This probe is available from Cayman Chemical.
This probe (hydrochloride) is available from Sigma, Tocris and Cayman Chemical .
The negative control (MS094) is available for purchase from Sigma.
| Probe | Negative control | |
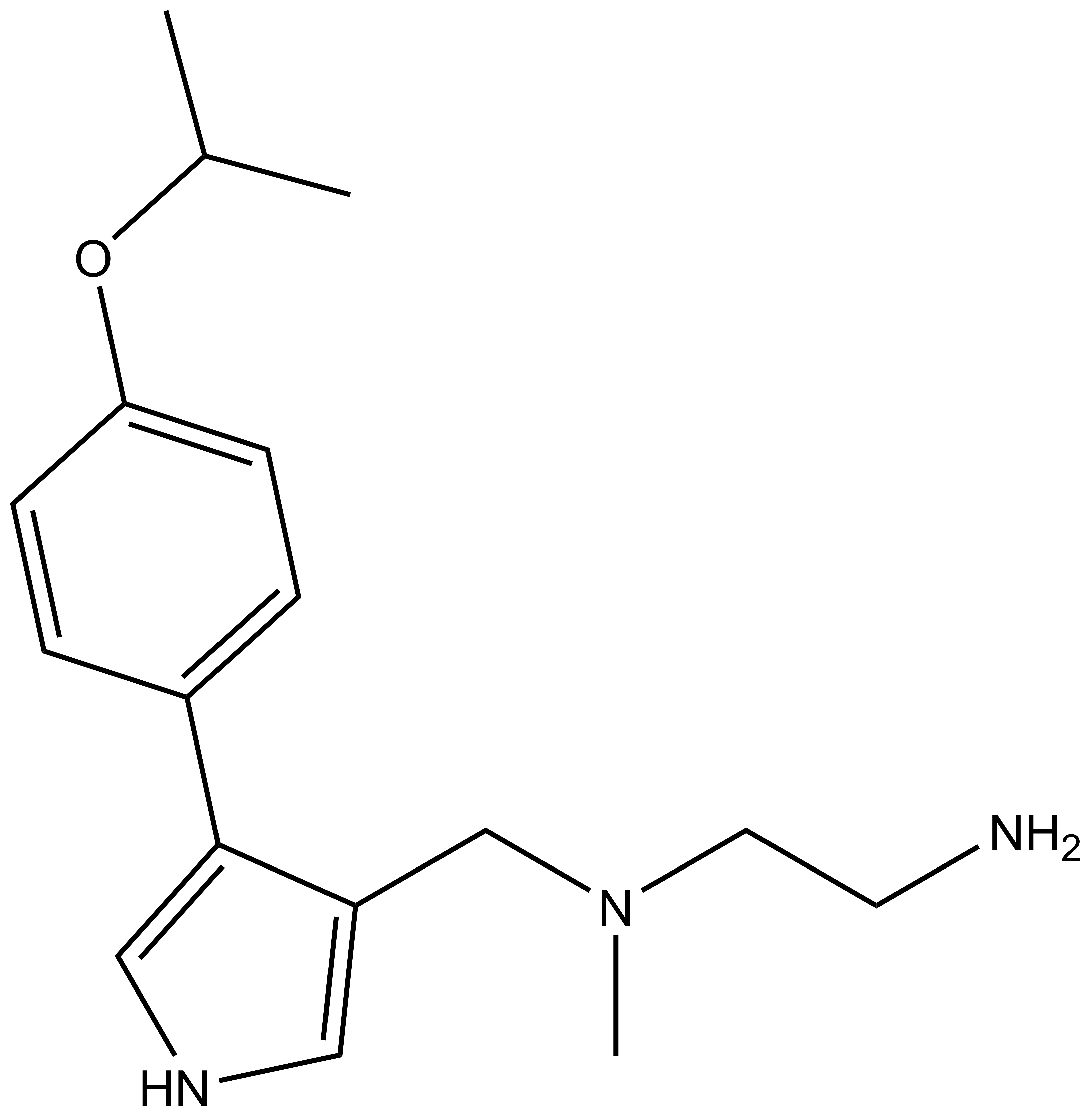 | 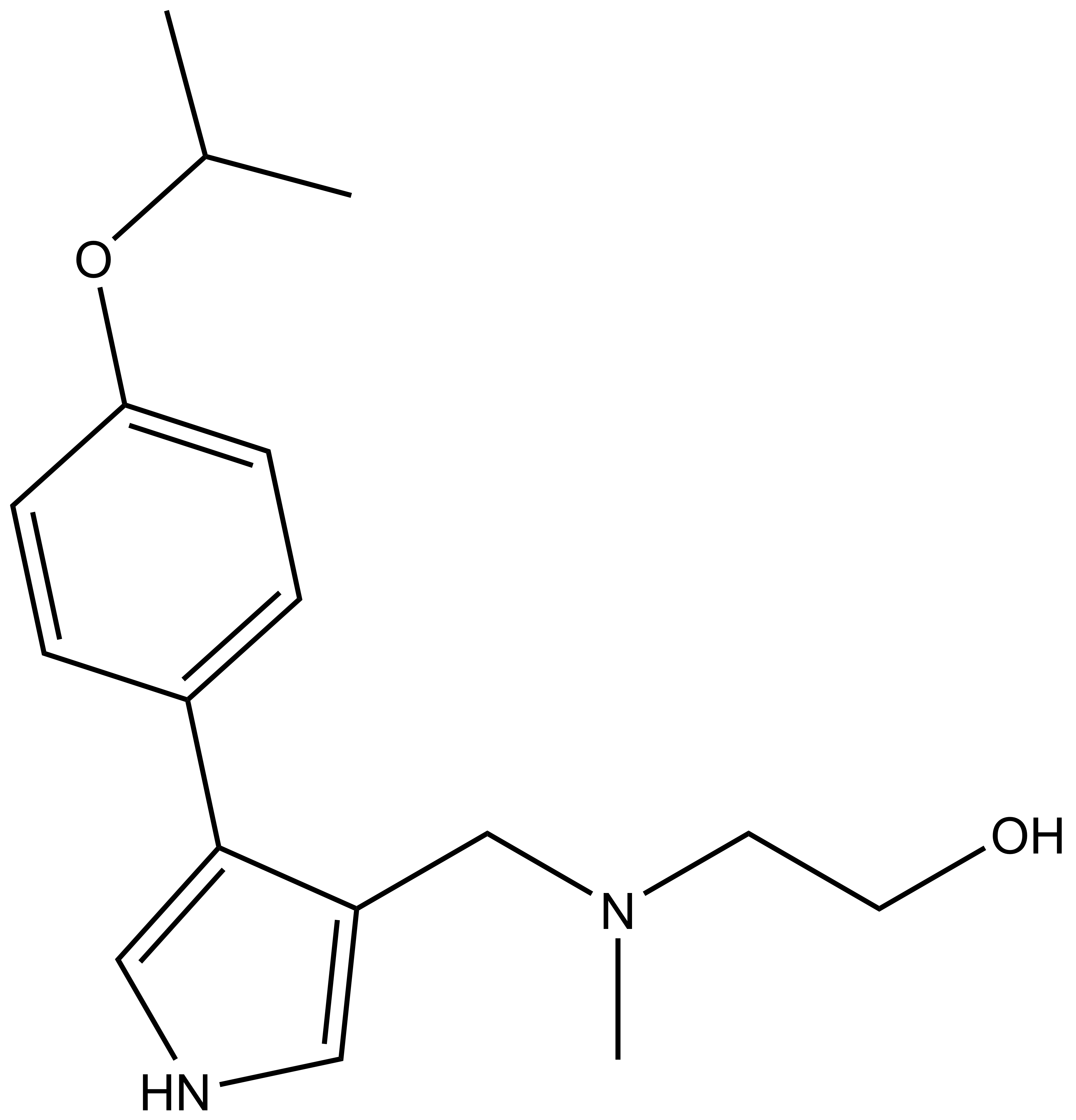 | |
MS023 |
| MS094 |
Protein arginine methyltransferases (PRMTs) play a crucial role in a variety of biological processes [1]. Overexpression of PRMTs has been implicated in various human diseases including cancer [2-4]. To date, nine PRMTs have been identified and they are grouped into three categories: types I, II and III. Type I PRMTs catalyze mono- and asymmetric dimethylation of arginine residues and include PRMT1, 3, 4 (also known as CARM1 (Co-activator-associated arginine methyltransferase 1)), 6 and 8. It has been shown that knocking down the expression of PRMT1 or PRMT6 genes (using siRNA) significantly reduces the growth of bladder and lung cancer cells [5]. Consequently, selective small-molecule inhibitors of PRMTs have been pursued by both academia and pharmaceutical industry as chemical tools for testing biological and therapeutic hypotheses [6,7].
