|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Acetylation of lysine residues (Kac) is one of the most frequently occurring post-translational modifications (PTMs) which control gene transcription and a vast array of diverse cellular functions. Acetylation levels are reversibly maintained by a group of enzymes, the histone acetyl-transferases (HATs) and histone deacetylases (HDACs) that “write” and “erase” acetylation marks on histones. Deregulation of acetylation levels has been associated with the development of many diseases and enzymes regulating acetylation have emerged as interesting targets for drug discovery.
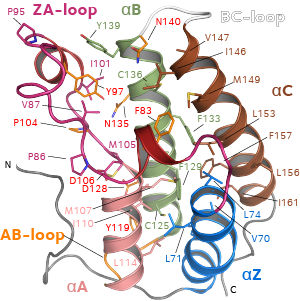
Bromdomains (BRDs) are the only known protein recognition module that selectively recognizes (ie “reads”) ε-N-acetylation of lysines. The human proteome encodes over 40 proteins that contain more than 60 diverse BRDs. Despite their low sequence identity all BRDs share a conserved fold comprising a left-handed bundle of four alpha helices, linked by diverse loop regions that contribute to substrate specificity. Co-crystal structures with substrate peptides showed that Kac is recognized by a central hydrophobic cavity and is anchored by a hydrogen bond with an asparagine residue present in most BRDs. We established that the Kac docking pocket is an attractive binding site for the development of inhibitors. Our aim is to generate high quality potent and selective chemical probes targeting BRD modules that can be used to elucidate the biological function of individual bromodomain containing proteins.