This probe is available from Cayman Chemical and Tocris (dihydrochloride).
The control may be requested by clicking here.
| Probe | Negative control | |
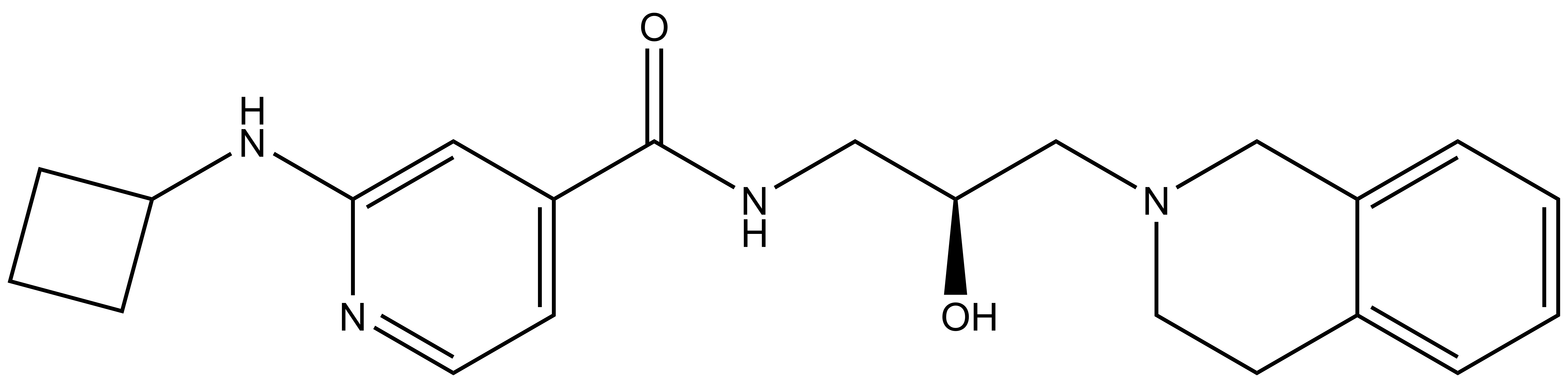 |
| 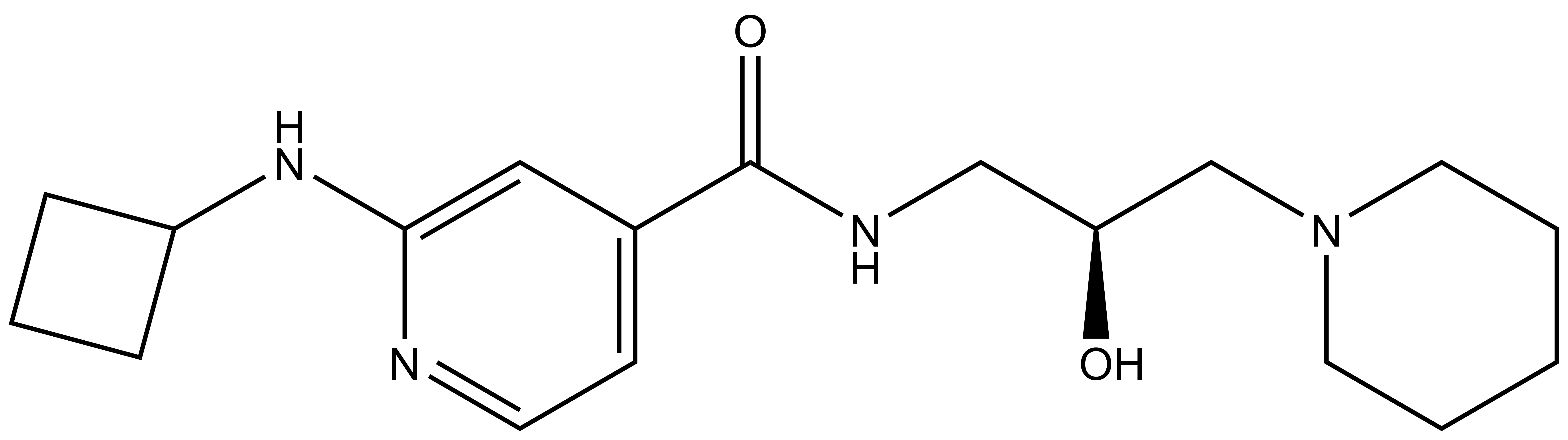 |
GSK591 |
| SGC2096 |
Protein arginine methyltransferases (PRMTs) play a crucial role in a variety of biological processes [1]. Overexpression of PRMTs has been implicated in various human diseases including cancer [2-4]. To date, nine PRMTs have been identified and they are grouped into three categories: types I, II and III. Type II PRMTs, 5 and 9, catalyze symmetric dimethylation of arginine residues, however, PRMT5 is the predominant enzyme for this process. PRMT5 interacts with a number of binding partners that influence its substrate specificity. In particular, MEP50, a member of the WD40 family of proteins, is required for PRMT5 methyltransferase activity.
