| Probe | Negative control | |
 |
|  |
MU1742 |
| MU2027 |
Casein kinases 1 (CK1) belong to the family of serine/threonine kinases.1 There are six CK1 isoforms (CK1α, CK1γ1, CK1γ2, CK1γ3, CK1δ, CK1ε) and several splice variants in humans.1,2 All CK1 isoforms share highly conserved kinase domain, with the highest homology displayed by CK1δ and CK1ε.3 They are generally cofactor-independent, and depend on N-terminal acidic and/or phosphorylated amino acids for substrate recognition.4 The cellular activity of CK1 can be regulated by sub-cellular localization, post-translational modifications or interaction with other proteins. The major post-translational modifications comprise activating and inhibitory phosphorylation which can be performed site-selectively by other kinases or via autophosphorylation.1,3 For instance, inhibitory autophosphorylation at C-terminus has been described for all human CK1 isoforms.1,3 It was found that CK1δ forms a dimer, which could possibly have negative regulatory effect on the CK1δ kinase activity in vivo.3 Substrate recognition motifs for CK1 kinases are widely distributed in cellular proteins and more than 140 substrates for CK1 isoforms have been reported, indicating their pleiotropic character.3 CK1 regulates Wnt, Hh and Hippo pathways, which are important for growth, development and homeostasis.3,5,6 Thus, CK1s