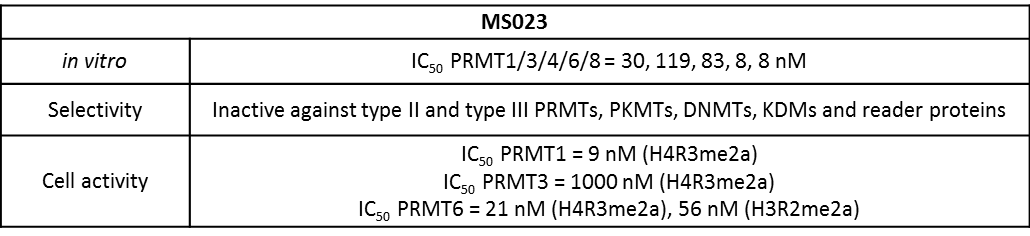
A collaboration between the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and the SGC has resulted in MS023 [8], a chemical probe for type I PRMTs, and a structurally similar control compound, MS094. The in vitro and cell-based activity of MS023 is summarized in the table and the Western blots.
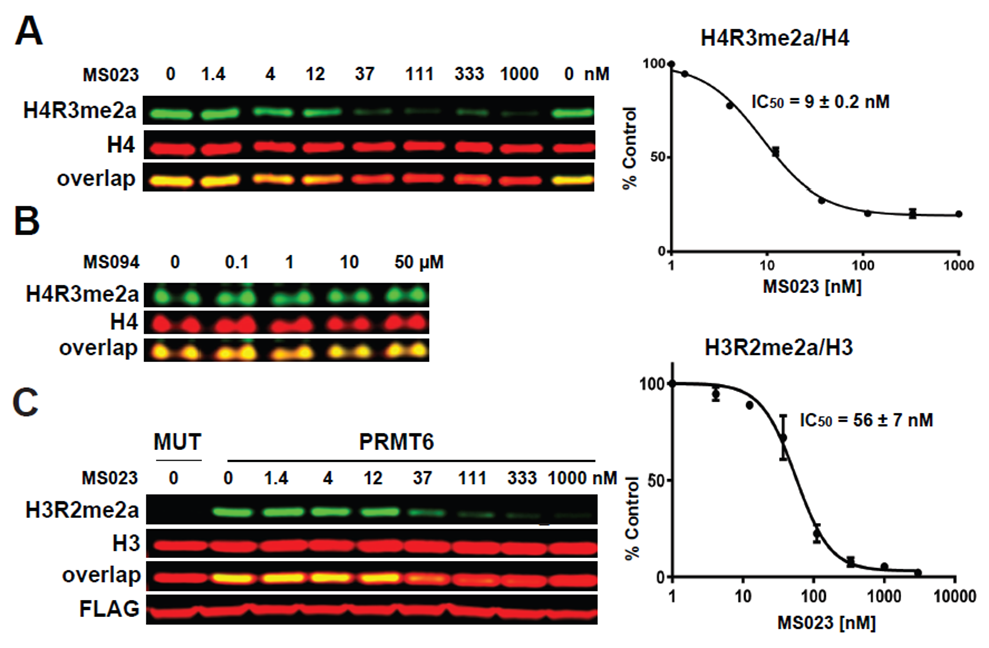
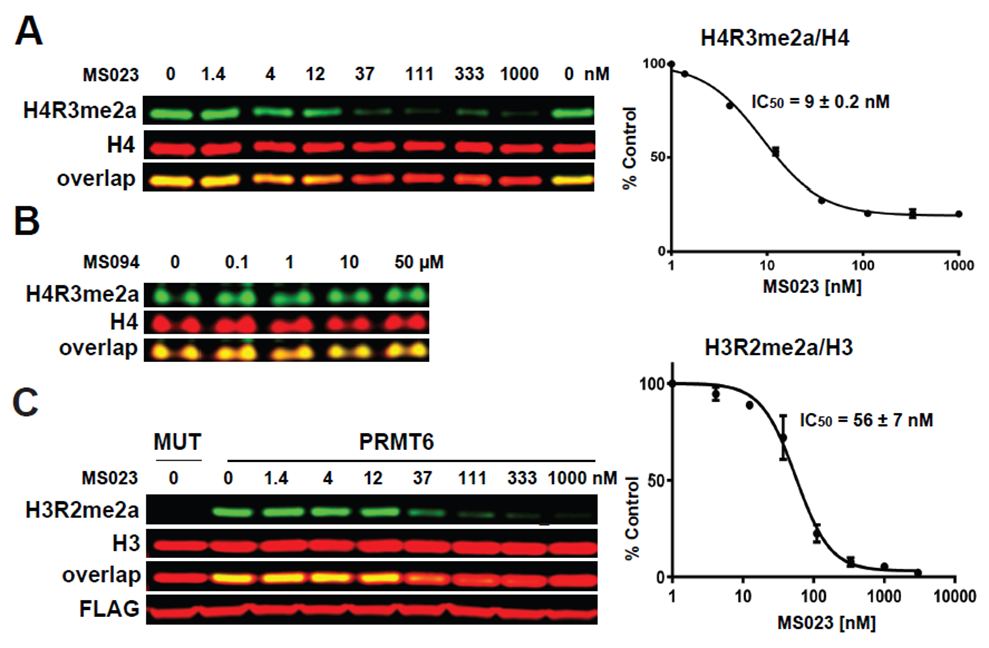
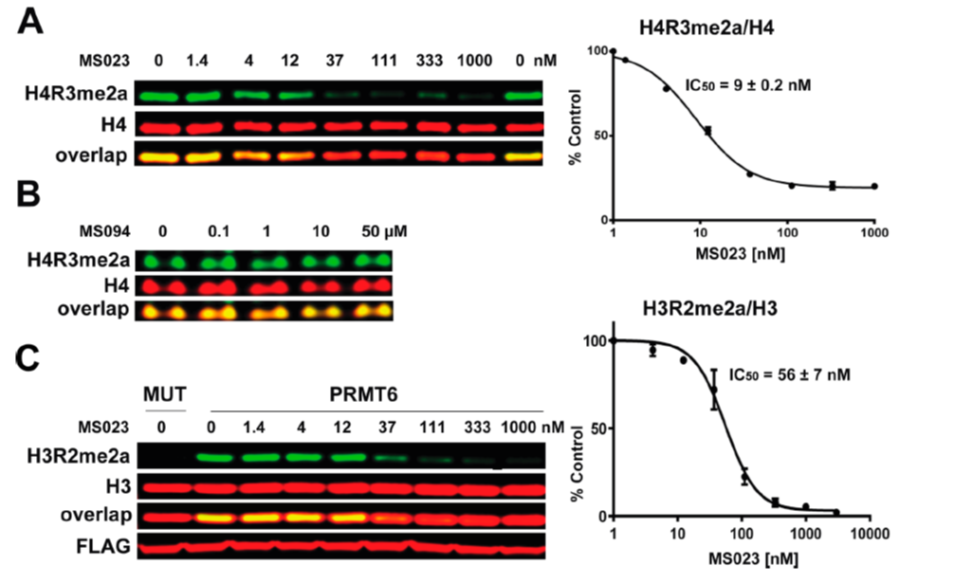
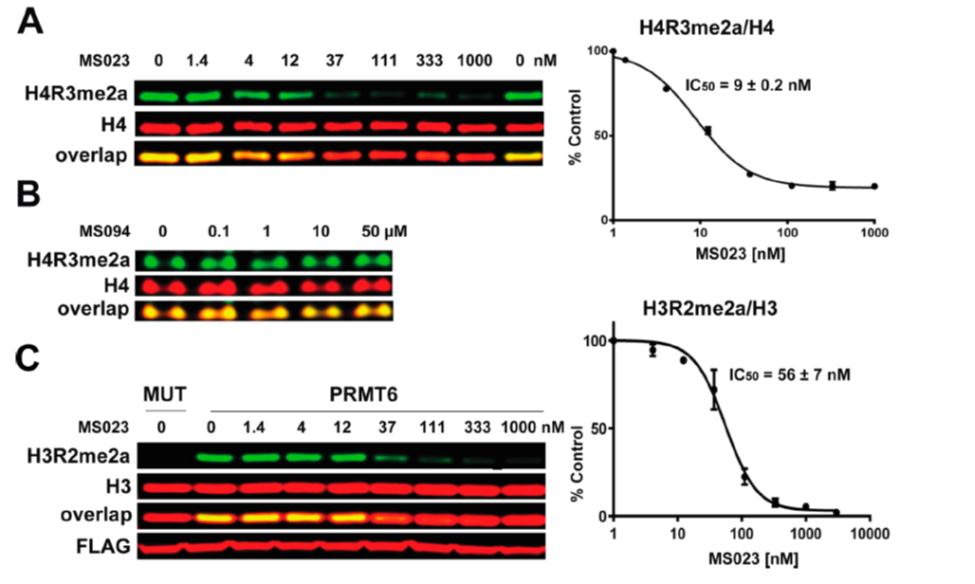
(A) MS023 inhibits PRMT1 methyltransferase activity in MCF7 cells. (B) MS094 does not inhibit PRMT1 methyltransferase activity in MCF7 cells. MCF7 cells were treated with MS023 (A) or MS094 (B) at indicated concentrations for 48 h and H4R3me2a levels were determined by Western blot. The graphs represent nonlinear fits of H4R3me2a signal intensities normalized to total histone H4. The results are MEAN ± SEM of two experiments done in triplicate. (C) MS023 inhibits PRMT6 methyltransferase