This probe is available from Sigma and Cayman Chemical.
The negative control GSK8573 is available from Sigma.
| Probe | Negative control | |
 |
|  |
GSK2801 |
| GSK8573 |
Biology of the BAZ2 Bromodomains
BAZ2A/B belong to a family of ubiquitously expressed bromodomain containing proteins. Proteins of the BAZ (bromodomain adjacent zinc finger) family are characterized by a carboxy-terminal bromodomain adjacent to a PHD finger and a WACZ motif. In addition four other conserved motifs are typically found in the N-terminus of BAZ family members, namely the LH motif (a leucine-rich helical domain), the ZB2 motif (conserved between ZK783.4 and BAZ2 proteins) and the BAZ 1 and BAZ 2 motifs (conserved between all BAZ proteins, Acf, and ZK783.4).
Little is known about the biological function of BAZ2B but it has been suggested to regulate nucleosome mobilization by the ATP-dependent chromatin remodelling factor ISWI. Interaction of BAZ2B with ISWI is mediated by the BAZ1 motif [1]. The BAZ2B locus has also been identified as associated with sudden cardiac death [2]. The related BAZ2A (also called TIP5) protein plays a central role in the NoRC (nucleolar remodelling complex). BAZ2A is essential for heterochromatin formation leading to transcriptional silencing of certain rRNAs [3].
GSK2801: A Chemical Probe for BAZ2A/B
GSK2801 a BAZ2A/B selective inhibitor is the result of a collaboration with GSK [4]. A second probe against this target, BAZ2-ICR, has also been reported [5].
An inactive control GSK8573 has also been reported (see properties tab).
Co-crystal structure
The co-crystal structure of GK2801 and BAZ2B has been solved (pdb id: 4RVR).
Potency Against Target Family
GSK2801 has been shown by ITC to bind to BAZ2A with a KD of 257 nM and to BAZ2B with a KD of 136 nM.
Selectivity
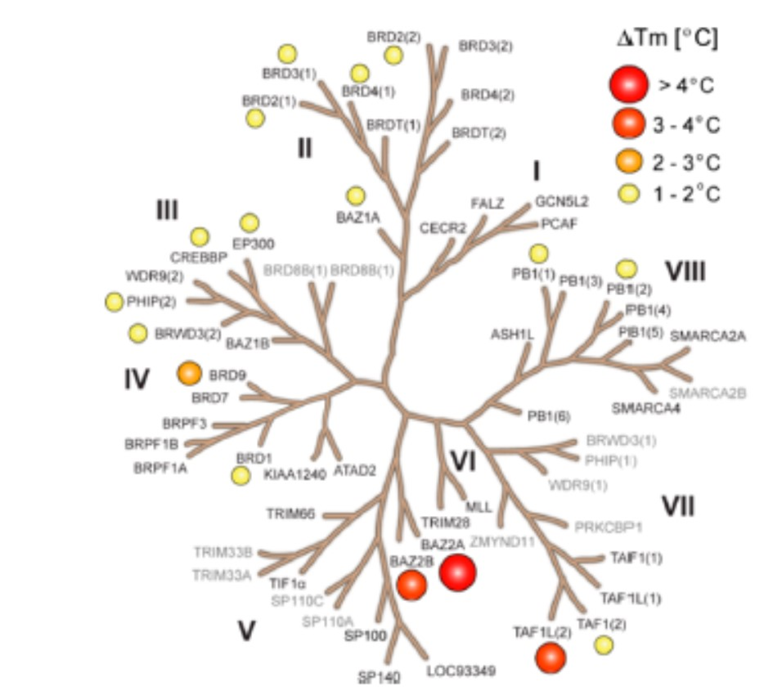
GSK2801 was screened at 10 μM concentration against 47 bromodomains using a thermal shift assay. Moderate activity was observed against TAF1L and BRD9 but GSK2801 was otherwise selective. The screened targets are labelled on the phylogenetic tree; targets that have not been screened are shown in grey. Temperature shifts are represented as spheres as indicated in the figure.
Selectivity Beyond Target Family
GSK2801 was screened in a binding assay against 55 receptors and ion channels and was found to be inactive against all but the Melatonin (MT-1) receptor.
