This probe is available from Cayman Chemical, Sigma and Tocris.
| Probe | Negative control | |
 |
|  |
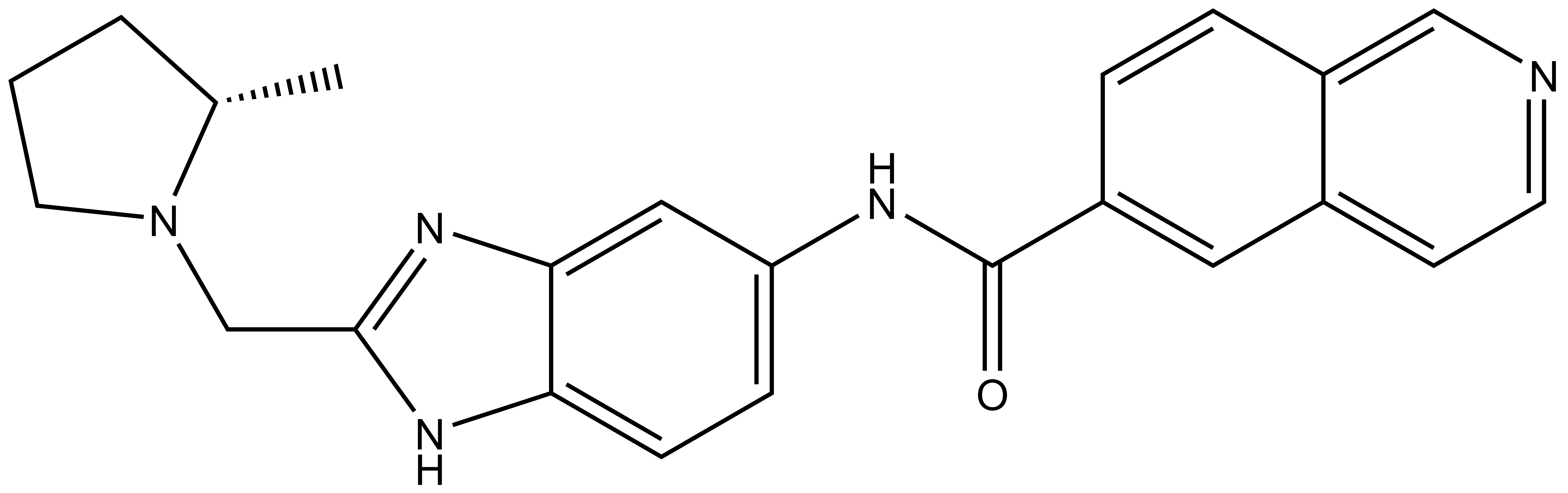
NVS-MLLT-1 |
| NVS-MLLT-C |
MLLT1 (also known as ENL, LTG19 and YEATS1) is a fusion gene partner within the MLL oncogene, involved in chromosome translocation [1]. In MLL1 rearranged mixed lineage leukaemia, MLLT1 acts as fusion partner for the transcriptional co-activation of MLL1. This interaction leads to linkage of MLL1 with the super elongation complex, and histone methyl transferase DOT1L, ultimately driving the dysregulation of oncogenes [2-6].
Accumulating evidence suggests that MLLT1 can also be a driver in non-MLLT1 rearranged acute myeloid leukaemia (AML). The MLLT1 epigenetic reader domain (YEATS domain) recognises acylated lysine residues on histone 3 (mainly acetyl lysine) (Figure 1). In AML, the MLLT1 YEATS domain directly links the epigenetic readout to the oncogenic dysregulation of gene expression [7,8]
MLLT1 CRISPR/Cas9 studies have shown significant reductions in cell proliferation, and invasiveness of AML cell lines. Subsequent rescue with ectopically expressed native MLLT1 restores the disease phenotype, while rescue with mutants that are deficient in the binding pocket (where MLLT1 recognises acyl lysine residues) is unable to restore the phenotype [8]. These studies, combined with the knowledge of known epigenetic readers being used as tractable targets for small molecule inhibitors, indicate that inhibition of MLLT1 may be a viable approach for the treatment of AML. The SGC therefore develped SGC-iMLLT, a first in class potent and selective inhibitor of YEATS proteins [9]. Expanding this work, a probe with improved in cell activity was developed with Novartis. Here, we present NVS-MLLT-1 as a potent and selective inhibitor of YEATS proteins.
