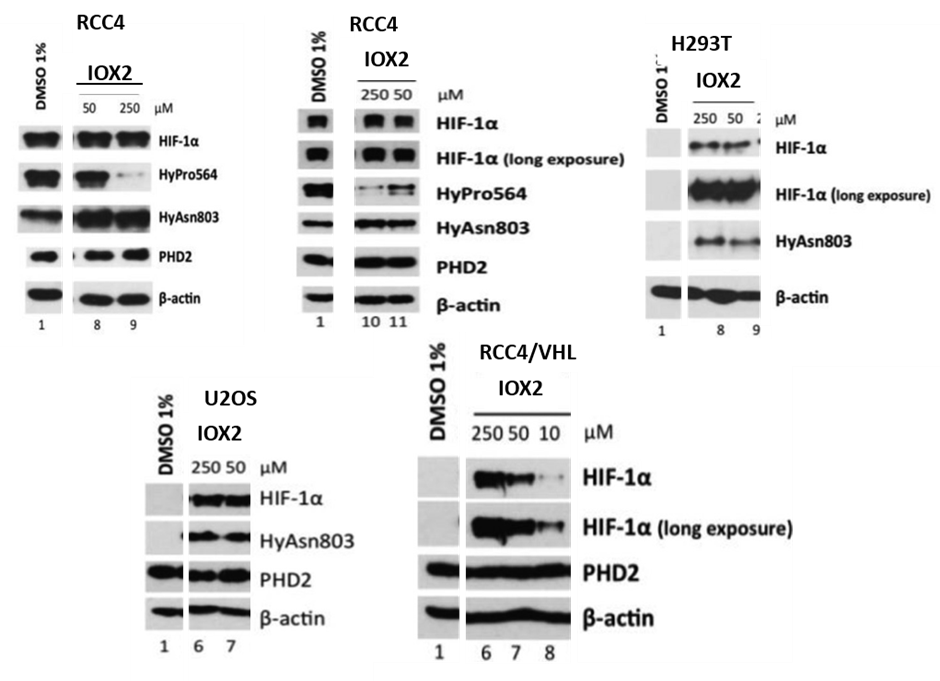
Selective inhibition of IOX2 in human cell lines. Selectivity of the tested inhibitors for HIF-1α prolyl- over asparaginyl- hydroxylation in RCC4 after 6h of treatment. Upregulation of HIF-1α by inhibitors in various cell types (after 6h of treatment): HEK293T, U2OS and RCC4 stably-transfected with C-HA-tagged wildtype VHL.
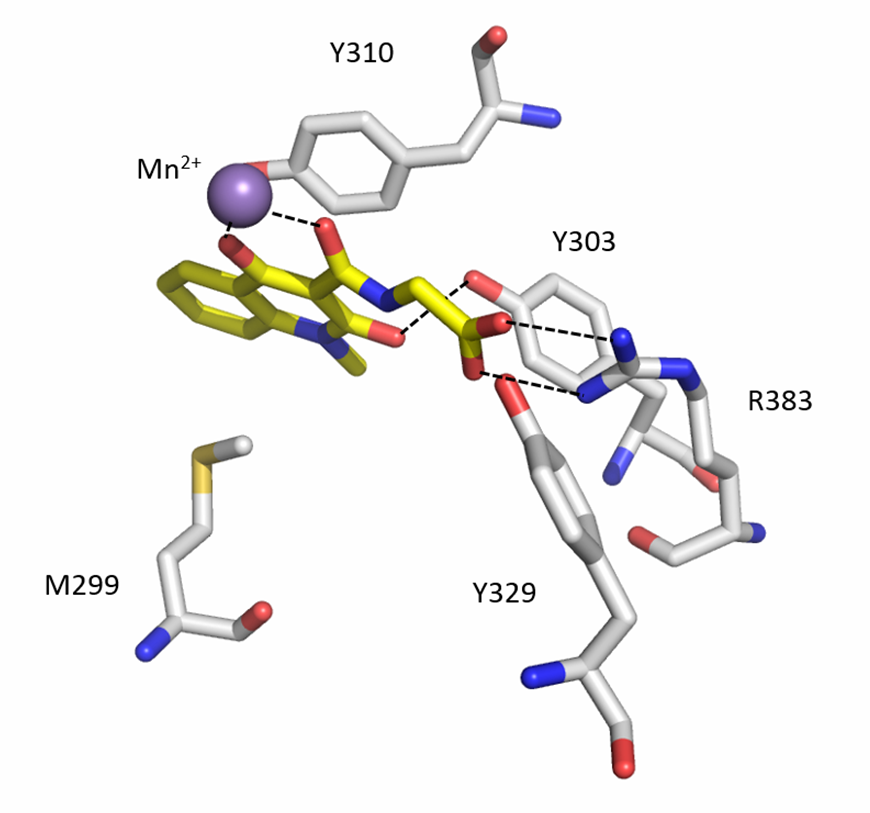
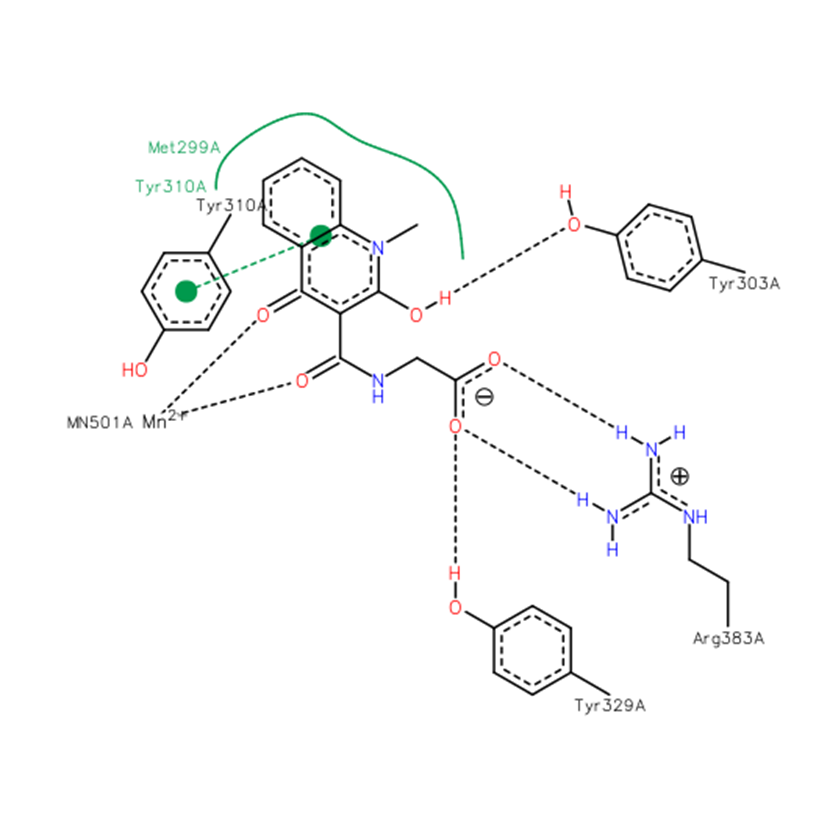
A co-crystal structure of PHD2’s catalytic domain with a methyl group on the isoquinoline nitrogen, compound 1, (rather than benzyl group in IOX2) group has been solved (pdb id 4BQW).