are involved in the regulation of various cellular states, processes and functions such as chromosome segregation, gene expression, cellular morphology, immune response and inflammation, membrane trafficking, cytokinesis, autophagy, cell stemness and differentiation, cell survival, proliferation and apoptosis.1–3,7 Although CK1 isoforms are similar in their structure and function (especially CK1δ/ε), they have also distinct and specific functions.
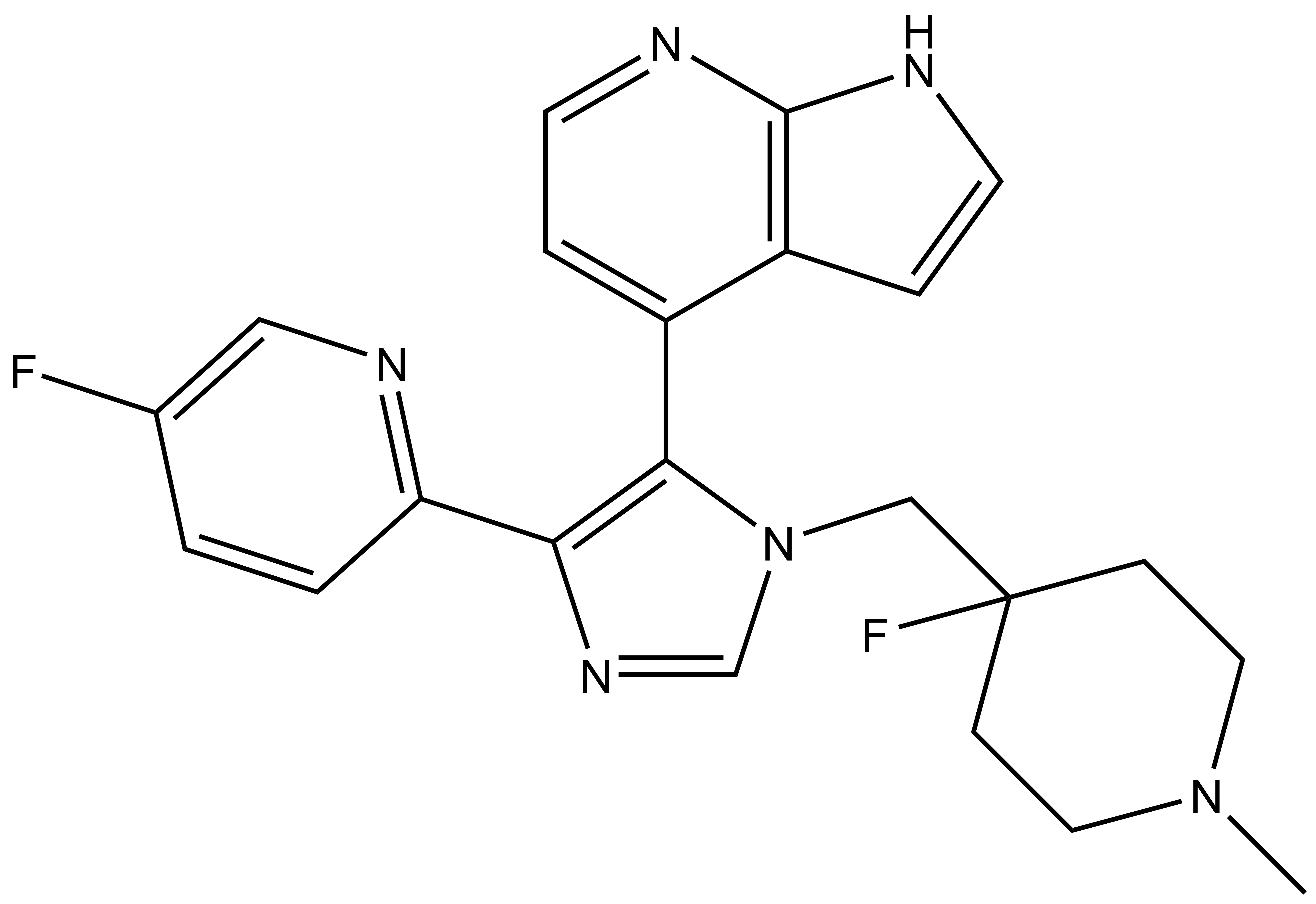
SGC has developed in collaboration with Prof. Kamil Paruch (Masaryk University, Brno, Czech Republic) and Prof. Vitezslav Bryja (Masaryk University, Brno, Czech Republic) quality chemical probe MU1742 for CK1δ and CK1ε protein kinases, including the corresponding negative control compound MU2027. The chemical probe MU1742 exhibits excellent kinome-wide selectivity, high potency against CK1δ/ε in vitro and in cellulo. Moreover, MU1742 has suitable PK profile which allows utilization in vivo.
| Probe | Negative control | |
 |
|  |
MU1742 |
| MU2027 |
| Physical and chemical properties MU1742 | |
| Molecular weight | 408.46 |
| Molecular formula | C22H22F2N6 |
| IUPAC name | 4-(1-((4-fluoro-1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)methyl)-4-(5-fluoropyridin-2-yl)-1H-imidazol-5-yl)-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine |
| ClogP | 2.39 |