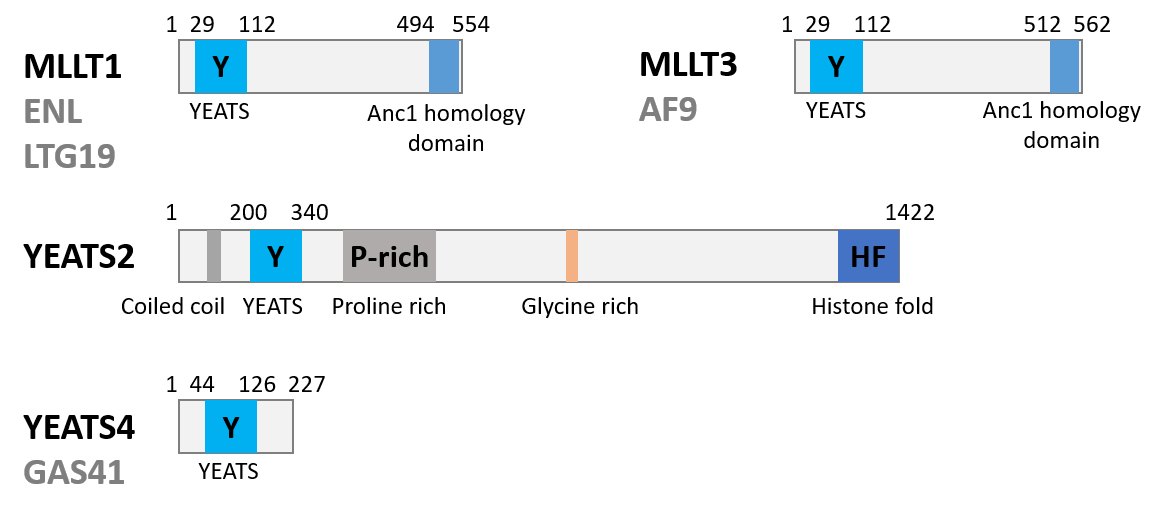
Figure 1: Biology of the Targets.
Potency Against Target Family
An AlphaScreen competition assay was used to assess the potency of SGC-iMLLT against all four human YEATS domains. NVS-MLLT-1 showed inhibition of both MLLT1 and MLLT3 at 0.15 µM and 0.254 µM respectively (Table 1). Conversely, the negative control molecule NVS-MLLT-C did not show any inhibition in the assay. More information on MLLT1 as a target can be found in our TEPs repository: https://www.thesgc.org/tep/mllt1.
| In vitro assays | NVS-MLLT-1 IC50 (µM) | NVS-MLLT-C IC50 (µM) |
| TR-FRET MLLT1 | 0.15 | > 20 |
| TR-FRET MLLT3 | 0.254 | > 20 |
| TR-FRET YEATS2 | > 20 | > 20 |
| TR-FRET YEATS4 | > 20 | > 20 |
| KD BLI MLLT1 | 0.075 | - |
| KD ITC MLLT1 | 0.109 | - |
Table 1: Potency Against Target Family and biophysical properties
Selectivity
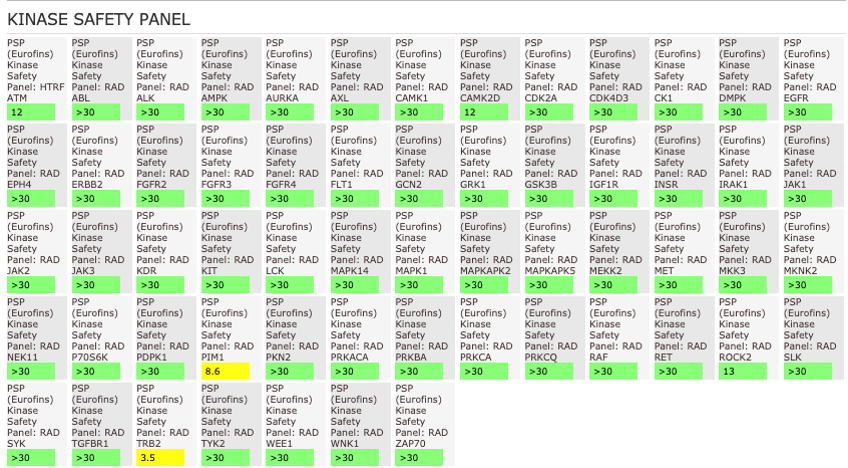
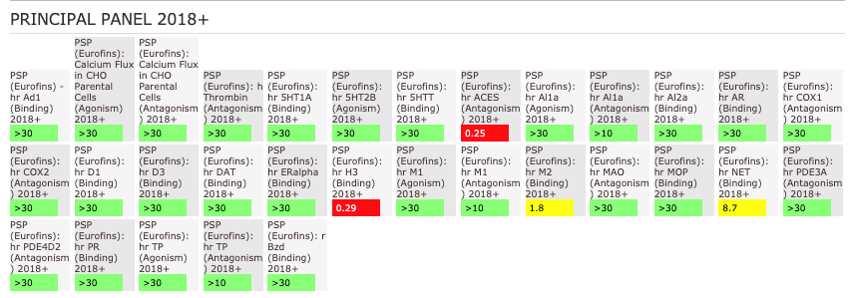
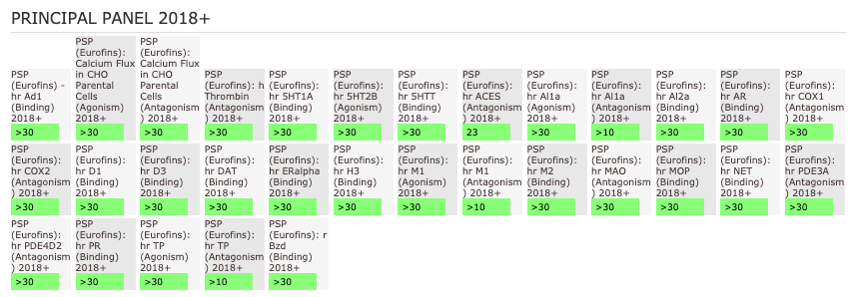
NVS-MLLT-1 shoes potent activity on MLLT1/3 whilst being selective for YEATS2/4. NVS-MLLT-1 shows selectivity across all bromodomains (CERC2 IC50 > 40 µM) and no activity was shown in a kinase panel. NVS-MLLT-1 has some activity on ACES and H3 binding.