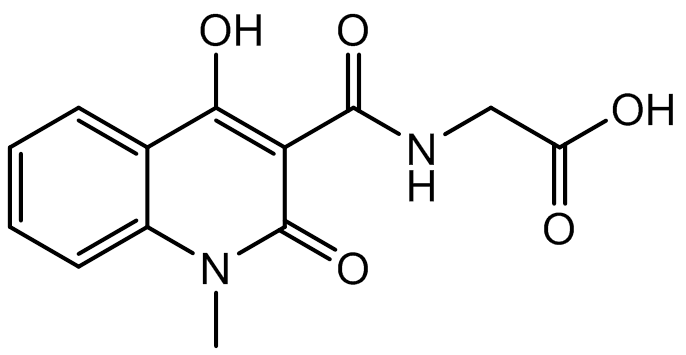
Compound 1
The bicyclic heteroaromatic ring of IOX2 is sandwiched between the hydrophobic side chains of Tyr310, Met299 and Trp389. IOX2 coordinates Mn(II) (substituting for Fe(II)) in a bidentate fashion with the side chain amide-carbonyl and phenolic oxygen. The side chain carboxylate of IOX2 is positioned to hydrogen bond with Arg383 and Tyr329. The Tyr303 phenol is positioned to hydrogen bond to the isoquinoline-2-OH. The aromatic rings of IOX2 project through the active site opening and likely make a steric clash with the hydroxylated HIF-1α.