| PSA | 55.59 |
| No. of chiral centres | 0 |
| No. of rotatable bonds | 4 |
| No. of hydrogen bond acceptors | 6 |
| No. of hydrogen bond donors | 1 |
| Storage | Stability not tested. Recommendation: Long term storage at -20 °C. Short term storage at room temperature. |
| Dissolution | It is possible to prepare at least 10 mM DMSO solution. For aqueous solutions (in vivo experiments) we recommend to formulate MU1742 as a dihydrochloride salt (.2HCl). |
SMILES: FC1=CN=C(C2=C(N(C=N2)CC3(CCN(CC3)C)F)C4=CC=NC5=C4C=CN5)C=C1
InChI: InChI=1S/C22H22F2N6/c1-29-10-6-22(24,7-11-29)13-30-14-28-19(18-3-2-15(23)12-27-18)20(30)16-4-8-25-21-17(16)5-9-26-21/h2-5,8-9,12,14H,6-7,10-11,13H2,1H3,(H,25,26)
InChIKey: SWOIFXHMBKFCRM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
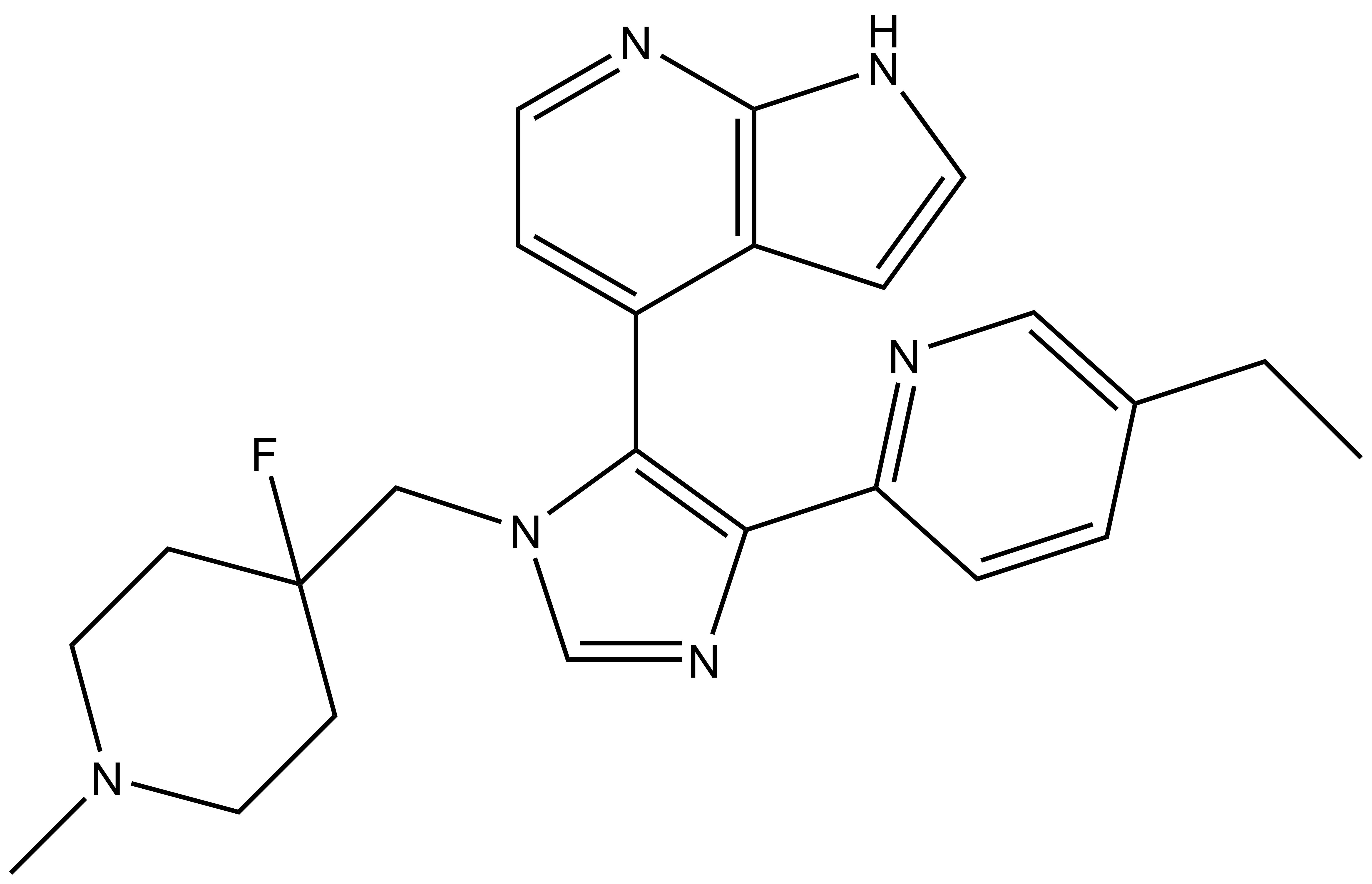
| Physical and chemical properties MU2027 | |
| Molecular weight | 418.518 |
| Molecular formula | C24H27N6F |
| IUPAC name | 4-(4-(5-ethylpyridin-2-yl)-1-((4-fluoro-1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)methyl)-1H-imidazol-5-yl)-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine |
| ClogP | 3.05 |
| PSA | 62.63 |
| No. of chiral centres | 0 |
| No. of rotatable bonds | 5 |
| No. of hydrogen bond acceptors | 6 |
| No. of hydrogen bond donors | 1 |
| Storage | Stability not tested. ecommendation:
ong term storage at -20 °C.