activity in HEK293 cells. HEK293 cells were transfected with FLAG-tagged PRMT6 or its catalytically inactive mutant V86K/D88A (MUT) and treated with MS023 at indicated concentrations for 20 h. H3R2me2a levels were determined by Western blot. The graphs represent nonlinear fits of H3R2me2a signal intensities normalized to total histone H3. The results are MEAN ± SEM of 3 replicates.
| Probe | Negative control | |
 |  | |
MS023 |
| MS094 |
| Physical and chemical properties for MS023 | |
| Molecular weight | 287.2 |
| Molecular formula | C17H25N3O |
| IUPAC name | 3-(((2-amino-ethyl)-methyl-amino)-methyl)-4-(4-(1-methyl-ethoxy)-phenyl)-1H-pyrrole |
| MollogP | 1.798 |
| PSA | 42.64 |
| No. of chiral centres | 0 |
| No. of rotatable bonds | 7 |
| No. of hydrogen bond acceptors | 3 |
| No. of hydrogen bond donors | 3 |
| Physical and chemical properties for MS094 (Negative Control) | |
| Molecular weight | 288.2 |
| Molecular formula | C17H24N2O2 |
| IUPAC name | 2-(methyl-((4-(4-(1-methyl-ethoxy)-phenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)-methyl)-amino)-ethanol |
| MollogP | 2.397 |
| PSA | 38.15 |
| No. of chiral centres | 0 |
| No. of rotatable bonds | 7 |
| No. of hydrogen bond acceptors | 3 |
| No. of hydrogen bond donors | 2 |
MS023 is a potent Type 1 PRMT inhibitor.
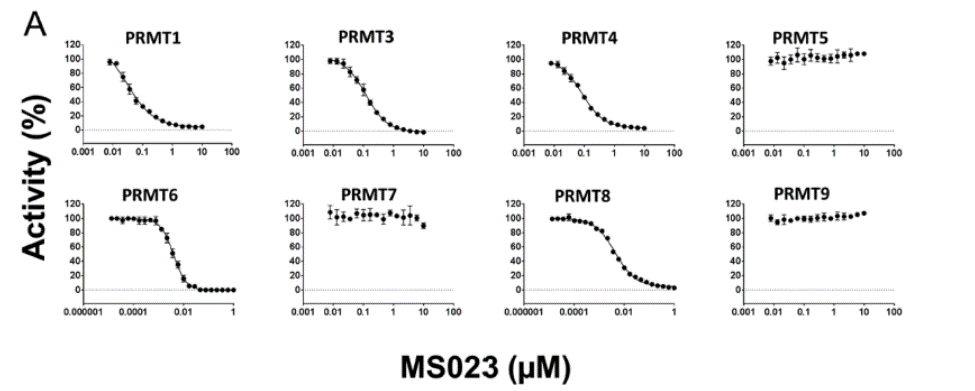
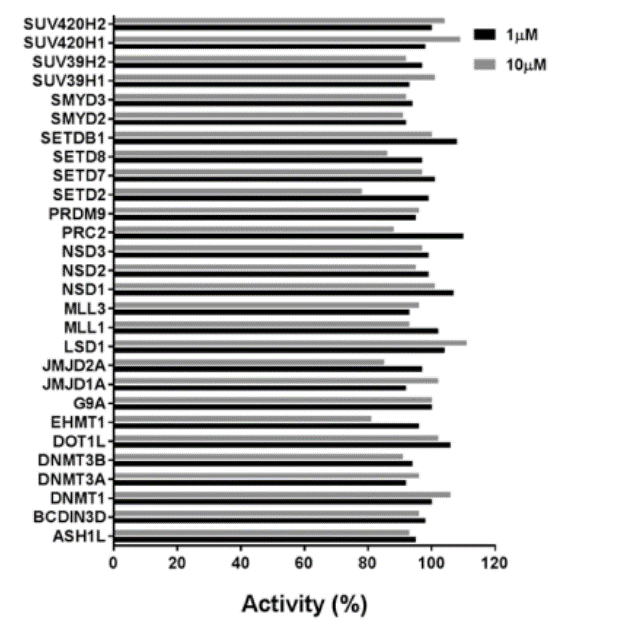
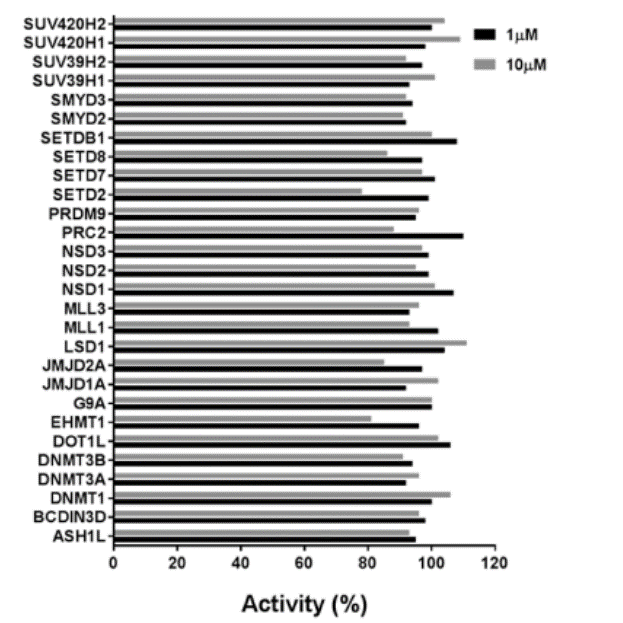
Selectivity
Selectivity of MS023 within methyltransferase family
Cellular activity
MS023 is a potent inhibitor of H4R3 and H3R2 methylation in cells. At 50 microM the negative control, MS094, does not affect H4R3 methylation.
[1] Bedford M T and Clarke SG (2009) Protein Arginine Methylation in Mammals: Who, What, and Why, Mol. Cell 33, 1-13.
[2] Wei H, Mundade R, Lange KC, et al. (2014) Protein arginine methylation of non-histone proteins and its role in diseases, Cell Cycle 13, 32-41.
[3] KaniskanH Ü, Konze KD, and Jin J. (2015) Selective Inhibitors of Protein Methyltransferases, J. Med. Chem. 58, 1596-1629.
[4] Yang YZ and Bedford MT (2013) Protein arginine methyltransferases and cancer, Nat. Rev. Cancer 13, 37-50.
[5] Yoshimatsu M, Toyokawa G, Hayami S, et al. (2011) Dysregulation of PRMT1 and PRMT6, Type I arginine methyltransferases, is involved in various types of human cancers, Int. J. Cancer 128, 562-573.
[6] Kaniskan HÜ, Szewczyk MM, Yu Z, et al. (2015) A potent, selective and cell-active allosteric inhibitor of protein arginine methyltransferase 3 (PRMT3). Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 54, 5166-70.
[7] Mitchell LH, Drew AE, Ribich SA, et al. (2015) Aryl Pyrazoles as Potent Inhibitors of Arginine Methyltransferases: Identification of the First PRMT6 Tool Compound. ACS Med Chem Lett. 6, 655-9.
[8] Eram MS, Shen Y, Szewczyk M, et al. (2015) A Potent, Selective and Cell-active Inhibitor of Human Type I Protein Arginine Methyltransferases, ACS Chemical Biology DOI: 10.1021/acschembio.5b00839.
Main features