| Probe | Negative control | |
 |
|  |
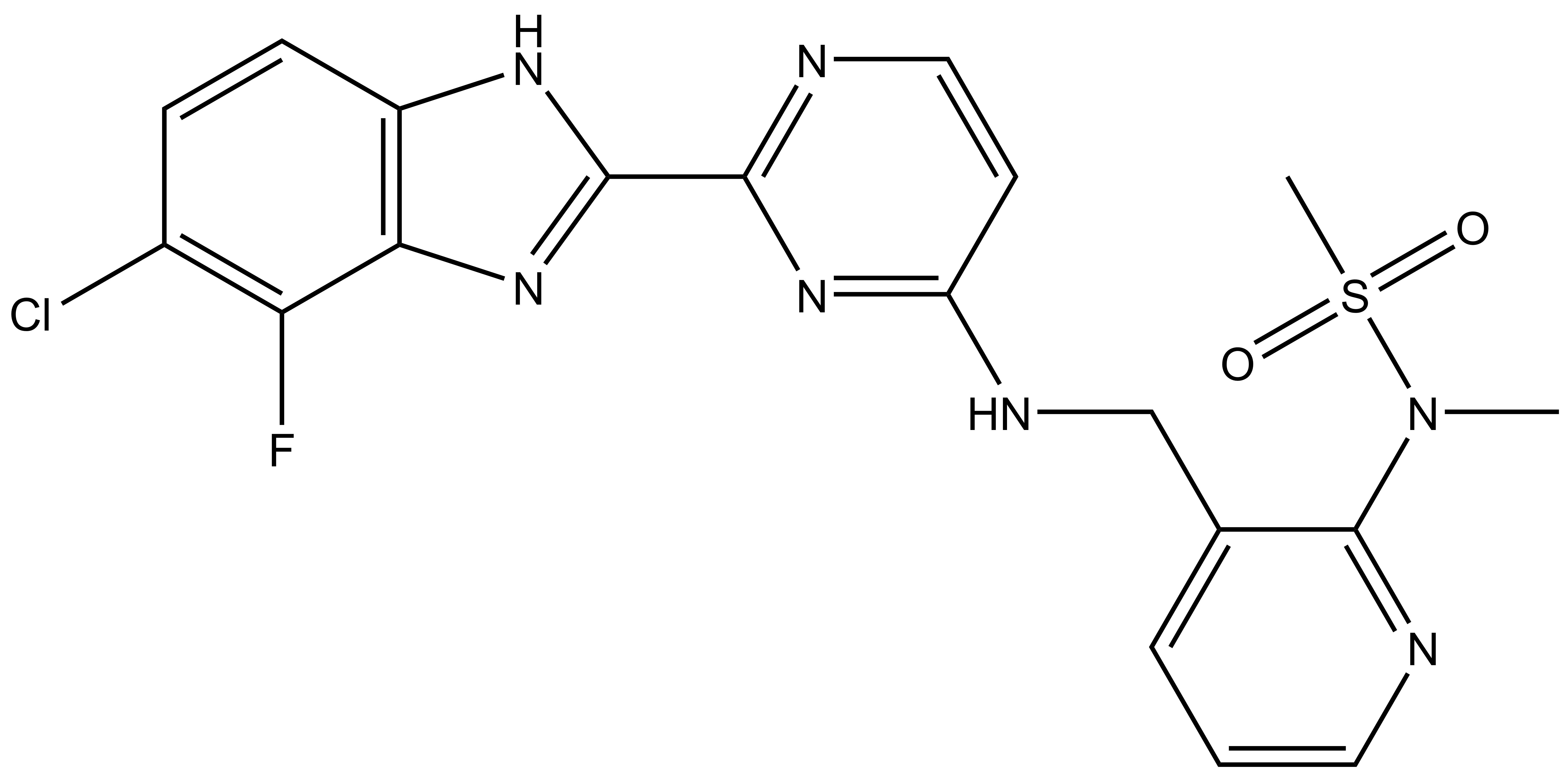
MSC1186 |
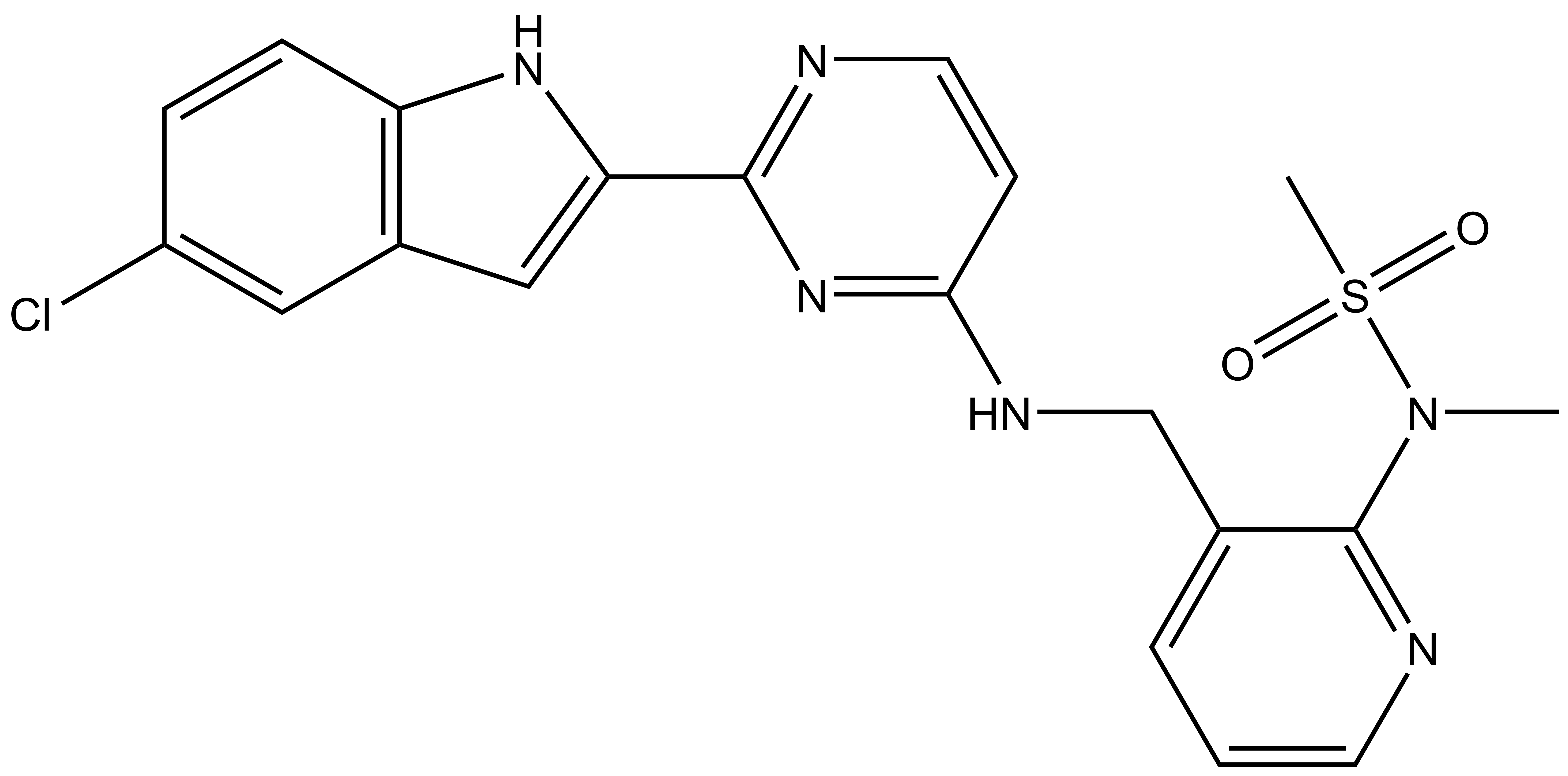
| MSC5360 |
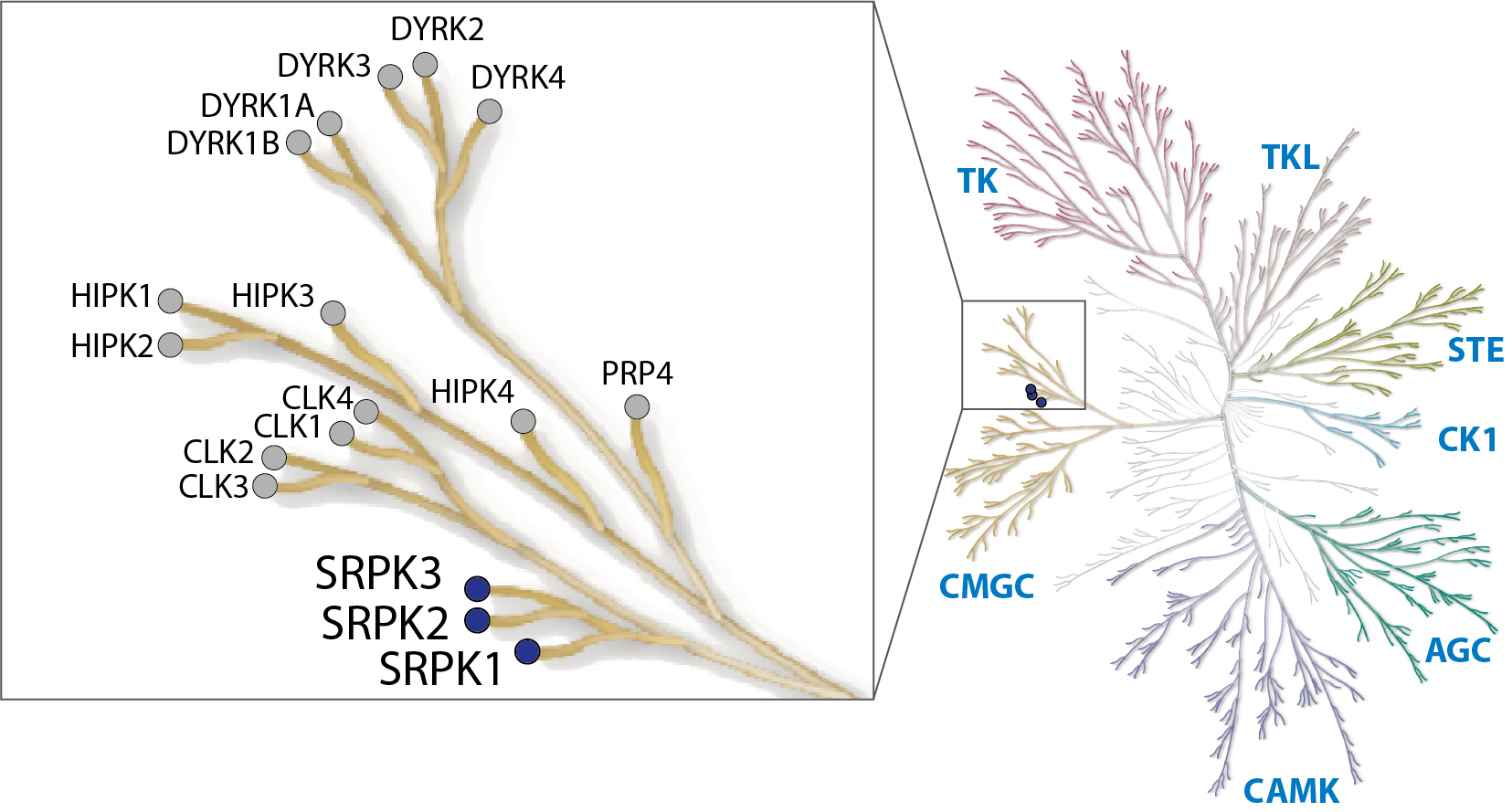
Serine-arginine protein kinases (SPRKs) are a subfamily of serine-threonine kinases, regulating pre-mRNA splicing in response to extracellular stimuli by phosphorylating serine/arginine (SR)-rich splicing factors. The human genome encodes three SRPK genes, SRPK1, SRPK2 and SRPK3. While SRPK1 has been detected in many human tissues at varying expression levels, SRPK2 and SRPK3 exhibit a more tissue-specific expression. Most of SRPK1 is localized in the cytoplasm where it catalyses SR-domain phosphorylation of splicing-regulating proteins such as SRSFs to facilitate shuttling to the nucleus (Kataoka et al., 1999; Lai et al., 2001; Zhong