hort term storage at room temperature.
|
| Dissolution | It is possible to prepare at least 10 mM DMSO solution. |
SMILES: FC1(CN2C(C3=CC=NC4=C3C=CN4)=C(N=C2)C5=NC=C(C=C5)CC)CCN(CC1)C
InChI: InChI=1S/C24H27FN6/c1-3-17-4-5-20(28-14-17)21-22(18-6-10-26-23-19(18)7-11-27-23)31(16-29-21)15-24(25)8-12-30(2)13-9-24/h4-7,10-11,14,16H,3,8-9,12-13,15H2,1-2H3,(H,26,27)
InChIKey: SRSOVGVHVNSXTC-UHFFFAOYSA-N
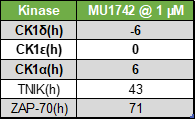
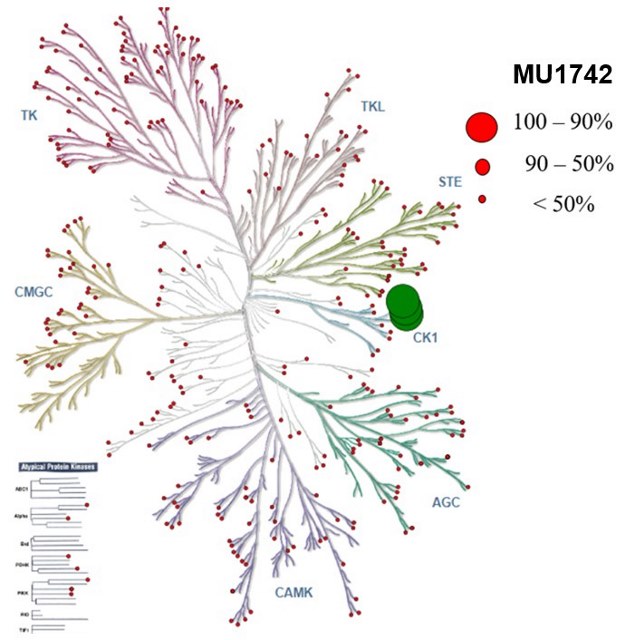
The selectivity profile of MU1742 was determined by a kinome-wide screening against 415 protein kinases at 1 µM concentration (Reaction biology). The result shows that only CK1 kinases were strongly inhibited and no off target were observed below the threshold of 40 % residual activity.
Top hits from kinome-wide profiling (415 kinases):
Kinome tree representation of kinome-wide profiling:
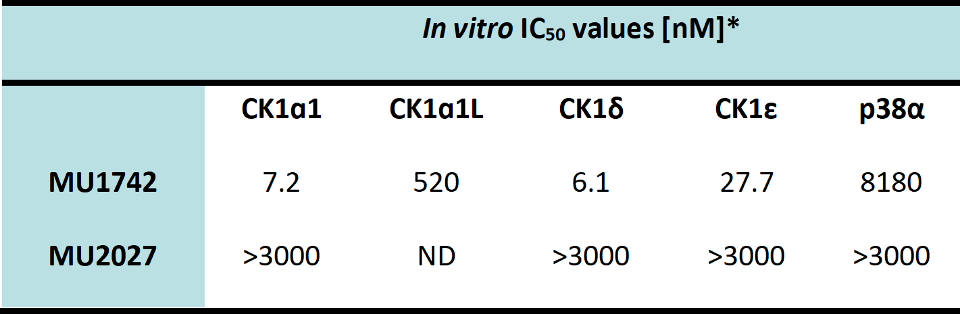
The in vitro potency and selectivity of MU1742 (chemical probe) and MU2027 (negative control compound) was further assessed by a determination of IC50 values (at Reaction Biology, 10 mM ATP conc.) against CK1α, CK1α1L, CK1δ, CK1ε and p38 α which is a common off target of CK1 inhibitors.