Dosage
Use between 1 and 10 µM for cellular assays, and 1 µM for screening at a single shot.
In vitro Activity
In the NanoBRET cellular target engagement assay, NVS-MLLT-1 displayed potent inhibition, with an average IC50 value of 0.5 μM (±0.12) (Figure 2). In comparison,NVS-MLLT-C had no inhibitory properties (up to 30 μM). Further in cell validation was used to confirm target inhibition by NVS-MLLT-1.
| Probe |
 |
NVS-MLLT-1 |
| Physical and chemical properties for NVS-MLLT-1 | |
| Molecular weight | 385.47 |
| Molecular formula | C23H23N5O |
| IUPAC name | (S)-N-(2-((-methylpyrrolidin-1-yl)methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazel-5-yl)isoquinoline-6-carboxamide |
| MollogP | 3.6 |
| PSA | 69.09 |
| No. of chiral centres | 1 |
| No. of rotatable bonds | 5 |
| No. of hydrogen bond acceptors | 5 |
| No. of hydrogen bond donors | 2 |
| Storage | DMSO stock solutions (up to 50mM) are stable at -20 °C |
| Dissolution | Soluble in DMSO up to 50mM |
| Negative control |
 |
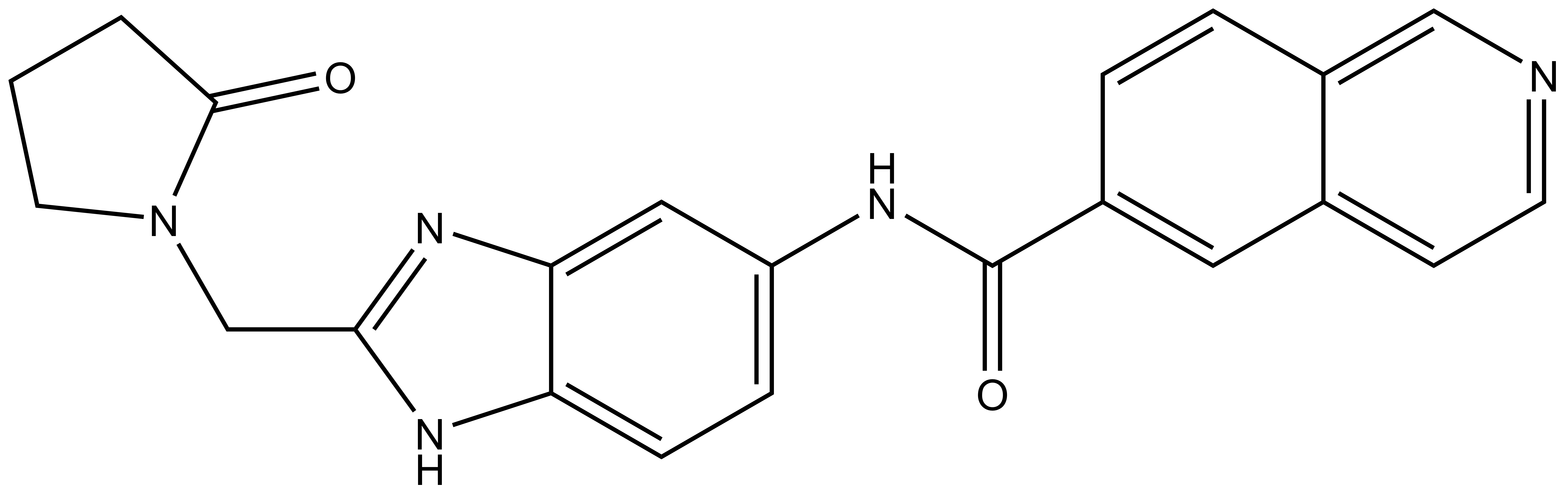
NVS-MLLT-C |
| Physical and chemical properties for NVS-MLLT-C | |
| Molecular weight | 385.43 |
| Molecular formula | C22H19N5O2 |
| IUPAC name | N-(2-((2-oxopyrrolidin-1-yl)methyl)-1Hbenzo[d]imidazol-5-yl)isoquinoline-6-carboxamide |
| MollogP | |
| PSA | 86.16 |
| No. of chiral centres | 0 |
| No. of rotatable bonds | 5 |
| No. of hydrogen bond acceptors | 6 |
| No. of hydrogen bond donors | 2 |
| Storage | DMSO stock solutions (up to 50mM) are stable at -20 °C |
| Dissolution | Soluble in DMSO up to 50mM |
SMILES:
NVS-MLLT-1: C[C@H]1CCCN1CC2=NC3=CC(NC(C4=CC5=CC=NC=C5C=C4)=O)=CC=C3N2
NVS-MLLT-C: O=C(C1=CC2=CC=NC=C2C=C1)NC3=CC=C(N4)C(N=C4CN5C(CCC5)=O)=C3
InChI:
NVS-MLLT-1: 1S/C23H23N5O/c1-15-3-2-10-28(15)14-22-26-20-7-6-19(12-21(20)27-22)25-23(29)17-4-5-18-13-24-9-8-16(18)11-17/h4-9,11-13,15H,2-3,10,14H2,1H3,(H,25,29)(H,26,27)/t15-/m0/s1