Cellular Activity
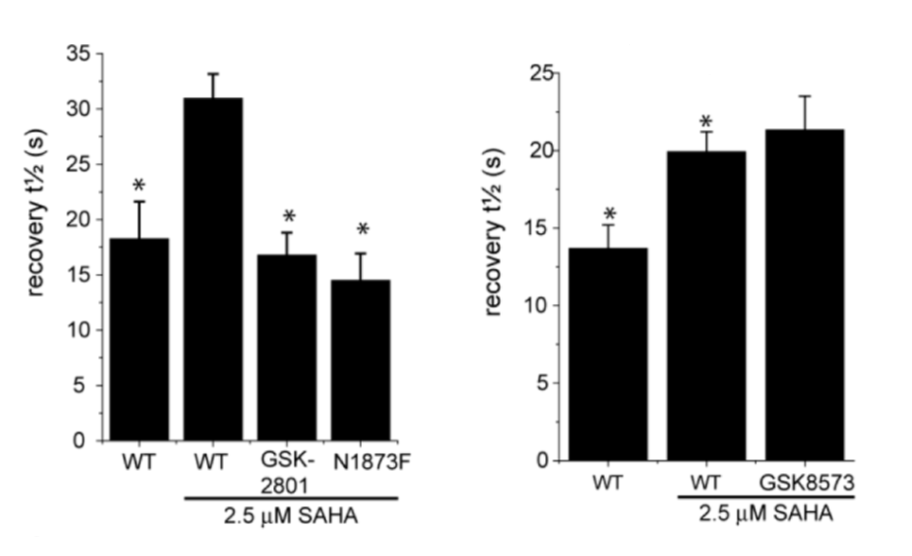
GSK2801 accelerated FRAP half-recovery time to the same extent as observed for the mutant construct indicating that the compound was able to displace BAZ2A from chromatin FRAP assay.
| GSK2801 |
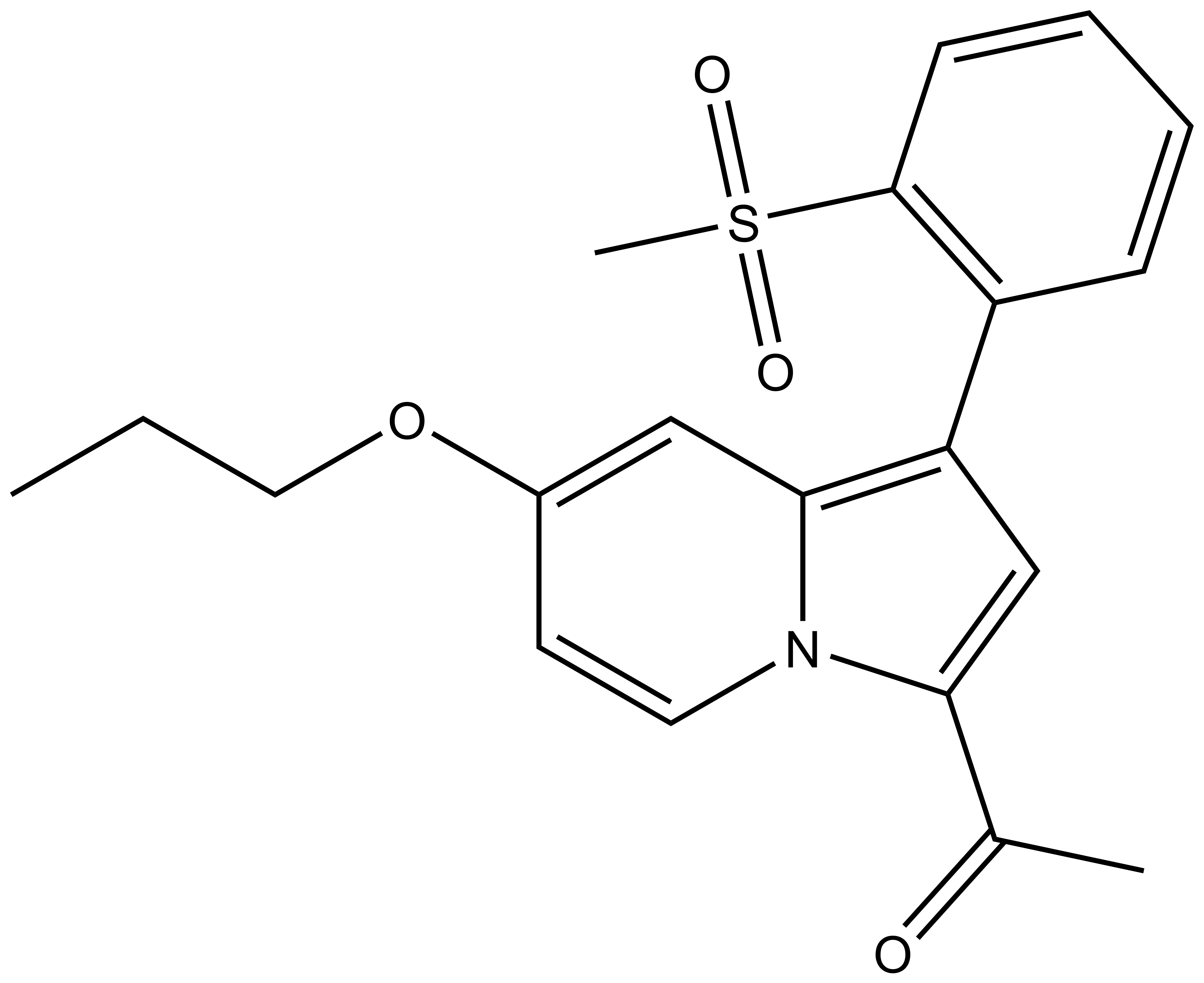 |
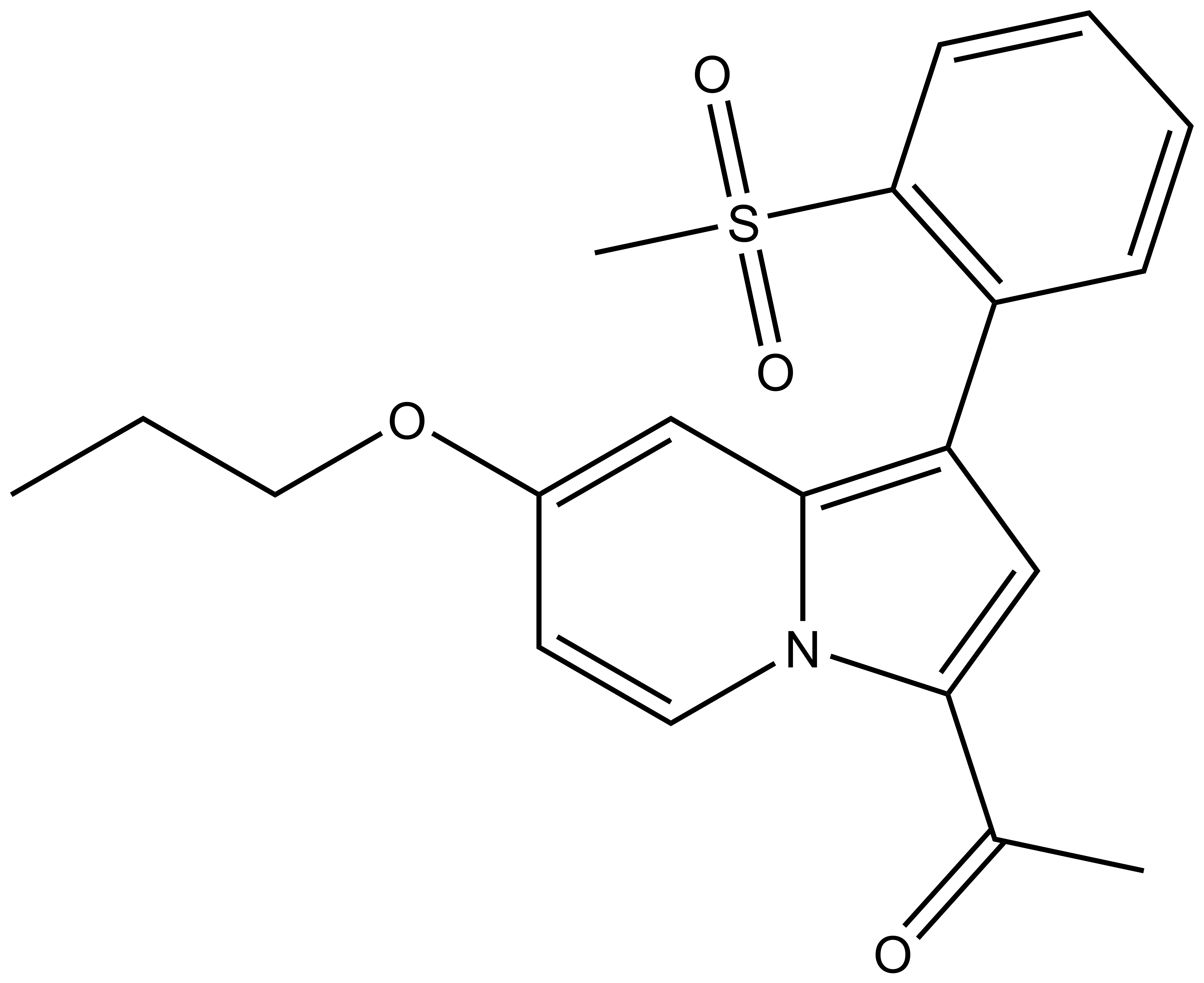
1-(1-(2-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-7-propoxyindolizin-3-yl)ethan-1-one |
| Physical and chemical properties | |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | 371.45 |
| Molecular formula | C20H21NO4S |
| IUPAC name | 1-(1-(2-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-7-propoxyindolizin-3-yl)ethan-1-one |
| logP | 3.54 |
| PSA | 63.68 |
| No. of chiral centres | 0 |
| No. of rotatable bonds | 6 |
| No. of hydrogen bond acceptors | 5 |
| No. of hydrogen bond donors | 0 |