Biochemical assay:
*Tested in Reaction Biology
Concentration of ATP: 10 µM
Enzyme conc. used in the assays: CK1α1: 2.5 nM, CK1δ: 15 nM, CK1ε: 45 nM, p38a: 20 nM
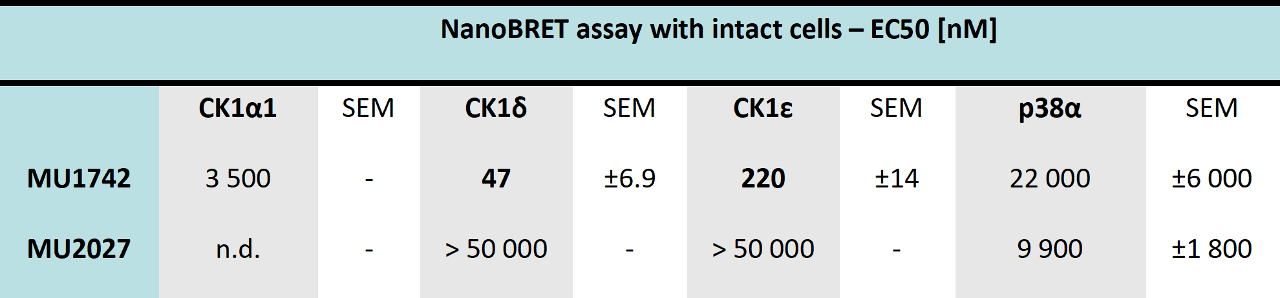
The cellular potency of MU1742 was subsequently tested using NanoBRET assay with intact cells (HEK 293), demonstrating in cellulo target engagement. Interestingly, the cellular potency towards CK1α1 was more than 2 orders lower in cellulo than in vitro.
Cellular target engagement assay:
The cellular activity has been further demonstrated using additional orthogonal assays such as western blotting. The inhibition of CK1δ and CK1ε was monitored via their effect on autophosphorylation. Since CK1δ and CK1ε are functionally redundant, CK1δ- and CK1ε-knock out cell lines were generated and used to differentiate the inhibitory activity on individual isoforms. As a readout for CK1α inhibition, we monitored an effect on B-catenin stabilization, compound BTX-A51 was used as the positive control. MU1742 was tested together with structurally analogous CK1 inhibitors MU1250 and MU1500 which exhibit different isoform selectivity.