NVS-MLLT-C: 1S/C22H19N5O2/c28-21-2-1-9-27(21)13-20-25-18-6-5-17(11-19(18)26-20)24-22(29)15-3-4-16-12-23-8-7-14(16)10-15/h3-8,10-12H,1-2,9,13H2,(H,24,29)(H,25,26)
InChIKey:
NVS-MLLT-1: ZRTFTZCKJUNZIU-HNNXBMFYSA-N
NVS-MLLT-C: GMSVIEOZPBLYCQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
The AlphaScreen assays were employed to screen NVS-MLLT-1 and NVS-MLLT-C against a panel of bromodomains. NVS-MLLT-1 shows potent activity on MLLT1/3 whilst being selective for YEATS2/4. NVS-MLLT-1 shows selectivity across all bromodomains (CERC2 IC50 > 40 μM). NVS-MLLT-1 shows no activity on kinases tested, NVS-MLLT-1 has some activity on ACES and E3 binding. NVS-MLLT-C shows no activity in a panel of kinases, and no activties on other targets tested.
| In vitro assays | NVS-MLLT-1 IC50 (µM) | NVS-MLLT-C IC50 (µM) |
| TR-FRET MLLT1 | 0.15 | > 20 |
| TR-FRET MLLT3 | 0.254 | > 20 |
| TR-FRET YEATS2 | > 20 | > 20 |
| TR-FRET YEATS4 | > 20 | > 20 |
| KD BLI MLLT1 | 0.075 | - |
| KD ITC MLLT1 | 0.109 | - |
Table 1: Potency Against Target Family and biophysical properties
General Selectivity- NVS-MLLT-1
NVS-MLLT-1 shows no activity on kinases tested. NVS-MLLT-1 has some activity on ACES and H3 binding.
General Selectivity- NVS-MLLT-C
NVS-MLLT-C shows no activity on kinases tested. NVS-MLLT-C shows no activities on other targets tested
Cellular target Engagement
In the NanoBRET cellular target engagement assay, NVS-MLLT-1 displayed potent inhibition, with an average IC50 value of 0.5 μM (±0.12) (Figure 1). In comparison, NVS-MLLT-C had no inhibitory properties (up to 30 μM) (Figure 1). Further in cell validation using a Fluorescence Recovery After Photobleaching (FRAP) assay was used to confirm target inhibition by NVS-MLLT-1 (Figure 2) .