| Storage | Stable as solid in the dark at -20°C. NB making aliquots rather than freeze-thawing is recommended |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO at least up to 50uM |
SMILES: CCCOC1=CC2=C(C3=C(S(=O)(C)=O)C=CC=C3)C=C(C(C)=O)N2C=C1
InChI: InChI=1S/C20H21NO4S/c1-4-11-25-15-9-10-21-18(14(2)22)13-17(19(21)12-15)16-7-5-6-8-20(16)26(3,23)24/h5-10,12-13H,4,11H2,1-3H3
InChI Key: KHWCPNJRJCNVRI-UHFFFAOYSA-N
| The negative control GSK8573 has the following properties |
 |
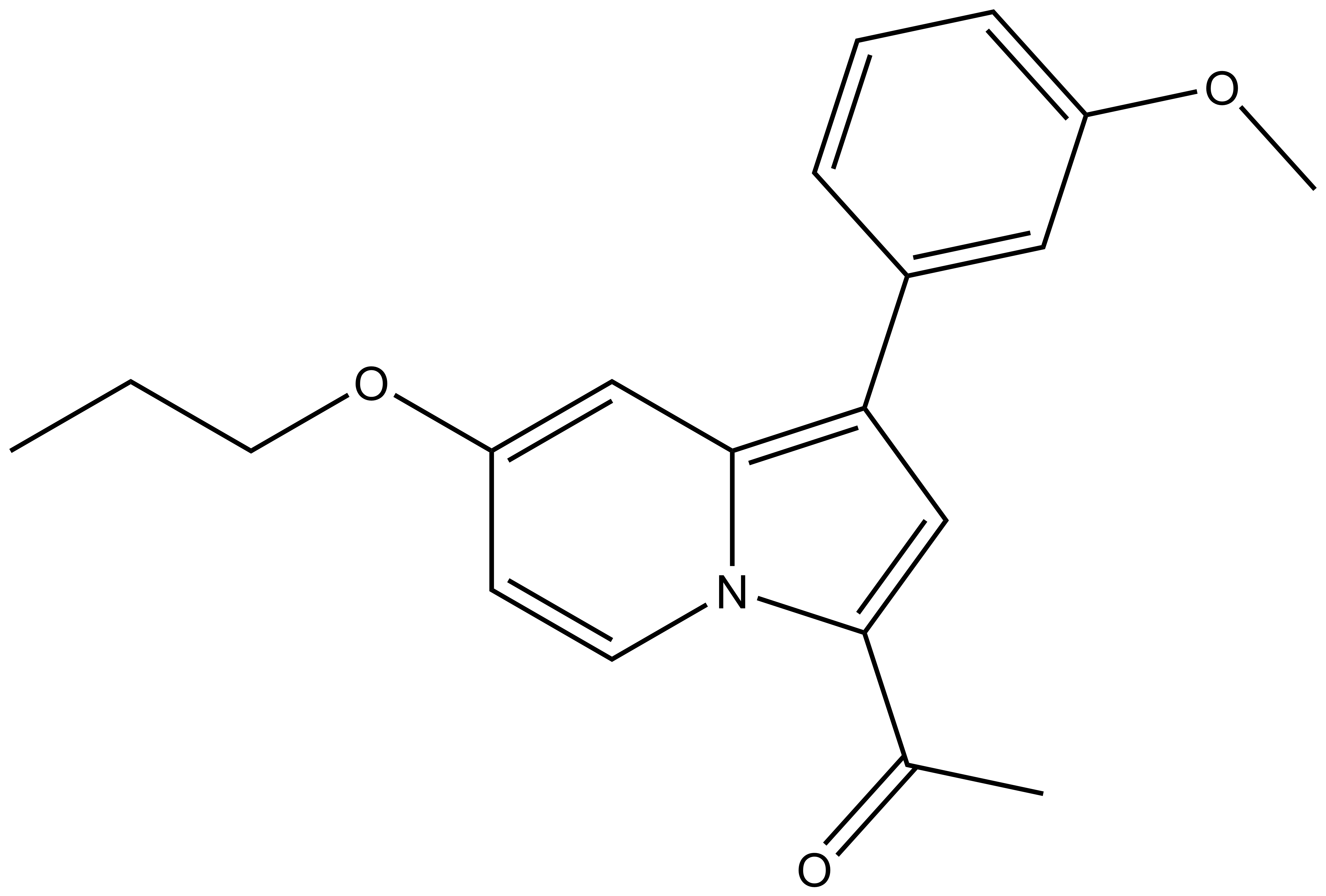
| 1-(1-(3-methoxyphenyl)-7-propoxyindolizin-3-yl)ethan-1-one For SDF click here |
| Physical and chemical properties | |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | 323.39 |
| Molecular formula | C20H21NO3 |
| IUPAC name | 1-(1-(3-methoxyphenyl)-7-propoxyindolizin-3-yl)ethan-1-one |
| logP | 3.10 |
| PSA | 38.77 |
| No. of chiral centres | 0 |
| No. of rotatable bonds | 6 |
