This tool compound is available from Cayman Chemical, Sigma and Tocris.
| Probe |
 |
IOX1 |
Biology of the 2-oxoglutarate and ferrous iron dependent oxygenases
Histone lysine demethylases antagonize the action of histone methyltransferases in a site- and methylation state-specific manner. Nε-Methyl lysine demethylases that use 2-oxoglutarate as co-factor are associated with diverse human diseases, including cancer, inflammation and X-linked mental retardation; they are proposed as targets for the therapeutic modulation of transcription.
2-oxoglutarate (2OG) oxygenases are a ubiquitous and biologically important family of enzymes [1]. In human their roles include catalysing steps in collagen and carnitine biosynthesis, lipid metabolism, nucleic acid repair and modification, hypoxic sensing as well as histone demethylation. Impaired 2OG oxygenase activity is linked to the cellular hypoxic response and various diseases including cancer. Non-selective generic inhibitors of 2OG oxygenases include iron-chelators, Co(II) ions and 2OG analogues. The most widely used 2OG analogues are pyridine-2, 4-dicarboxylate and N-oxalylglycine. However, these compounds suffer from the lack of breadth of selectivity and their poor cell permeability often necessitates the use of pro-drug diester derivatives
IOX1: A tool compound for 2-oxoglutarate oxygenases
IOX1 a broad-spectrum, cell permeable inhibitor of most 2OG oxygenases which does not require application in a pro-drug form [2]. It was discovered following a high throughput screening campaign against the JMJD2 (KDM4) family of 2-oxoglutarate-dependent histone demethylases [3]. A cell permeable n-octyl ester analogue of IOX1 with an improved cellular potency has recently been reported [4].
Potency Against Target Family
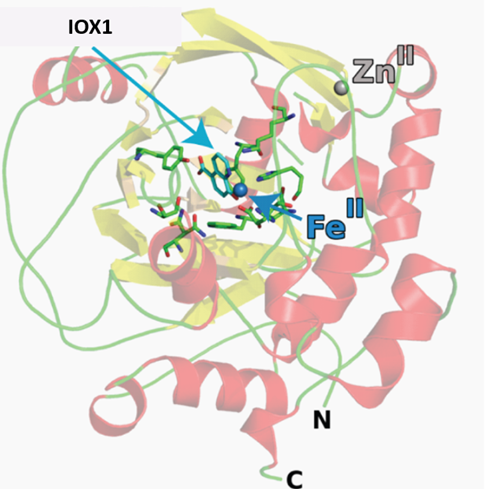
The co-crystal structures of IOX1 with JMJD2A (pdb id: 3NJY), JMJD3, (pdb id: 2XXZ) and FIH, (pdb id: 3OD4) have been solved. OX1 inhibits by binding to the active site Fe(II). Click on the 'Co-Crystal structures' tab above for more details.
Selectivity Beyond Target Family
IOX1 was found to be inactive against a panel of 55 receptors and ion channels (CEREP panel) at 10µM.
Cellular Activity
IOX1 exhibited cellular potency in a HeLa cell immunofluorescence assay, with EC50 values of 86 uM (KDM4A), 37 uM (KDM6B) and 24 uM (KDM2A).