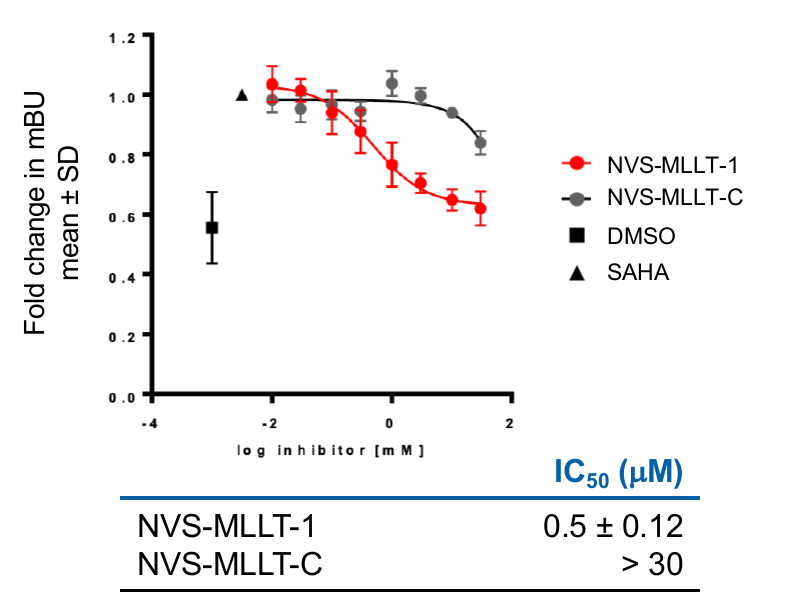
Figure 1: A NanoBRET assay was used in HEK293 cells to determine target engagement in cells. All probes were tested for 24h in the presence of 2.5 μM SAHA (24h). Graph represents Mean±SEM, n=3 independent replicates, with n=4 technical replicates. mBU: BRET units
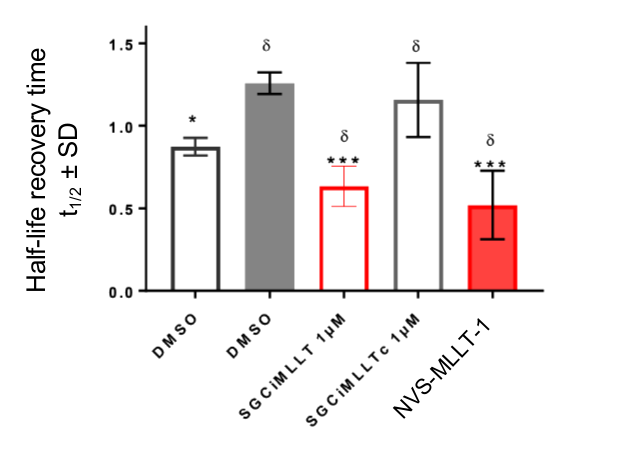
Figure 2: Further confirmation of MLLT1 target engagement in cells. Fluorescence Recovery After Photobleaching analysis shows NVS-MLLT-1 decreases the half-life recovery time of cells. n=3 independent experiments, Mean±SEM, fold change from SAHA treatment alone. One way ANOVA, Dunnett's multiple comparisons.
Materials and Methods
NanoLuciferase Bioluminescent Resonance Energy Transfer (NanoBRET) Assay
Cellular activity against MLLT3 was assessed using a NanoBRET assay. HEK293 cell (8 x 105) were plated a 6-well plate, after 6h cells were co-transfected with C-terminal HaloTag-Histone 3.3 (NM_002107) and an N-terminal NanoLuciferase fusion of MLLT3 (original MLLT3 WT sequences from Promega HaloTag® human ORF in pFN21A or MLLT3 MUT - Y78A Tyrosine is changed to an Alanine) at a 1:10 (NanoLuc® to HaloTag®) ratio respectively with FuGENE HD transfection reagent. Sixteen hours post-transfection, cells were collected, washed with PBS, and exchanged into media containing phenol red-free DMEM and 4% FBS in the absence (control sample) or the presence (experimental sample) of 100 nM NanoBRET 618 fluorescent ligand (Promega). Cells were then re-plated in a 96-well assay white plate (Corning Costar #3917) at 2x104 cells per well. Compounds were then added directly to the cells (in the presence of SAHA 2.5 µM) at final concentrations 0-30 μM or an equivalent amount of DMSO as a vehicle control, and the plates were incubated for 24 h at 37°C in the presence of 5% CO2. NanoBRET Nano-Glo substrate (Promega) was added to both control and experimental samples at a final concentration of 10 µM. Readings were performed within 10 minutes using a ClarioSTAR (BMG Labtech) equipped with 460 nm and 610 nm filters. A corrected BRET ratio was calculated and is defined as the ratio of the emission at 610 nm/460 nm for experimental samples minus the emission at 610 nm/460 nm for control samples (without NanoBRET fluorescent ligand). BRET ratios are expressed as milliBRET units (mBU), where 1 mBU corresponds to the corrected BRET ratio multiplied by 1000.