| No. of hydrogen bond acceptors | 4 |
| No. of hydrogen bond donors | 0 |
| Storage | Stable as solid in the dark at -20°C. NB making aliquots rather than freeze-thawing is recommended |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSA at least up to to 50uM |
Potency against Target
GSK2801 has been shown by ITC to bind to BAZ2A with a KD of 257 nM and to BAZ2B with a KD of 136 nM. The ΔH for binding to BAZ2B is -10.69 (+/- 0.07) kcal/mol.
Selectivity Within Target family
GSK2801 showed significant thermal shifts of 4.1 and 2.7 °C for BAZ2A and BAZ2B respectively. GSK2801 did not show significant thermal shifts against all other bromodomains, except for BRD9 (ΔTm: 2.9 °C) and TAF1L (ΔTm: 3.4 °C) was observed. The KD of GSK2801 binding to BRD9 and TAF1L were determined to be 1.2 and 3.2 μM respectively by ITC.
Because of the limited sensitivity of BAZ2A/B in the thermal stability assay, the selectivity of GSK2801 was measured by BLI. Forty-two bromodomains modified with a Bir A biotin ligase targeting sequence were co-expressed in bacteria with the enzyme. The biotinylated proteins were used in BLI experiments probing the interaction of GSK2801 at two concentrations (0.2 and 1.0 μM). In agreement with the ΔTm data, BRD9 and TAF1(L) were detected as the major off-targets, while no other significant interactions were detected within the bromodomain family.
The structurally related GSK8573 proved to be inactive against BAZ2A/B and all other bromodomains except BRD9 in the BLI assay
Selectivity Beyond Target Family
GSK2801 (10 µM) was screened in a binding assay against 55 receptors and ion channels and was found to be inactive against all but the Melatonin (MT-1) receptor where inhibition was 4% of the control.
