
Dr. Dalia Barsyte-Lovejoy, PhD is an Assistant Professor at the Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology, UofT, and Principal Investigator at the SGC-Toronto, working to understand fundamental regulatory mechanisms of epigenetic proteins and their pharmacological modulation in cancer. The group’s research focuses on disease mechanisms, therapeutic targets, and chemical probe discovery, resulting in over 30 extensively characterized compounds that have helped shape the emerging field of epigenetics and enabled over 50 collaborative projects that are uncovering new epigenetic mechanisms in cancer and its treatment.
We are interested in understanding the mechanism of epigenetic regulators and posttranslational modifications that control cancer cell growth, differentiation, and therapy response. Protein lysine and arginine methyltransferases regulate transcription, genome stability, splicing, RNA metabolism, and other cell processes dictated by which substrates these enzymes methylate. Lysine methyltransferases such as EZH2 and NSD2 primarily methylate histones to establish repressive and active chromatin. In contrast, arginine methyltransferases have a broad scope of substrates ranging from histones to signaling molecules, enzymes, and structural proteins. Epigenetic chromatin regulation, transcriptome, and cellular signaling are fine-tuned by ubiquitin modification. Our work seeks to understand how these posttranslational modifications are misregulated in cancer and identify new therapeutic targets.
Through multidisciplinary research that includes cell and chemical biology, protein structural biology, and many collaborative studies with colleagues across industry and academia, the SGC chemical probes project has generated several probes for methyltransferases, ubiquitin ligases, and deubiquitylases. We are currently using these chemical probes to explore the cellular pathways in poor prognosis acute myeloid leukemia, pancreatic, lung and breast cancer.
Chemical probes as tools for cancer target discovery
|
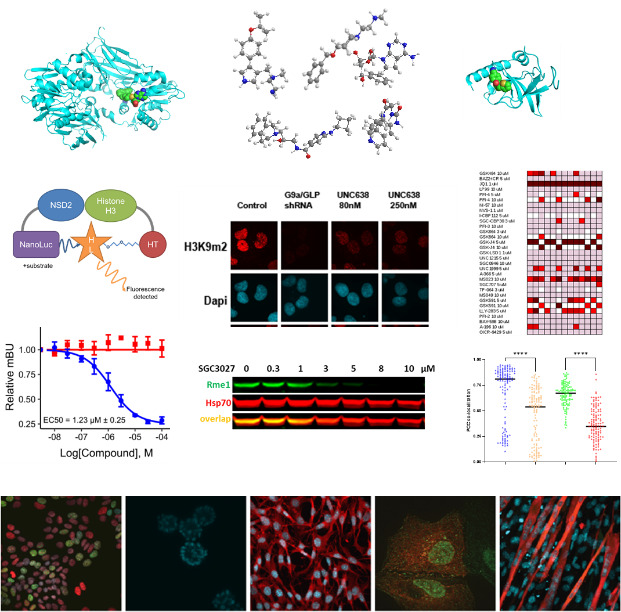
To study epigenetic modifier proteins, we need genetic and pharmacological tools. Chemical probe compounds that potently and selectively inhibit or degrade the target proteins in cells provide tools for modulating activating/repressing histone marks and other cellular signaling pathways. By discovering and using chemical probes, we expand our understanding of the protein function and its therapeutic utility to establish a biological rationale in cancer therapy.