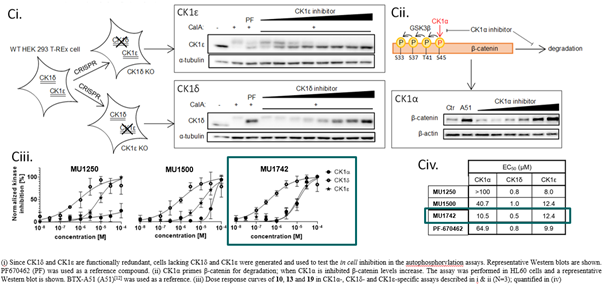
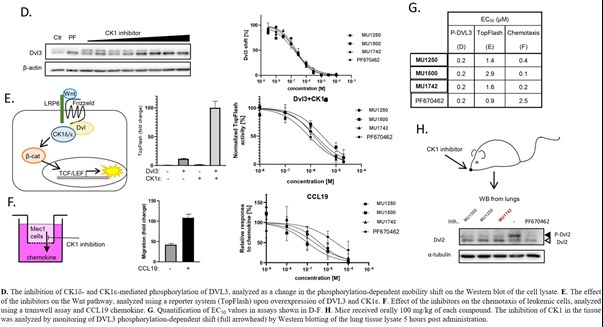
In addition, the in cellulo CK1δ/ε inhibition was evaluated via an effect on phosphorylation of DVL3 as the phosphorylation dependent mobility shift on the Western blot. The effect on modulation of Wnt signaling was also confirmed by TopFlash reporter system upon overexpression of DVL3 and CK1ε. Furthermore, the inhibition of Wnt signaling and chemotaxis of leukemic cells by MU1742 was documented using trans-well assay and CCL19 chemokine. The in vivo activity of MU1742 was demonstrated via effect on phosphorylation of DVL2 from lung tissue after per oral administration of MU1742 (100 mg/kg).
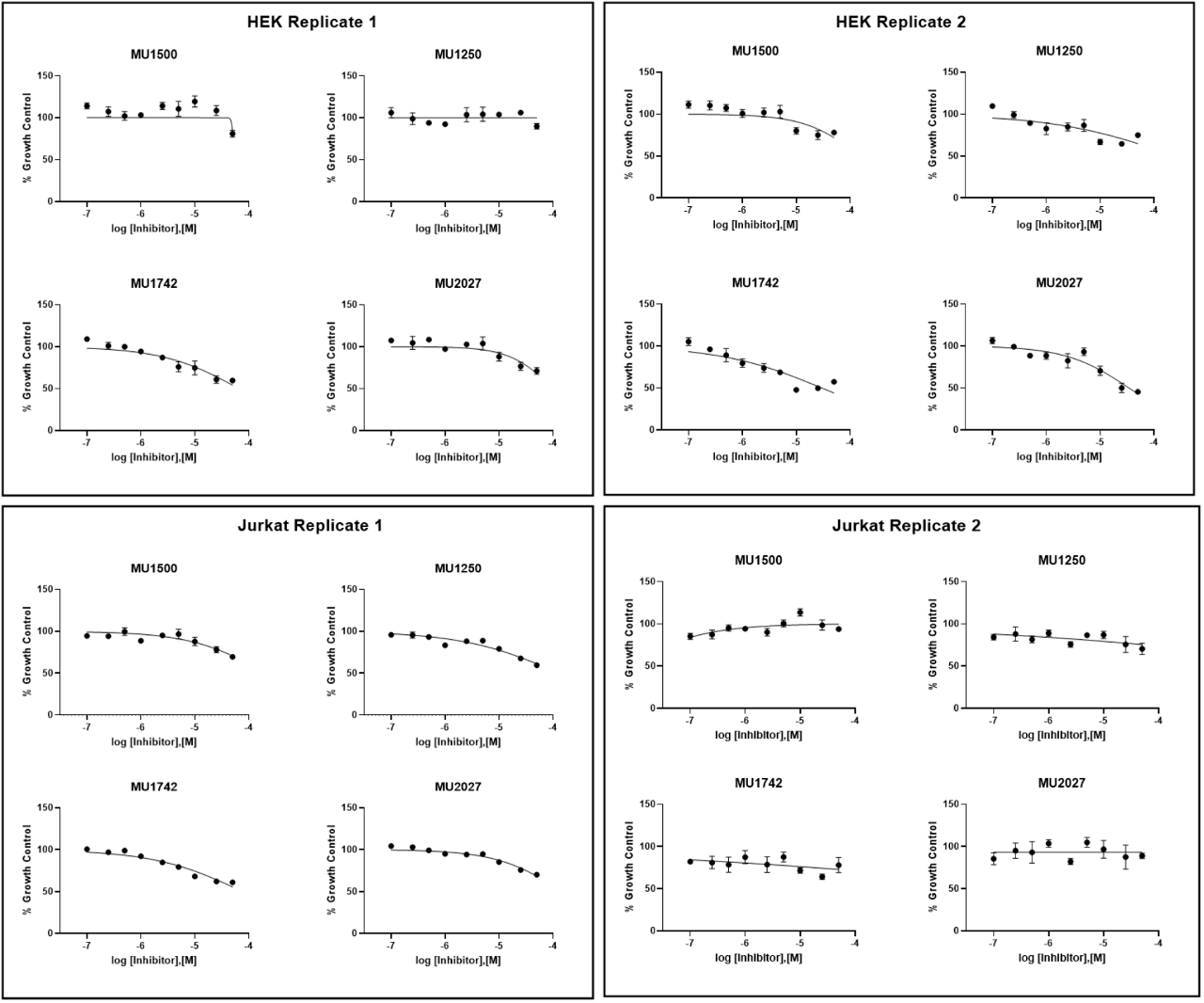
The crude cytotoxic effect was tested in JURKAT and HEK 293 cell lines over 24 hours using Alamar blue as an indicator.