FRAP
To investigate whether GSK2801 can displace BAZ2 bromodomains from chromatin in living cells, we performed a fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) assay utilizing GFP-tagged BAZ2A full length protein transfected into human osteosarcoma cells (U2OS). Mutant BAZ2A (N1873F) was used as a control that does not bind acetylated lysine containing peptides and therefore mirrors the behavi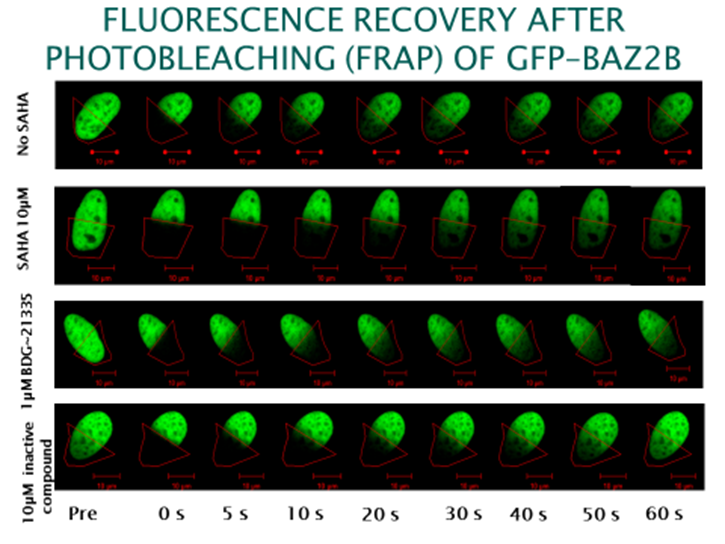 our of inhibitor bound BAZ2A. The histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) was used to increase overall levels of histone acetylation, resulting in a sufficient assay window to enable the measurement of differences in recovery time and demonstrating the acetylation dependence of the FRAP experiments. GSK2801 at 1 μM GSK2801 accelerated FRAP half-recovery time to the same extent as observed for the mutant construct indicating that the compound was able to displace BAZ2A from chromatin. Conversely, the inactive GSK-8573 did not have any effect on the half-recovery time of GFP-BAZ2A
our of inhibitor bound BAZ2A. The histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) was used to increase overall levels of histone acetylation, resulting in a sufficient assay window to enable the measurement of differences in recovery time and demonstrating the acetylation dependence of the FRAP experiments. GSK2801 at 1 μM GSK2801 accelerated FRAP half-recovery time to the same extent as observed for the mutant construct indicating that the compound was able to displace BAZ2A from chromatin. Conversely, the inactive GSK-8573 did not have any effect on the half-recovery time of GFP-BAZ2A
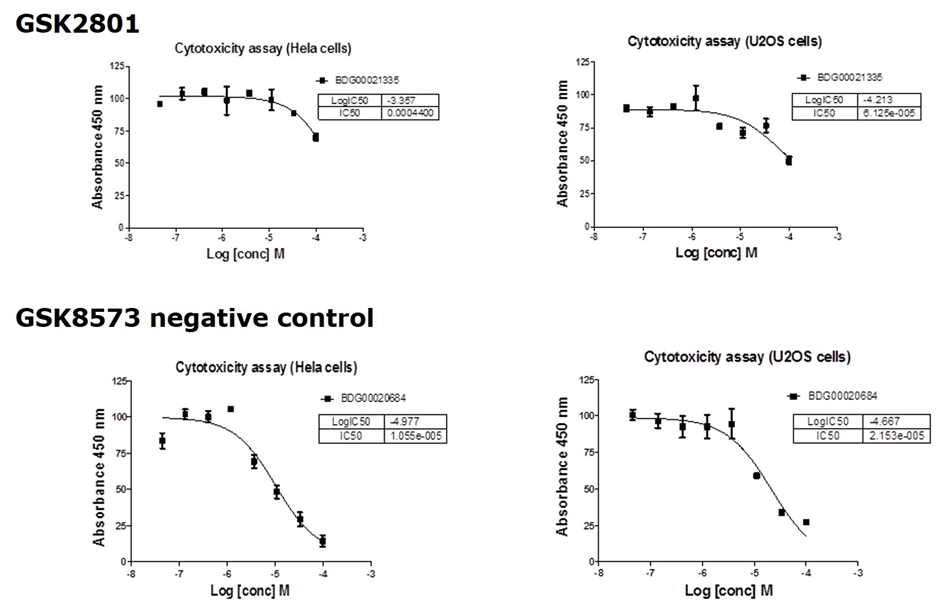
Cytotoxicity
GSK2801 showed no significant toxicity against U02S or HeLa cells
A Novel Family of Bromodomain Genes,
Jones, M. H.; Hamana, N.; Nezu, Ji.; Shimane, M., Genomics, 63, 40– 45 (2000)