IOX1
 |
8-hydroxyquinoline-5-carboxylic acid |
| Physical and chemical properties | |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | 189.17 |
| Molecular formula | C10H7N1O3 |
| IUPAC name | 8-hydroxyquinoline-5-carboxylic acid |
| logDpH7.4 | -1.55 |
| PSA | 69.9 |
| No. of chiral centres | 0 |
| No. of rotatable bonds | 1 |
| No. of hydrogen bond acceptors | 4 |
| No. of hydrogen bond donors | 2 |
| Storage | Store at 4°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in DMSO and to 100 mM in 1eq. NaOH |
An inactive, negative control compound for IOX-1 has not yet been identified
SMILES:
OC1=CC=C(C(O)=O)C2=CC=CN=C21
InChI:
InChI=1S/C10H7NO3/c12-8-4-3-7(10(13)14)6-2-1-5-11-9(6)8/h1-5,12H,(H,13,14)
InChIKey:
JGRPKOGHYBAVMW-UHFFFAOYSA-N
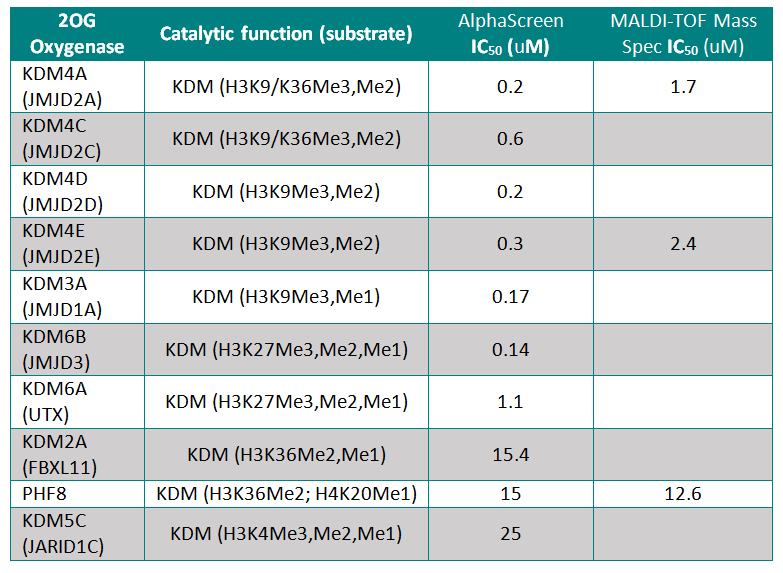
Potency against Target (JmjC-domain containing histone lysine demethylases)
IOX1 was screened against 10 JmjC-domain containing histone lysine demethylases by AlphaScreen or by MALDI-TOF Mass Spectroscopy. IOX1 showed nanomolar affinity for all except KDM2A and PHF8
Binding of the IOX1 may also indirectly affect substrate binding, supported by the observation of mixed mode inhibition kinetics when IOX1 was tested with varying concentrations of 2OG in a formaldehyde dehydrogenase assay.
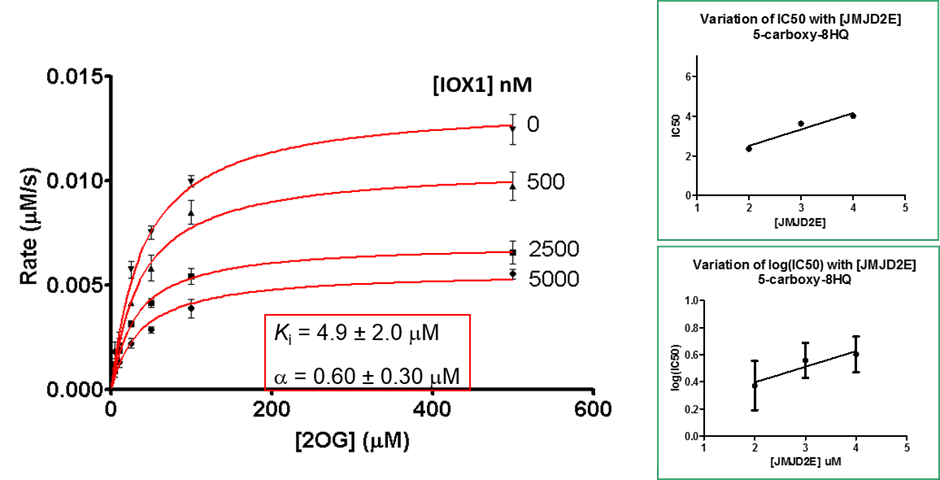
Selectivity
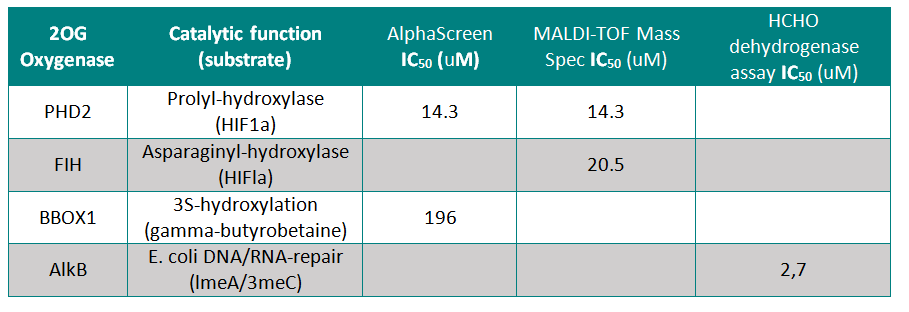
IOX1 was screened against 4 other active 2OG Oxygenases where it showed moderate to weak activity
Selectivity Beyond Target Family
IOX1 was found to be inactive against a panel of 55 receptors and ion channels (CEREP panel) at 10µM.