et al., 2009). This process can be accelerated in response to extracellular stimuli (Nowak et al., 2010). Once in the nucleus, SRPK1 synergizes with other SR protein kinases, such as members of the CLK family of kinases, predominantly localized in the nucleus, to further phosphorylate SR proteins promoting spliceosome assembly (Aubol et al., 2016). During splicing, SR proteins are dephosphorylated by nuclear phosphatases. This highly coordinated process is crucial during development and it is often dysregulated in diseases. Alteration of SRPK expression has been found to induce a large number of aberrant alternative splicing events, leading to tumorigenesis (Corkery et al., 2015).
Merck KGaA in collaboration with the SGC has developed MSC1186, a potent, cell active chemical probe for SRPK. MSC1186 shows high in vitro as well as cellular potency for all three SRPK isoforms and does not show any activity towards the CLKs. MSC1186 is accompanied by a negative control (MSC5360), which is structurally closely related to the probe molecule.
| Probe | Negative control | |
 |
|  |
MSC1186 |
| MSC5360 |
Physical and chemical properties MSC1186 | |
| Molecular weight | 461.90 |
| Molecular formula | C19H17ClFN7O2S |
| IUPAC name | N-(3-(((2-(5-chloro-4-fluoro-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)pyrimidin-4-yl)amino)methyl)pyridin-2-yl)-N-methylmethanesulfonamide |
| clogP | 3.4 |
| tPSA | 125.1 |
| No. of chiral centres | 0 |
| No. of rotatable bonds | 7 |
| No. of hydrogen bond acceptors | 8 |
| No. of hydrogen bond donors | 2 |
| Storage | r. t. |
| Dissolution | <0.0010 mg/ml |