Peptide Displacement Assay
Peptide displacement assays were set up with biotinylated peptides (chosen based on ChIPseq data from the literature and purchased from LifeTein) and 6His tagged protein (Table 2). For detection, two orthogonal technologies were used, i. AlphaScreen® technology from Perkin Elmer and ii. HTRF from Cisbio. Compounds were dispensed in duplicate at single concentration (100 µM) for the initial screen and as 11-point dose response curves starting from 200 µM for IC50 value determination.
| YEATS domain | Peptide shorthand | Position | Peptide sequence |
| MLLT1 | H3K18ac | 12-30 | GGKAPR(K-acetyl)QLATKAARKSAPY(K-biotin) |
| MLLT3 | H3K9ac | 2-20 | ARTKTAR(K-acetyl)STGGKAPRKQLY(K-biotin) |
| YEATS2 | H3K27cro | 15-32 | biotin-GKPRKQLATAAR(K-crotonyl)SAPAT |
| YEATS4 | H3K27cro | 15-32 | biotin-GKPRKQLATAAR(K-crotonyl)SAPAT |
Table 2: Peptides used for the peptide displacement assays
To determine optimal assay conditions for each protein prep, proteins and peptides were titrated against each other in a 16 by 16 matrix in 1:1 dilutions, starting from 3.2 µM. For the final ratio of protein and peptide to use in the assay, the point representing the EC90 in the two-dimensional titration was chosen. Typically, final assay concentrations for protein and peptide fell between 25 and 200 nM. For AlphaScreen®, AlphaScreen Histidine (Nickel Chelate) Detection Kit donor and acceptor beads were used at a 1:2500 dilution from purchased stock; for HTRF, SA-XL665 and anti-6His antibody were used at 1:2000 and 1:10000 dilution from purchased stock, respectively. Assays were performed on 384 well ProxiPlates (Perkin Elmer) at a final volume of 20 µl and plates were read using a Pherastar FSX plate reader (BMG Labtech).
Isothermal Titration Calorimetry
Isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) was carried out using a TA NanoITC (standard volume) instrument. Protein was prepared by dialysis (overnight at 4°C) against a ~1000 times excess of buffer (20 mM Tris at pH 7.5, 500 mM NaCl, 5% (v/v) glycerol, 2 mM DTT) using SnakeSkin® Dialysis Tubing with a 7 kDa MWCO and then concentrated to 300 µM. The experiment was carried out at 20°C in reverse mode with the compound in the cell at 50 µM and the protein in the syringe at 300 µM due to the solubility of the compound with the first injection at 4 µl and the following 30 at 8 µl. Data was analysed using the NanoAnalyze software package by TA Instruments.
Differential Scanning Fluorimetry