Arking, D. E.; Junttila, M. J.; Goyette, P.; Huertas-Vazquez, A.; Eijgelsheim, M.; Blom, M. T.; Newton-Cheh, C.; Reinier, K.; Teodorescu, C.; Uy-Evanado, A.; Carter-Monroe, N.; Kaikkonen, K. S.; Kortelainen, M. L.; Boucher, G.; Lagace, C.; Moes, A.; Zhao, X.; Kolodgie, F.; Rivadeneira, F.; Hofman, A.; Witteman, J. C.; Uitterlinden, A. G.; Marsman, R. F.; Pazoki, R.; Bardai, A.; Koster, R. W.; Dehghan, A.; Hwang, S. J.; Bhatnagar, P.; Post, W.; Hilton, G.; Prineas, R. J.; Li, M.; Kottgen, A.; Ehret, G.; Boerwinkle, E.; Coresh, J.; Kao, W. H.; Psaty, B. M.; Tomaselli, G. F.; Sotoodehnia, N.; Siscovick, D. S.; Burke, G. L.; Marban, E.; Spooner, P. M.; Cupples, L. A.; Jui, J.; Gunson, K.; Kesaniemi, Y. A.; Wilde, A. A.; Tardif, J. C.; O’Donnell, C. J.; Bezzina, C. R.; Virmani, R.; Stricker, B. H.; Tan, H. L.; Albert, C. M.; Chakravarti, A.; Rioux, J. D.; Huikuri, H. V.; Chugh, S. S., PLoS Genet., 7, e1002158 (2011)
Guetg, C.; Lienemann, P.; Sirri, V.; Grummt, I.; Hernandez‐Verdun, D.; Hottiger, M.O.; Fussenegger, M.; Santoro, R., The NoRC complex mediates the heterochromatin formation and stability of silent rRNA genes and centromeric repeats, Embo J., 29, 2135-2146, (2010)
The pharmacokinetic parameters GSK2801 for in vivo experiments were measured after intraperitoneal and oral dosing in male CD1 mice. This PK study showed that GSK2801 has reasonable in vivo exposure after oral dosing, modest clearance, and reasonable plasma stability. These properties should allow GSK2801 to be used as a BAZ2A/B bromodomain inhibitor in vivo.
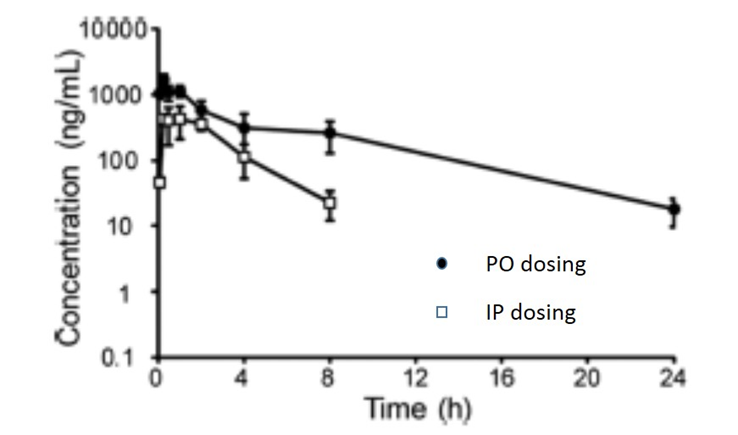
| IP 30 mg/kg | PO 30 mg/kg | |
| Tmax (h) | 0.25 | 1.0 |
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 1670 | 435 |
| Terminal t½ (h) | 4.5 | 1.5 |
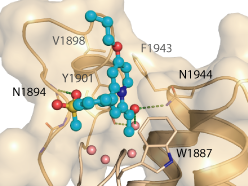
The co-crystal structure of GSK2801 and BAZ2B has been solved (pdb id: 4RVR).