SMILES: CN(C1=NC=CC=C1CNC1=NC(=NC=C1)C1=NC2=C(N1)C=CC(Cl)=C2F)S(C)(=O)=O
InChI: 1S/C19H17ClFN7O2S/c1-28(31(2,29)30)19-11(4-3-8-23-19)10-24-14-7-9-22-17(26-14)18-25-13-6-5-12(20)15(21)16(13)27-18/h3-9H,10H2,1-2H3,(H,25,27)(H,22,24,26)
InChIKey: WBFJDKLBAAHKIL-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Physical and chemical properties MSC5360 | |
| Molecular weight | 442,92 |
| Molecular formula | C20H19ClN6O2S |
| IUPAC name | N-(3-(((2-(5-chloro-1H-indol-2-yl)pyrimidin-4-yl)amino)methyl)pyridin-2-yl)-N-methylmethanesulfonamide |
| clogP | 4.3 |
| tPSA | 112.2 |
| No. of chiral centres | 0 |
| No. of rotatable bonds | 7 |
| No. of hydrogen bond acceptors | 8 |
| No. of hydrogen bond donors | 2 |
| Storage | r. t. |
SMILES: CN(S(C)(=O)=O)C1=NC=CC=C1CNC2=NC(C3=CC4=C(C=CC(Cl)=C4)N3)=NC=C2