1. Schittek, B. & Sinnberg, T. Biological functions of casein kinase 1 isoforms and putative roles in tumorigenesis. Mol Cancer 13, 231 (2014).
2. Qiao, Y. et al. Small molecule modulators targeting protein kinase CK1 and CK2. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 181, 111581 (2019).
3. Knippschild, U. et al. The CK1 Family: Contribution to Cellular Stress Response and Its Role in Carcinogenesis. Front. Oncol. 4, (2014).
4. Behrend, L. Interaction of casein kinase 1 delta (CK1d) with post-Golgi structures, microtubules and the spindle apparatus. European Journal of Cell Biology 79, 240–251 (2000).
5. Yang, K. et al. The evolving roles of canonical WNT signaling in stem cells and tumorigenesis: implications in targeted cancer therapies. Lab Invest 96, 116–136 (2016).
6. Jiang, J. CK1 in Developmental Signaling. in Current Topics in Developmental Biology vol. 123 303–329 (Elsevier, 2017).
7. Jiang, S., Zhang, M., Sun, J. & Yang, X. Casein kinase 1α: biological mechanisms and theranostic potential. Cell Commun Signal 16, 23 (2018).
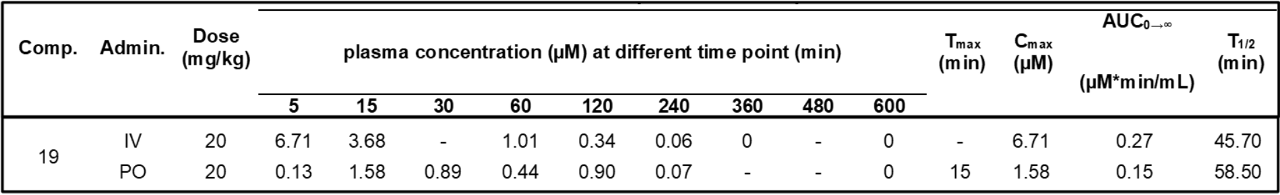