Isothermal Titration Calorimetry
Experiments were carried out on a VP-ITC titration microcalorimeter from MicroCalTM, LLC (Northampton, MA), at 15 °C while stirring at 295 rpm, in ITC buffer (50 mM HEPES, 150 mM NaCl). All titrations were conducted using an initial injection of 2 µl followed by 34 identical injections of 8 µl with a duration of 16 sec/injection and a spacing of 250 sec between injections. The heat of dilution was determined by independent titrations (protein into buffer) and was subtracted from the experimental data. MicroCalTM Origin software was used to calculate enthalpies of binding (ΔH) and binding constants (KB). Thermodynamic parameters were calculated (ΔG = ΔH - TΔS = -RTlnKB, where ΔG, ΔH and ΔS are the changes in free energy, enthalpy and entropy of binding respectively). In all cases a single binding site model was employed.
Differential Scanning Fluorimetry (DSF)
Thermal melting experiments were carried out using an Mx3005p Real Time PCR machine (Stratagene). Proteins were buffered (10 mM HEPES, 500 mM NaCl) and assayed at a final concentration of 2 µM. Compounds were added at a final concentration of 10 µM. SYPRO Orange (Molecular Probes) was added as a fluorescence probe at a dilution of 1:1000. Excitation and emission filters were set to 465 nm and 590 nm respectively. The temperature was raised with a step of 3 °C per minute from 25 °C to 96 °C and fluorescence readings were taken at each interval. Data was analysed as previously reported [6]
Biolayer interference assays
BAZ2A and BAZ2B were expressed in frame with a C-terminal Avi tag and a His-TEV tag enabling enzymatic conjugation of a single biotin using the biotin ligase (BirA) which had been co-expressed in E. coli. Cells grown in the presence of 0.1 mM biotin were lysed and purified using a similar procedure. Incorporation of biotin was confirmed by ESI-MS spectroscopy. The biotin labelled BAZ2B and BAZ2A was immobilized on SuperStreptavidin BLI sensors. BioLayer Interferometry (BLI) experiments were performed on a 16-channel ForteBio Octet RED384 instrument at 25°C (25 mM HEPES, pH 7.5, 0.05% Tween and 100 mM NaCl buffer). The reference sensors without attached bromodomain were used to subtract background binding to SuperStreptavidin sensors. Data were processed and analysed using ForteBio Analysis software.
CEREP assay
GSK2801 (10 µm) was screened against a panel of 55 ligand receptors, ion channels and transports using an established and widely utilized commercial assay platform (ExpresSProfile; CEREP, Paris, FRANCE).
Fluorescence Recovery After Photobleaching (FRAP) Assay
FRAP studies were performed using U20S cells expressing full-length BAZ2A or BRD4 protein fused with an N-terminal eGFP as previously described [4]. Six hours after transfection 2.5uM SAHA (to increase global histone acetylation) was added and GSK2801 was added 1 hour before imaging. Imaging was carried out 24 hours after transfection. Percent inhibition was calculated between the DMSO treated (0%) and N1873F expressing mutant (100%)
Cytotoxicity Assay
U20S cells were harvested from exponential phase cultures and plated in a 96-well opaque flat bottomed plates at a cell density of 3 x 103 cells/well (100uL). Compounds were dissolved in DMSO at 10 uM and serial dilutions performed. 5 uL of compound solution was added to each well and incubated for 24 or 72 hours at 37˚C in a humidified atmosphere containing CO2 (5%). 10 uL of WST-1 (Roche) was added and the plates returned to the incubator. Plates were read on a plate reader at 450 nm after 2 h for cells treated with GSK2801 for 24 h. Results plotted as % of DMSO control.
Pharmacokinetics
These PK studies were performed by Shanghai ChemPartner Co. Ltd. The IP and PO dosing solutions were prepared in 0.5% CMC+1% Tween 80. No clinical symptoms were observed during the entire in-life study. Male CD-1 mice, 28-32g were used (with free access to food and water). A dose of 30 mg/kg (10 mL/kg) was used via intraperitoneal injection (N=9) and for oral dosing 30 mg/kg (10 mL/kg) via gavage (N=9). The animals were restrained manually for blood collection and approx. 110 μL blood/time point was collected, centrifuged at 4°C (2000 g, 5min) to obtain plasma within 15 min after sample collection. Plasma samples were stored at -70℃ until analysis. An UPLC/MS-MS-002 (API-4000) was used for sample analysis, with Dexamethasone as internal standard. An aliquot of 20 μL sample was added with 200 μL ACN containing 50 ng/mL dexamethasone. The mixture was vortexed for 2 min and centrifuged at 14000 rpm for 5 min. An aliquot of 1 μL supernatant was injected for LC-MS/MS analysis.