| Probe | Negative control | |
 |
|  |
SGC-CAF382-1 |
| SGC-CAF268-1N |
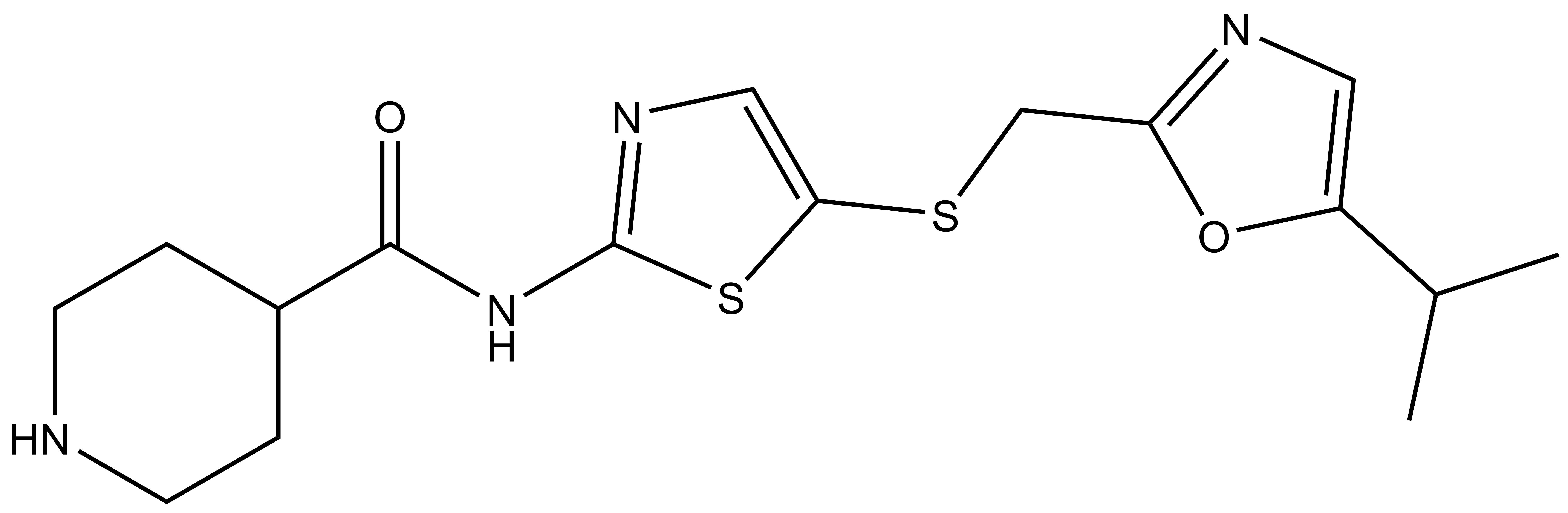
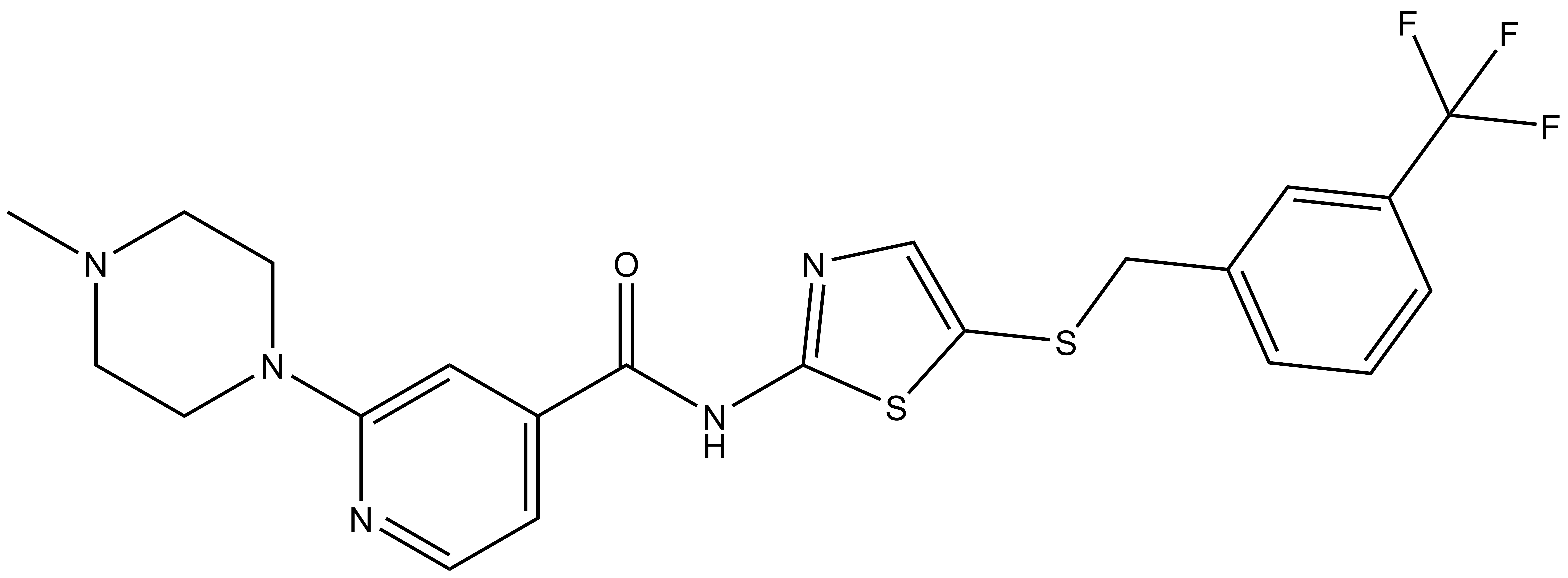
From a library of SNS-032 analogs, we identified a potent and cell-active chemical probe (SGC-CAF382-1) that inhibits cyclin-dependent kinase-like 5 (CDKL5) and several cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK9, CDK16, CDK17, and CDK18). Comprehensive evaluation of kinome-wide selectivity confirmed that this chemical probe demonstrates good selectivity. A structurally similar analog (SGC-CAF268-1N) was characterized as a negative control that does not bind to CDKL5, CDK9, CDK16, CDK17, or CDK18 in corresponding cellular target engagement assays. SGC-CAF382-1 is devoid of GSK3 inhibition when used at an appropriate concentration. At nanomolar concentrations, our chemical probe promoted motor neuron survival when iPSC-derived motor neurons were subjected to ER stress. An orthogonal CDKL5 chemical probe, SGC-CDKL5/GSK3-1, represents a distinct chemotype with non-overlapping kinase off-targets that can be profiled in parallel. When used at ≤100 nM in cell-based assays, our chemical probe set can help the community further characterize the underexplored roles of CDKL5.
| Probe | Negative control | |
 |
|  |
SGC-CAF382-1 |
| SGC-CAF268-1N |