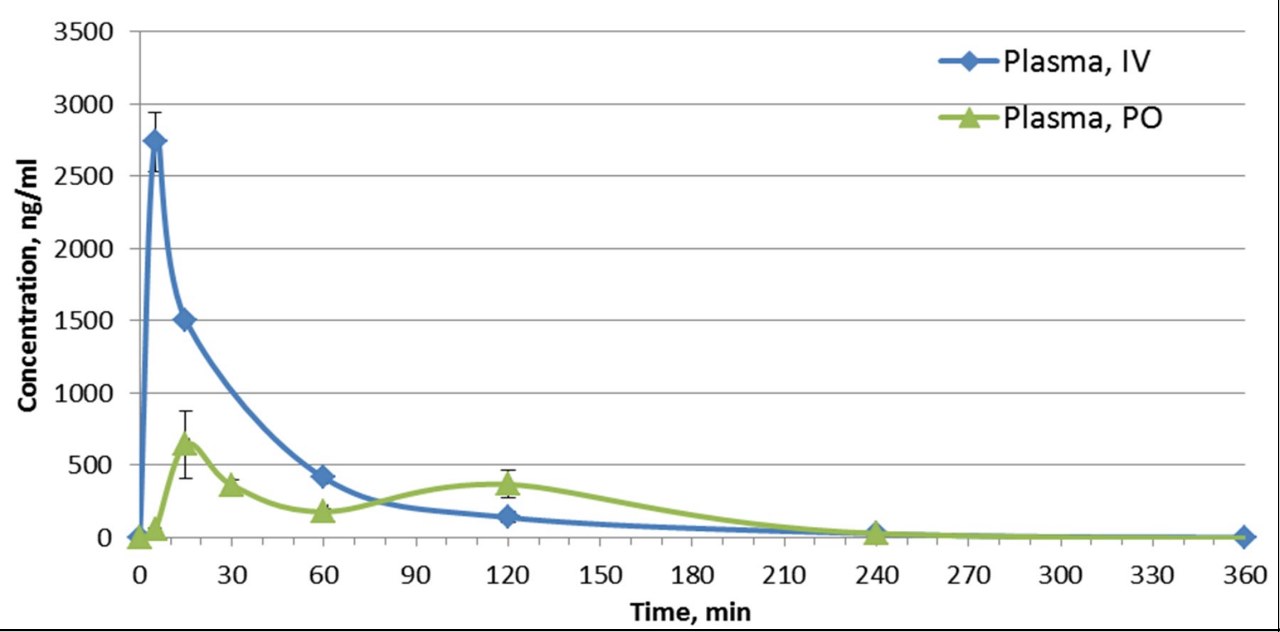
The in vivo pharmacokinetic (PK) profile of MU1742 has been evaluated in mice. After a PO administration of 20 mg/kg of MU1742 .2HCl (formulated as dihydrochloride salt), compound exhibits 57 % PO bioavailability and relatively stable plasma concentrations. Additional PK parameters are summarized in the table, indicating that MU1742 is a suitable chemical probe for in vivo experiments.
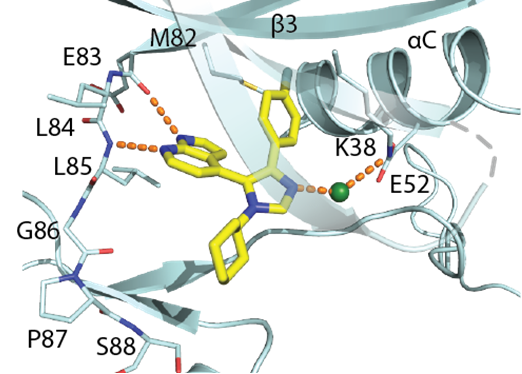
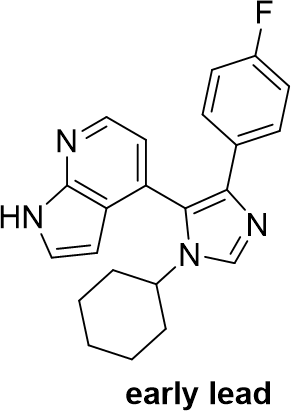
Several analogues, which are structurally similar to MU1742, have been successfully co-crystalized with CK1δ. All structurally related compounds share a very similar binding mode which is characterized by, for instance, the hinge interaction with the pyrrolopyridine moiety, the back pocket interaction with the (hetero)aryl moiety and the interaction with water molecule (in green). Based these observations we assume that MU1742 interacts analogously with CK1α/δ/ε. One example of the co-crystal structure with early lead-CK1δ co-crystal structure is located below (PDB: 7QRA).