InChI: InChI=1S/C20H19ClN6O2S/c1-27(30(2,28)29)20-13(4-3-8-23-20)12-24-18-7-9-22-19(26-18)17-11-14-10-15(21)5-6-16(14)25-17/h3-11,25H,12H2,1-2H3,(H,22,24,26)
InChIKey: InChIKey=MXAVRMOXZMBKGE-UHFFFAOYSA-N
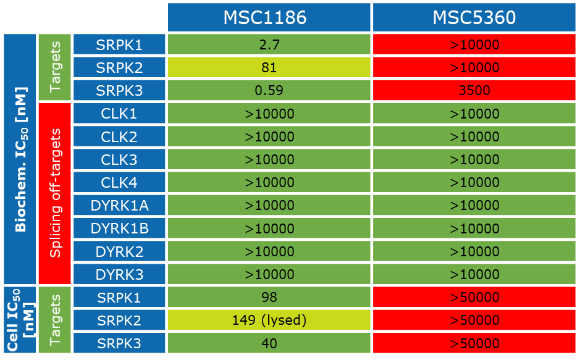
Kinome-wide selectivity profile of MSC1186 was determined at Reaction Biology at 1 µM and on- and off targets were evaluated with in cellulo IC50 with NanoBRET assay.
 |
| 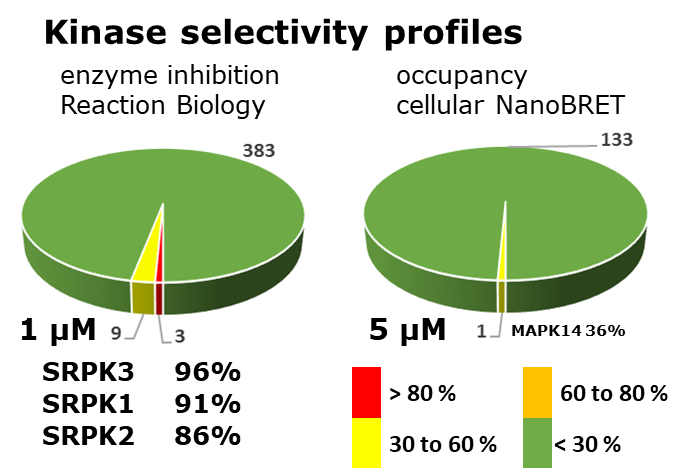 |
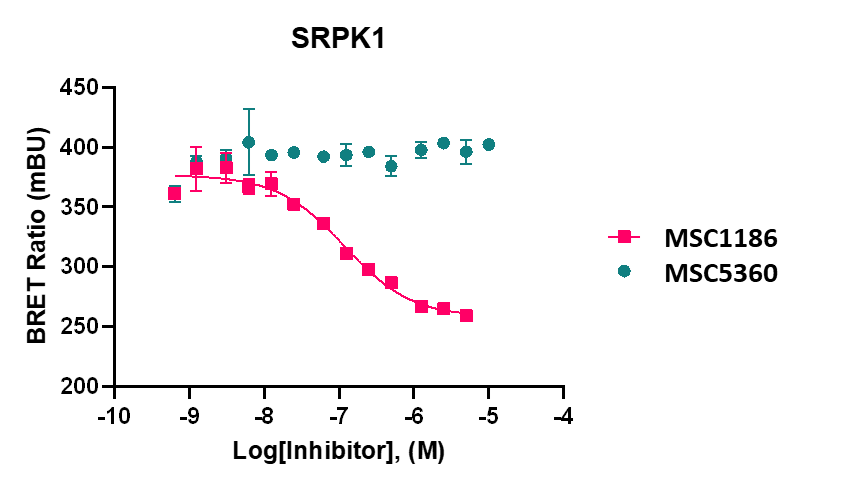
The negative control MSC5360 showed no activity in biochemical assays and no activity was detected by NanoBRET assays in intact and in lysed cells.
 |  |
 |
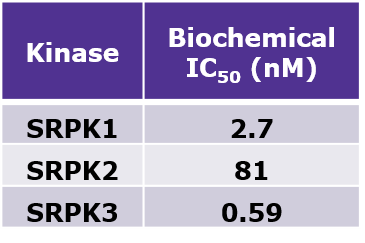 |
MSC1186 had an IC50 of 2.7 nM, 81 nM, and 0.59 nM to SRPK1, SRPK2 and SRPK3, respectively in the biochemical biochemical activity assay performed at Reaction Biology.