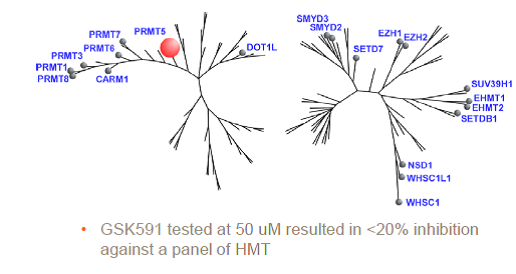
PRMT5 is reported to have a role in mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) as evidenced by its upregulation in patient samples [5,6]. Consequently, a chemical probe of PRMT5 would be a very useful tool for testing biological and therapeutic hypotheses. The first chemical probe of PRMT5 was co-developed by Epizyme and GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) [7]. An analog of this compound, EPZ015866/GSK3203591 [8], has been kindly donated to the SGC for distribution as GSK591. In an in vitro biochemical assay, GSK591 potently inhibits the PRMT5/MEP50 complex from methylating (histone) H4 with IC50 = 11 nM. In Z-138 cells, GSK591 inhibits the symmetric arginine methylation of SmD3 with EC50 = 56 nM. Further, GSK591 is selective for PRMT5 (up to 50 micromolar) relative to a panel of methyltransferases.
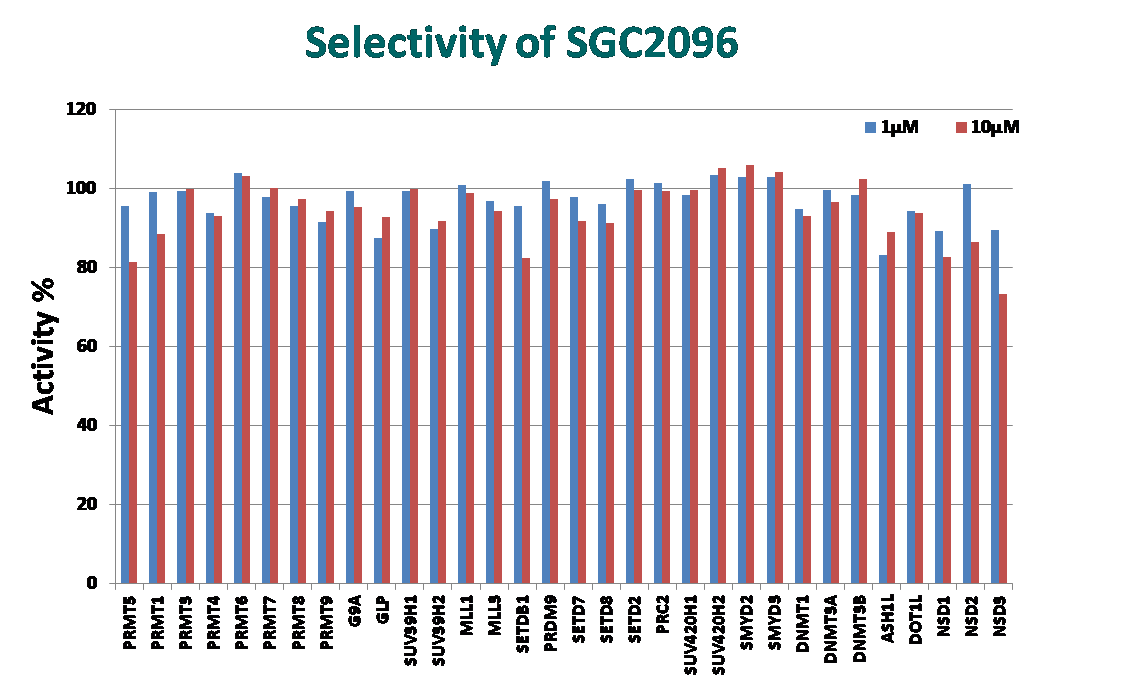
A control compound, SGC2096, that is inactive up to 10 micromolar is also available from the SGC.