| Physical and chemical properties for SGC-CAF382-1 | |
| Molecular weight | 366.50 |
| Molecular formula | C16H22N4O2S2 |
| IUPAC name | N-(5-(((5-isopropyloxazol-2-yl)methyl)thio)thiazol-2-yl)piperidine-4-carboxamide |
| ClogP | 0.16 |
| PSA | 133.59 |
| No. of chiral centers | 0 |
| No. of rotatable bonds | 7 |
| No. of hydrogen bond acceptors | 5 |
| No. of hydrogen bond donors | 2 |
| Storage | Stable as a solid at room temperature. DMSO stock solutions (up to 10 mM) are stable at -20oC |
| Dissolution | Soluble in DMSO up to 10 mM |
| Physical and chemical properties for SGC-CAF268-1N | |
| Molecular weight | 493.57 |
| Molecular formula | C22H22F3N5OS2 |
| IUPAC name | 2-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-N-(5-((3-(trifluoromethyl)benzyl)thio)thiazol-2-yl)isonicotinamide |
| ClogP | 2.33 |
| PSA | 114.90 |
| No. of chiral centers | 0 |
| No. of rotatable bonds | 8 |
| No. of hydrogen bond acceptors | 7 |
| No. of hydrogen bond donors | 1 |
| Storage | Stable as a solid at room temperature. DMSO stock solutions (up to 10 mM) are stable at -20oC |
| Dissolution | Soluble in DMSO up to 10 mM |
SMILES:
SGC-CAF382-1: O=C(C1CCNCC1)NC2=NC=C(SCC3=NC=C(C(C)C)O3)S2
SGC-CAF268-1N: O=C(NC1=NC=C(SCC2=CC=CC(C(F)(F)F)=C2)S1)C3=CC=NC(N4CCN(C)CC4)=C3
InChI:
SGC-CAF382-1: InChI=1S/C16H22N4O2S2/c1-10(2)12-7-18-13(22-12)9-23-14-8-19-16(24-14)20-15(21)11-3-5-17-6-4-11/h7-8,10-11,17H,3-6,9H2,1-2H3,(H,19,20,21)