Engagement of IOX1 in a cell assay
PHD2 and FIH are both inhibited in cells as demonstrated by lowered HIF1α hydroxylation levels (hydroxylated-Pro564 (PHD2) and hydroxylated-Asn803 (FIH)).
Using an indirect immunofluorescence assay to directly measure demethylase activity in vivo by prevention of depletion of H3K9me3 in JMJD2A overexpressing HeLa cells. Indirect immunofluorescence with anti-Flag (green), anti-H3K9me3 (red), and DAPI staining (blue) in HeLa cells overexpressing Flag-tagged JMJD2A. DMSO solvent treatment has no effect on JMJD2A demethylase activity (white arrows) while increasing concentrations of IOX1 treatment (100 µM to 300µM range) resulted in gradual increases in H3K9Me3 levels. The JMJD2A H188A enzymatic mutant does not affect H3K9Me3 levels when overexpressed.
Treatment with increasing IOX1 concentrations showed a dose-dependent increase in H3K9me3 fluorescence intensity, demonstrating that H3K9me3 demethylation by JMJD2A is inhibited by IOX1 in cells. The cellular IC50 value for IOX1 was determined to be 86.5 µM. Notably, this compound does not require modification to a “pro-drug” ester form in order to be active in cells, unlike previously reported N-oxalylglycine derivatives [5].
A similar effect was noted in JMJD3A overexpressing cells this time measuring the effect on H3K27me3
X-ray crystal structures of IOX1 in complex with various 2OG oxygenases; JMJD2A (pdb id: 3NJY), JMJD3, (pdb id: 2XXZ) and FIH, (pdb id: 3OD4) and AlkB (pdb id: 4JHT) have been solved.
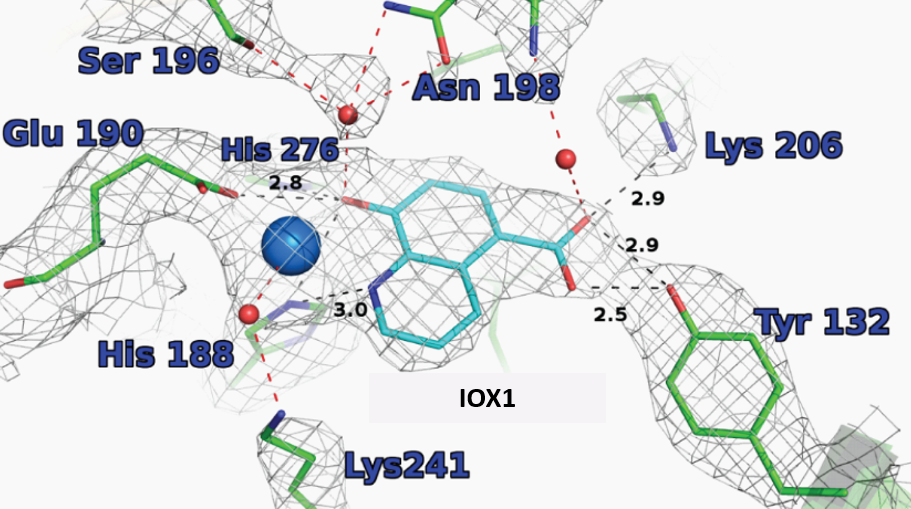
King et al. 2010 PLoSOne 5(11)e15535
Crystallisation of IOX1 in complex with JMJD2A revealed that IOX1 is positioned in a similar location to the 2OG analogue N-oxalylglycine in complex with JMJD2A and Ni(II) (which substitutes for Fe(II)); the 5-carboxy group of IOX1 and the C-5 carboxylates are positioned to interact with side chains Lys 206, Tyr 132. IOX1 is also positioned to coordinate with the active site Ni(II), in a bidentate fashion via its quinoline-nitrogen and 8-hydroxy group. Comparison of this structure with that of JMJD2A in complex with the H3K9me3 substrate peptide and N-oxalylglycine (PDB ID: 2OQ6) shows that the binding of the IOX1 is likely to compete with binding of 2OG and not directly with the peptide substrate.