ITC
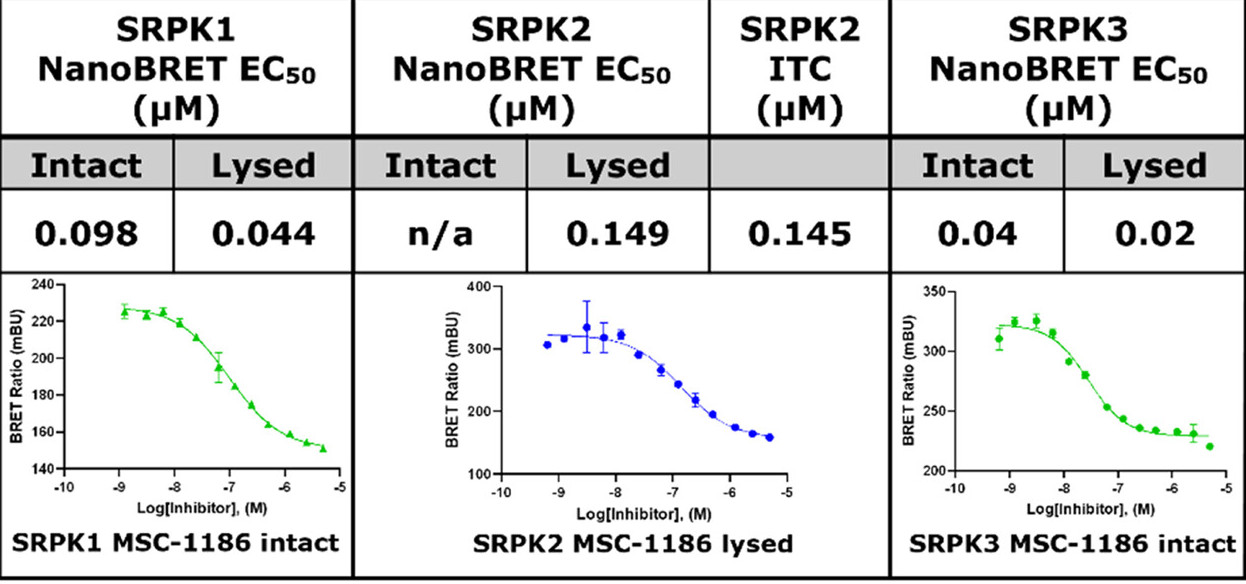
MSC1186 exhibited a Kd of 145 nM on SRPK2 in ITC.
Selectivity
MSC1186 was selective in an in vitro kinase panel from Reaction Biology at 1 µM against 395 Kinases, followed by cellular NanoBRET assays.
Dosage
Based on the potency and the selectivity of the chemical probe and to minimize the risk of unspecific cytotoxicity, we recommend a concentration of no higher than 1 µM for cell-based assays. After 48 hours of 1 µM of compound exposure to human osteosarcoma cells (U2OS) and human embryoic kidney cells (HEK293T), there was no detectable effect on cell viability compared to 0.1 % DMSO. At 10 µM we discovered off-target effects including modulation of tubulin function. Therefore, usage at higher concentrations is not recommended.
Cellular Activity
MSC1186 displayed an IC50 of 98 nM on SRPK1 and 40 nM on SRPK3 in intact cells and 44 nM on SRPK1, 149 nM on SRPK2 and 40nM on SRPK3 in lysed cells in NanoBRETTM assay.