SGC-CAF268-1N: InChI=1S/C22H22F3N5OS2/c1-29-7-9-30(10-8-29)18-12-16(5-6-26-18)20(31)28-21-27-13-19(33-21)32-14-15-3-2-4-17(11-15)22(23,24)25/h2-6,11-13H,7-10,14H2,1H3,(H,27,28,31)
InChIKey:
SGC-CAF382-1: MCLDWKVRXDHDEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N
SGC-CAF268-1N: RUYKDMMLESXEOA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
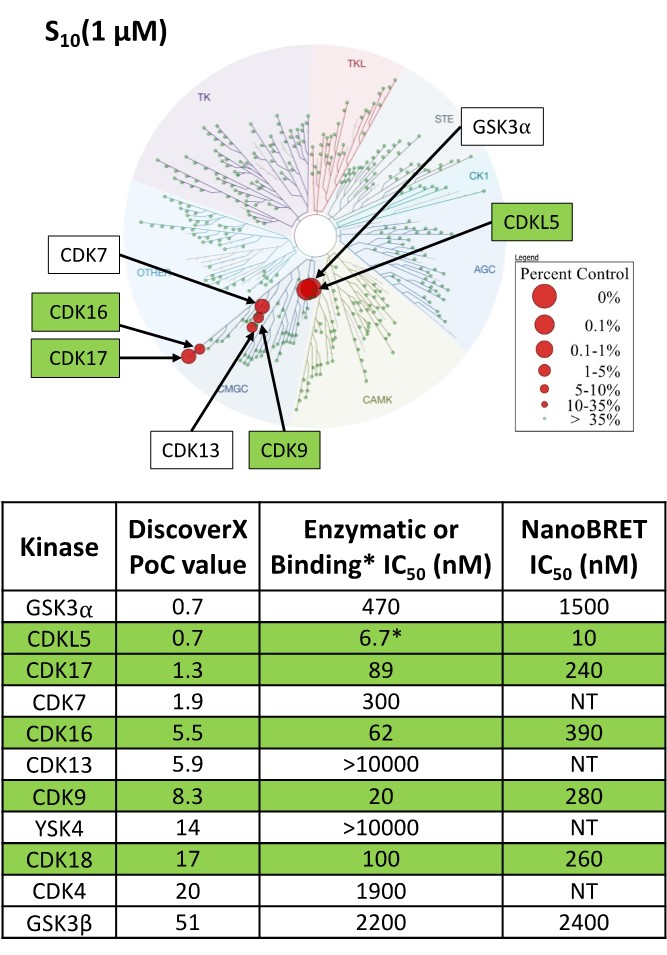
SGC-CAF382-1 was profiled in the DiscoverX scanMAX assay against 403 wild-type kinases at 1 μM. Only 7 kinases showed PoC <10 giving an S10(1 μM) = 0.017. When the PoC <35 fraction was examined, 10 kinases were included (S35(1 μM) = 0.024). Potential off-targets within the S35(1 μM) fraction and GSK3β (PoC = 51) were tested via biochemical enzymatic/binding assays plus NanoBRET target engagement assays for CDKL5, GSK3⍺, GSK3β, CDK9, CDK16, CDK17, and CDK18. Data corresponding with off-target kinase activity is shown in the table below.
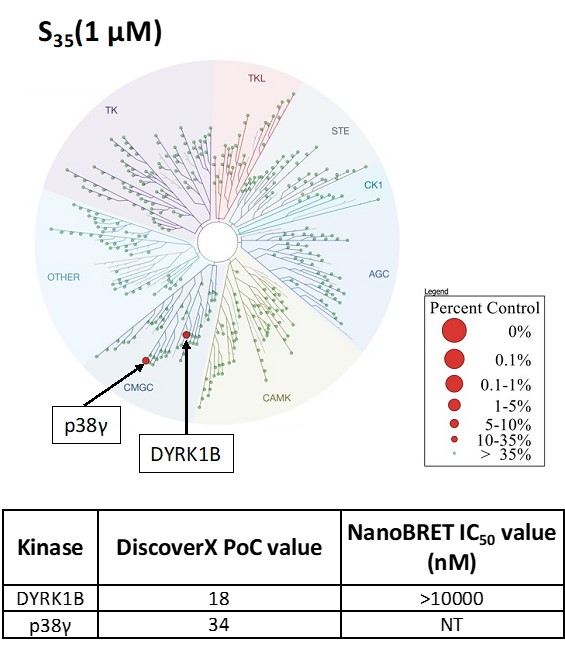
SGC-CAF268-1N was also tested in the DiscoverX scanMAX panel and 2 kinases had a PoC <35 (S35(1 μM) = 0.005). The negative control was evaluated in the corresponding NanoBRET assay for DYRK1B, the kinase that bound with the lowest PoC value in the kinome-wide screen. All results are in the table below.