In addition, a biotinylated inhibitor, SGC3185 is available
| Biotinylated inhibitor |
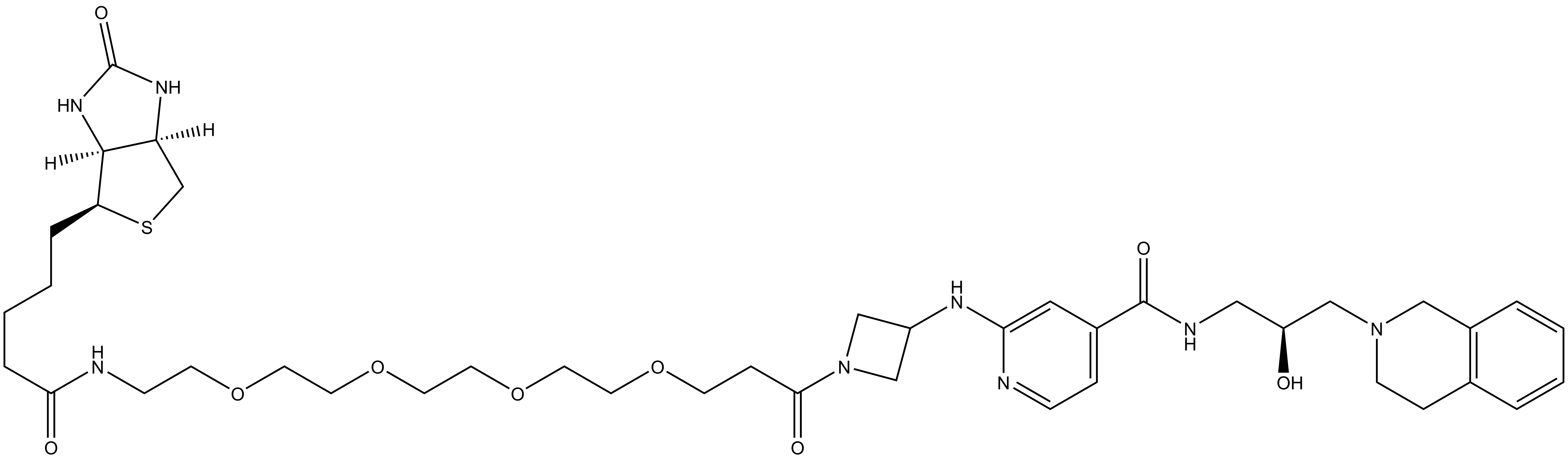 |
SGC3185 |
In Vitro potency
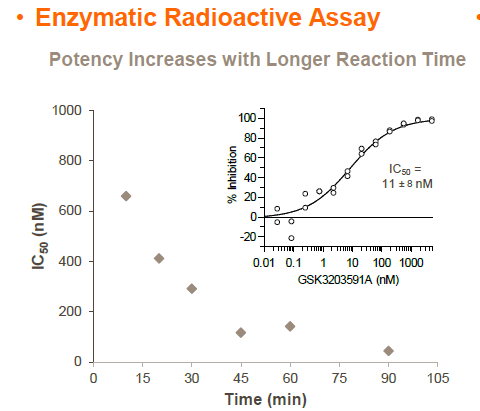
Radioactivity assay using H4 (1-15) as substrate

| Probe | Negative control | |
 |
|  |
GSK591 |
| SGC2096 |
| Physical and chemical properties for GSK591 | |
| Molecular weight | 380.2 |
| Molecular formula | C22H28N4O2 |
| IUPAC name | (3-(3-aza-bicyclo[4.4.0]deca-1(10),6,8-trien-3-yl)-2-hydroxy-propylamino)-(2-cyclobutylamino-pyridin-4-yl)-methanone |
| MollogP | 2.311 |
| PSA | 64.84 |
| No. of chiral centres | 1 |
| No. of rotatable bonds | 8 |
| No. of hydrogen bond acceptors | 5 |
| No. of hydrogen bond donors | 3 |
| Physical and chemical properties for SGC2096 | |
| Molecular weight | 332.2 |
| Molecular formula | C18H28N4O2 |
| IUPAC name | (2-cyclobutylamino-pyridin-4-yl)-(2-hydroxy-3-(piperidin-1-yl)-propylamino)-methanone |
| MollogP | 1.991 |
| PSA | 65.18 |
| No. of chiral centres | 1 |
| No. of rotatable bonds | 8 |
| No. of hydrogen bond acceptors | 5 |
| No. of hydrogen bond donors | 3 |
| Biotinylated inhibitor |
 |
SGC3185 |