MSC1186 displayed an IC50 of 98 nM on SRPK1 and 40 nM on SRPK3 in intact cells and 44 nM on SRPK1, 149 nM on SRPK2 and 40nM on SRPK3 in lysed cells in NanoBRETTM assay.
 |
MSC-1186, a Highly Selective Pan-SRPK Inhibitor Based on an Exceptionally Decorated Benzimidazole-Pyrimidine Core. M Schröder et al. J. Med. Chem. 2023. 837–854 https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c01705
Martin Schröder, Matthias Leiendecker, Ulrich Grädler, Juliane Braun, Andreas Blumet al. MSC-1186, a Highly Selective Pan-SRPK Inhibitor Based on an Exceptionally Decorated Benzimidazole-Pyrimidine Core. J. Med. Chem. 66, 837−854 (2023).
Kataoka N, Bachorik JL, Dreyfuss G. Transportin-SR, a nuclear import receptor for SR proteins. J Cell Biol. 145:1145–1152 (1999).
Lai MC, Lin RI, Tarn WY. Transportin-SR2 mediates nuclear import of phosphorylated SR proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 98:10154–10159 (2001).
Zhong XY, Ding JH, Adams JA, Ghosh G, Fu XD. Regulation of SR protein phosphorylation and alternative splicing by modulating kinetic interactions of SRPK1 with molecular chaperones. Genes Dev. 23:482–495 (2009).
Nowak DG, Amin EM, Rennel ES, Hoareau-Aveilla C, Gammons M, et al. Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) splicing from pro-angiogenic to anti-angiogenic isoforms: a novel therapeutic strategy for angiogenesis. J Biol Chem. 285:5532–5540 (2010).
Aubol BE, Wu G, Keshwani MM, Movassat M, Fattet L, et al. Release of SR Proteins from CLK1 by SRPK1: A Symbiotic Kinase System for Phosphorylation Control of Pre-mRNA Splicing. Mol Cell. 63: 218–228 (2016).
Corkery DP, Holly AC, Lahsaee S, Dellaire G. Connecting the speckles: Splicing kinases and their role in tumorigenesis and treatment response. Nucleus . 6:279-88 (2015).
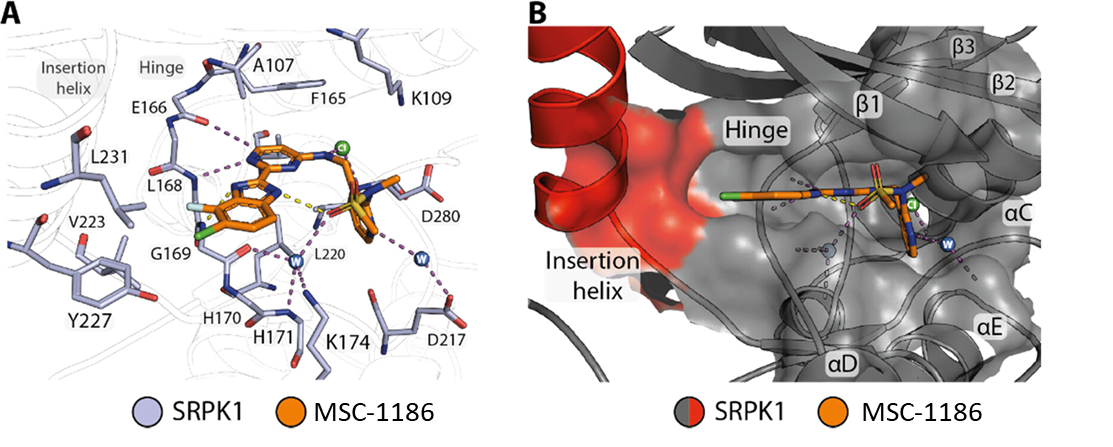
Co-crystal structure of SRPK1 in complex with MSC1186 (PDB ID: 7PQS).
 |