Differential scanning fluorimetry (DSF) to determine the effect of compounds on the thermal stability of proteins (DTm) was carried out on 384 well PCR plates using a LightCycler 480 (Roche). Protein at 10 µM was buffered in 10 mM HEPES at pH 7.5 and 500 mM NaCl. The experiment was carried out from 25 to 95°C with three acquisitions per degree. Compounds were added at 50 µM final concentration and DMSO reference and no-addition controls were also collected.
1. Doty, R.T., et al., The leukemia-associated gene Mllt1/ENL: characterization of a murine homolog and demonstration of an essential role in embryonic development. Blood Cells Mol Dis, 2002. 28(3): p. 407-17.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12367585
2. Mueller, D., et al., A role for the MLL fusion partner ENL in transcriptional elongation and chromatin modification. Blood, 2007. 110(13): p. 4445-54.DOI: 10.1182/blood-2007-05-090514.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17855633
3. Mueller, D., et al., Misguided transcriptional elongation causes mixed lineage leukemia. PLoS Biol, 2009. 7(11): p. e1000249.DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000249.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19956800
4. Yokoyama, A., et al., A higher-order complex containing AF4 and ENL family proteins with P-TEFb facilitates oncogenic and physiologic MLL-dependent transcription. Cancer Cell, 2010. 17(2): p. 198-212.DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2009.12.040.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20153263
5. Biswas, D., et al., Function of leukemogenic mixed lineage leukemia 1 (MLL) fusion proteins through distinct partner protein complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2011. 108(38): p. 15751-6.DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1111498108.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21896721
6. Monroe, S.C., et al., MLL-AF9 and MLL-ENL alter the dynamic association of transcriptional regulators with genes critical for leukemia. Exp Hematol, 2011. 39(1): p. 77-86 e1-5.DOI: 10.1016/j.exphem.2010.09.003.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20854876
7. Erb, M.A., et al., Transcription control by the ENL YEATS domain in acute leukaemia. Nature, 2017. 543(7644): p. 270-274.DOI: 10.1038/nature21688.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28241139