Alpha Screen Assay
All reagents were diluted in 50 mM HEPES, 0.1 % BSA, pH 7.5 supplemented with 0.01 % Tween20 and allowed to equilibrate to room temperature prior to addition to plates. Catalytic turnover assays were run in 10µL volumes in 384-well plates at RT with enzyme (0.5-25nM), biotinylated substrate peptide (30-1000nM), Fe(II) (1-10µM), Ascorbate (100µM), 2OG (5-40µM). EDTA was used to quench the reaction (5µL) and AlphaScreen donor (Streptavidin-conjugated) and acceptor (ProteinA-conjugated) beads preincubated with peptide product antibodies were added (5µL). Plates were protected from light, incubated at room temperature for 60 minutes and read on a PHERAstar FS plate reader (BMG Labtech) using an AlphaScreen 680nm excitation/570nm emission filter set. IC50 values were calculated after normalization against corresponding DMSO controls.
Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionisation-Time-of-flight (MALDI-TOF) Mass Spectrometry
KDM assays were carried out as reported [3] using an assay reaction consisting of JMJD2 (1 µM), Ferrous ammonium sulphate (10 µM), Ascorbate (100 µM), 2OG (10 µM), Histone H3 peptides (10 µM) in 50 mM HEPES (pH 7.5) with varying concentrations of inhibitors. The reaction was incubated at RT and 1:1 quenching with methanol followed by addition of four volumes of 20 mM triammonium citrate.
Cell-Based Assays
Flag-tagged JMJD2A was transiently overexpressed in HeLa cells either in the presence of a vehicle control (DMSO), 1 mM dimethyl-2,4-PDCA (a cell-permeable derivative of 2,4-PDCA), 2.5 mM dimethyloxalylglycine (DMOG, a cell-permeable derivative of N-oxalylglycine), or varying concentrations of IOX1. After 24 hours of incubation time cells were fixed and then analyzed by indirect immunofluorescence with Flag tag antibody to identify the cells overexpressing the demethylase and an antibody recognizing endogenous H3K9me3 to quantify the level of this histone modification. A series of images were collected for each treatment on a standard epifluorescence microscope and CellProfiler was used to analyze the images for DAPI signal thereby identifying the location of individual cells and create a boundary that delineates the volume of the nuclear compartment. As not all cells in a given field are transfected, the Flag-JMJD2A-expressing cells were identified by quantifying the immunofluorescence signal resulting from the Flag tag antibody staining and using the mock transfected cells as a baseline for the signal intensity of non-transfected cells. Once the transfected cells were identified, the nuclear H3K9me3 immunofluorescence signal for each cell was quantified by CellProfiler. The levels of H3K9me3 staining intensity were analyzed in the DMSO vehicle treated or inhibitor treated samples. As a control and a means of determining maximal possible inhibition of demethylase activity, cells expressing the JMJD2A H188A catalytically deficient mutant were also quantified in each experiment. The level of demethylase activity inhibition by IOX1 treatment was determined by quantifying the immunofluorescence signal from the DMSO treated sample (100% demethylase activity) compared to the maximal theoretical inhibition signal intensity as determined by the H3K9me3 signal in cells expressing the catalytically deficient JMJD2A H188A mutant (0% demethylase activity). For each treatment a minimum of 400 transfected cells was analyzed and the final values of inhibition were derived from inhibition experiments carried out on three separate days.