|
Link to Open Lab notebooks that features science community posts on our various projects https://openlabnotebooks.org/
Nguyen H, Allali-Hassani A, Antonysamy S, Chang S, Chen LH, Curtis C, Emtage S, Fan L, Gheyi T, Li F, Liu S, Martin JR, Mendel D, Olsen JB, Pelletier L, Shatseva T, Wu S, Zhang FF, Arrowsmith CH, Brown PJ, Campbell RM, Garcia BA, Barsyte-Lovejoy D, Mader M, Vedadi M
J. Biol. Chem.. 2015-3-30 . .doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.626861
PMID: 25825497Kaniskan HÜ, Szewczyk MM, Yu Z, Eram MS, Yang X, Schmidt K, Luo X, Dai M, He F, Zang I, Lin Y, Kennedy S, Li F, Dobrovetsky E, Dong A, Smil D, Min SJ, Landon M, Lin-Jones J, Huang XP, Roth BL, Schapira M, Atadja P, Barsyte-Lovejoy D, Arrowsmith CH, Brown PJ, Zhao K, Jin J, Vedadi M
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl.. 2015-2-27 . .doi: 10.1002/anie.201412154
PMID: 25728001Barsyte-Lovejoy D, Li F, Oudhoff MJ, Tatlock JH, Dong A, Zeng H, Wu H, Freeman SA, Schapira M, Senisterra GA, Kuznetsova E, Marcellus R, Allali-Hassani A, Kennedy S, Lambert JP, Couzens AL, Aman A, Gingras AC, Al-Awar R, Fish PV, Gerstenberger BS, Roberts L, Benn CL, Grimley RL, Braam MJ, Rossi FM, Sudol M, Brown PJ, Bunnage ME, Owen DR, Zaph C, Vedadi M, Arrowsmith CH
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.. 2014-8-18 . .doi: 10.1073/pnas.1407358111
PMID: 25136132Konze KD, Pattenden SG, Liu F, Barsyte-Lovejoy D, Li F, Simon JM, Davis IJ, Vedadi M, Jin J
ChemMedChem. 2014-1-17 . .doi: 10.1002/cmdc.201300450
PMID: 24443078Liu F, Barsyte-Lovejoy D, Li F, Xiong Y, Korboukh VK, Huang X, Allali-Hassani A, Janzen WP, Roth BL, Frye SV, Arrowsmith CH, Brown PJ, Vedadi M, Jin J
J. Med. Chem.. 2013-10-8 . .doi: 10.1021/jm401480r
PMID: 24102134Oudhoff MJ, Freeman SA, Couzens AL, Antignano F, Kuznetsova E, Min PH, Northrop JP, Lehnertz B, Barsyte-Lovejoy D, Vedadi M, Arrowsmith CH, Nishina H, Gold MR, Rossi FM, Gingras AC, Zaph C
Dev. Cell. 2013-7-9 . .doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2013.05.025
PMID: 23850191Konze KD, Ma A, Li F, Barsyte-Lovejoy D, Parton T, Macnevin CJ, Liu F, Gao C, Huang XP, Kuznetsova E, Rougie M, Jiang A, Pattenden SG, Norris JL, James LI, Roth BL, Brown PJ, Frye SV, Arrowsmith CH, Hahn KM, Wang GG, Vedadi M, Jin J
ACS Chem. Biol.. 2013-4-24 . .doi: 10.1021/cb400133j
PMID: 23614352Lovejoy DA, Barsyte-Lovejoy D
Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol.. 2013-3-14 . .doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2013.02.002
PMID: 23500148James LI, Barsyte-Lovejoy D, Zhong N, Krichevsky L, Korboukh VK, Herold JM, Macnevin CJ, Norris JL, Sagum CA, Tempel W, Marcon E, Guo H, Gao C, Huang XP, Duan S, Emili A, Greenblatt JF, Kireev DB, Jin J, Janzen WP, Brown PJ, Bedford MT, Arrowsmith CH, Frye SV
Nat. Chem. Biol.. 2013-1-6 . .doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1157
PMID: 23292653Senisterra G, Wu H, Allali-Hassani A, Wasney GA, Barsyte-Lovejoy D, Dombrovski L, Dong A, Nguyen KT, Smil D, Bolshan Y, Hajian T, He H, Seitova A, Chau I, Li F, Poda G, Couture JF, Brown PJ, Al-Awar R, Schapira M, Arrowsmith CH, Vedadi M
Biochem. J.. 2013-1-1 . 449(1):151-9 .doi: 10.1042/BJ20121280
PMID: 22989411