| Physical and chemical properties for GSK3185 | |
| Molecular weight | 854.4 |
| Molecular formula | C42H62N8O9S |
| IUPAC name | 6-(5-(2-(2-(2-(2-(3-(3-(4-((3-(3-aza-bicyclo[4.4.0]deca-1(10),6,8-trien-3-yl)-2-hydroxy-propylamino)-formyl)-pyridin-2-ylamino)-azetidin-1-yl)-3-oxo-propoxy)-ethoxy)-ethoxy)-ethoxy)-ethylamino)-5-oxo-pentyl)-7-thia-2,4-diaza-bicyclo[3.3.0]octan-3-one |
| MollogP | 1.341 |
| PSA | 175.1 |
| No. of chiral centres | 4 |
| No. of rotatable bonds | 30 |
| No. of hydrogen bond acceptors | 16 |
| No. of hydrogen bond donors | 6 |
SMILES: [H][C@@]12[C@H](CCCCC(NCCOCCOCCOCCOCCC(N3CC(C3)Nc3cc(ccn3)C(NC[C@@H](CN3CCc4ccccc4C3)O)=O)=O)=O)SC[C@]1([H])NC(N2)=O
InChI: InChI=1S/C42H62N8O9S/c51-34(28-49-14-10-30-5-1-2-6-32(30)25-49)24-45-41(54)31-9-12-43-37(23-31)46-33-26-50(27-33)39(53)11-15-56-17-19-58-21-22-59-20-18-57-16-13-44-38(52)8-4-3-7-36-40-35(29-60-36)47-42(55)48-40/h1-2,5-6,9,12,23,33-36,40,51H,3-4,7-8,10-11,13-22,24-29H2,(H,43,46)(H,44,52)(H,45,54)(H2,47,48,55)/t34-,35-,36-,40-/m0/s1
InChIKey: PZIWNLNYZRZJCY-VNLYVSNMSA-N
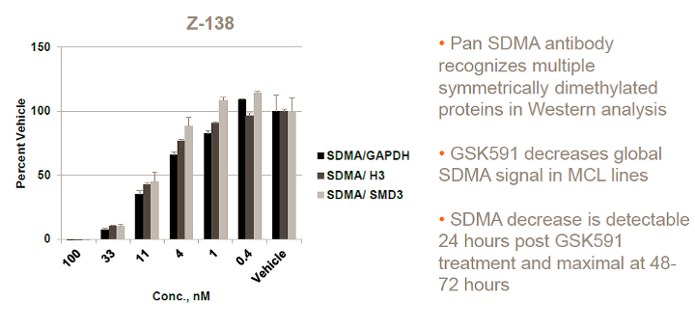
Dose-dependant decrease in SDMA in Z-138 cells
References
PDB 5C9Z
Main features