8. Wan, L., et al., ENL links histone acetylation to oncogenic gene expression in acute myeloid leukaemia. Nature, 2017. 543(7644): p. 265-269.DOI: 10.1038/nature21687.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28241141
9. Christott, T. et al., Discovery of a selective inhibitor for the YEATS domains of ENL/AF9. SLAS Discov, 2019. 24(2):133-141. DOI: 10.1177/2472555218809904. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30359161
10. Chaikuad, A., S. Knapp, and F. von Delft, Defined PEG smears as an alternative approach to enhance the search for crystallization conditions and crystal-quality improvement in reduced screens. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr, 2015. 71(Pt 8): p. 1627-39.DOI: 10.1107/S1399004715007968.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26249344
11. Moustakim, M., et al., Discovery of an MLLT1/3 YEATS Domain Chemical Probe. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl, 2018. 57(50): p. 16302-16307.DOI: 10.1002/anie.201810617.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30288907
12. Heidenreich, D., et al., Structure-Based Approach toward Identification of Inhibitory Fragments for Eleven-Nineteen-Leukemia Protein (ENL). J Med Chem, 2018. 61(23): p. 10929-10934.DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b01457.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30407816
In vitro Metabolic stability of NVS-MLLT-1
To establish the in cell half life of NVS-MLLT-1, metabolic stability studies were carried out exposing nominated compounds to samples of primary human hepatocytes. Results from ADME and phys chem experiments are summarised below.
| In vitro Metabolism (Liver microsomes) | NVS-MLLT-1 [CL int(µL/min/mg)]) |
| Human | 89 |
| Rat | 68 |
| Mouse | 90 |
Table 1: In vitro metabolism
Permeability
| NVS-MLLT-1 | |
| PAMPA: | |
| Log PAMPA (cm/s) | -5.1 |
| % FA | 49 |
| Low Efflux MDCK: | |
| Papp(A-B)(x10-6 ) | 11 |
| % FA | 80-100 |
| % Recovery | 81 |
Table 2: PhysChem Properties: Permeability
Solubility and pKa
| NVS-MLLT-1 | |
| Equilibrium Solubility | |
| pH 6.8 (g/L) | 0.375 |
| pKa1 | 4.6 |
| pKa2 | 2.1 |
Table 3: PhysChem Properties: Solubility and pKa
Solubility and pKa
| NVS-MLLT-1 | |
| clogP | 3.6 |
| logP (octanol) | 2.8 |
Table 4: PhysChem Properties: Lipophilicity
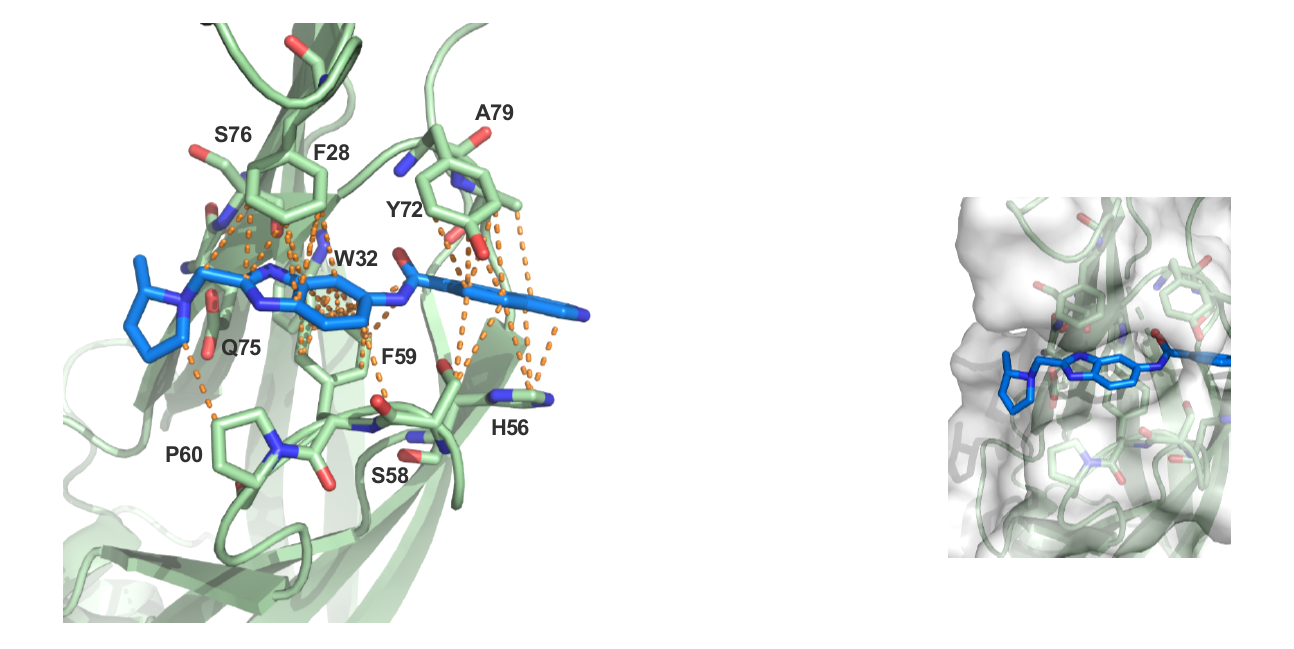
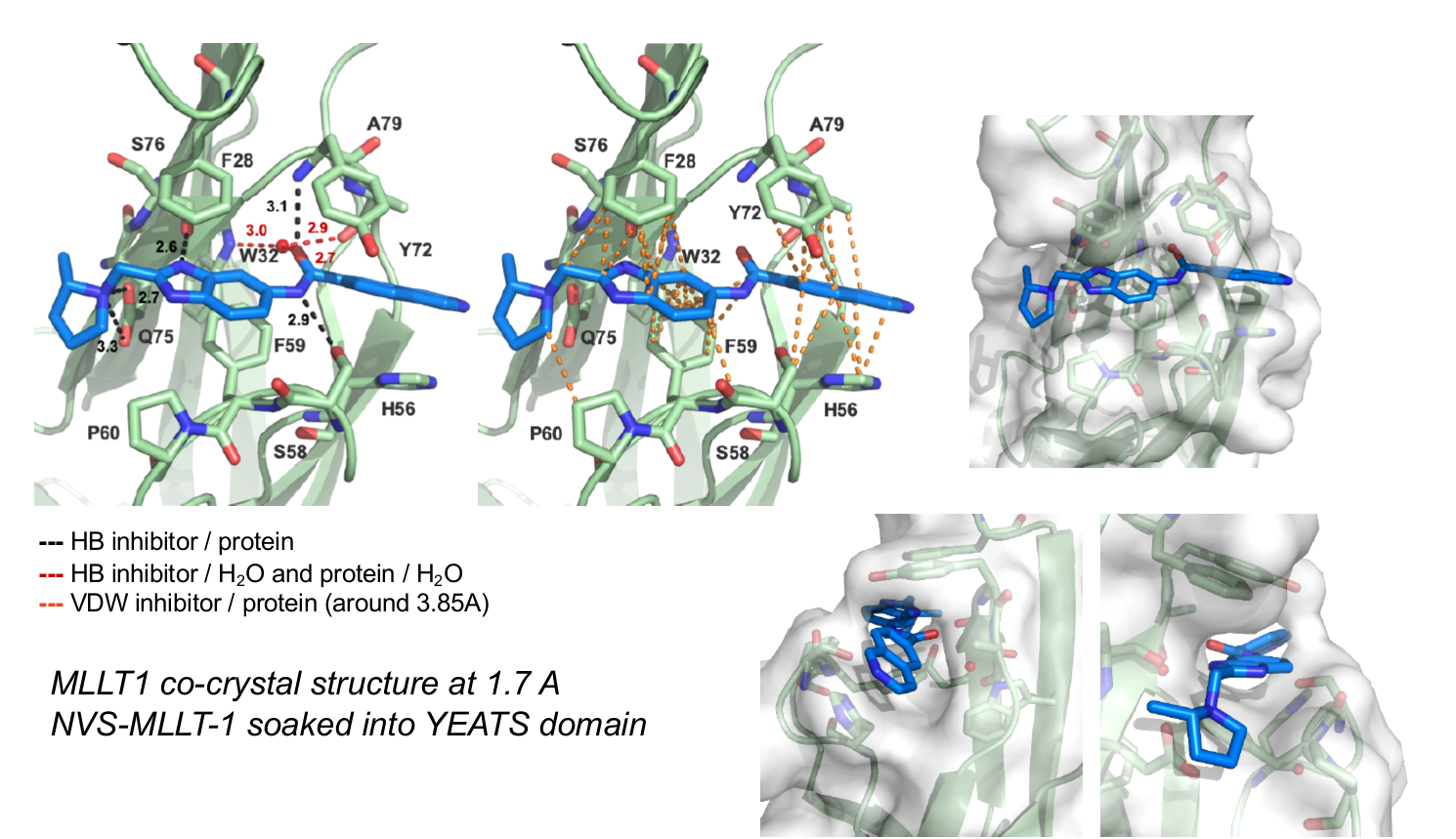
The figures below shows MLLT1 co-crystal strutcure at 1.7 Å. NVS-MLLT-1 is soaked into the YEATS domain. PDB codes will be added when they become available.