Biological activity summary:
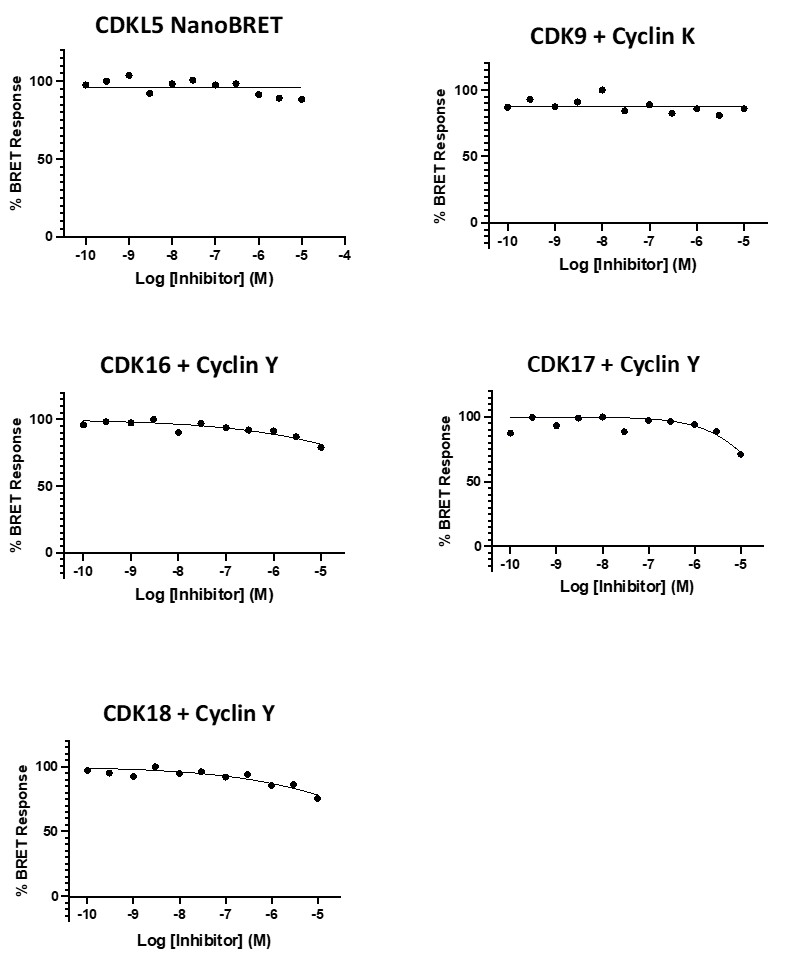
A NanoBRET assay was utilized to assess the binding affinity of SGC-CAF382-1 to CDKL5, CDK9, CDK16, CDK17, CDK18, GSK3⍺, and GSK3β. The negative control shows no binding affinity for CDKL5, CDK9, CDK16, CDK17, or CDK18.
Castano, A.; Silvestre, M.; Wells, C. I.; Sanderson, J. L.; Ferrer, C. A.; Ong, H. W.; Liang, Y.; Richardson, W.; Silvaroli, J. A.; Bashore, F. M.; Smith, J. L.; Genereux, I. M.; Dempster, K.; Drewry, D. H.; Pabla, N. S.; Bullock, A. N.; Benke, T. A.; Ultanir, S.; Axtman, A. D. Discovery and characterization of a specific inhibitor of serine-threonine kinase cyclin dependent kinase-like 5 (CDKL5) demonstrates role in hippocampal CA1 physiology. Elife 2023, 12, e88206; doi: 10.7554/eLife.88206.
Castano, A.; Silvestre, M.; Wells, C. I.; Sanderson, J. L.; Ferrer, C. A.; Ong, H. W.; Liang, Y.; Richardson, W.; Silvaroli, J. A.; Bashore, F. M.; Smith, J. L.; Genereux, I. M.; Dempster, K.; Drewry, D. H.; Pabla, N. S.; Bullock, A. N.; Benke, T. A.; Ultanir, S.; Axtman, A. D. Discovery and characterization of a specific inhibitor of serine-threonine kinase cyclin dependent kinase-like 5 (CDKL5) demonstrates role in hippocampal CA1 physiology. BioRxiv 2023, doi: 10.1101/2023.04.24.538049.