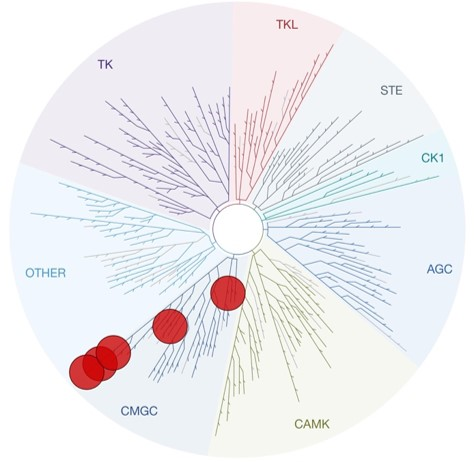
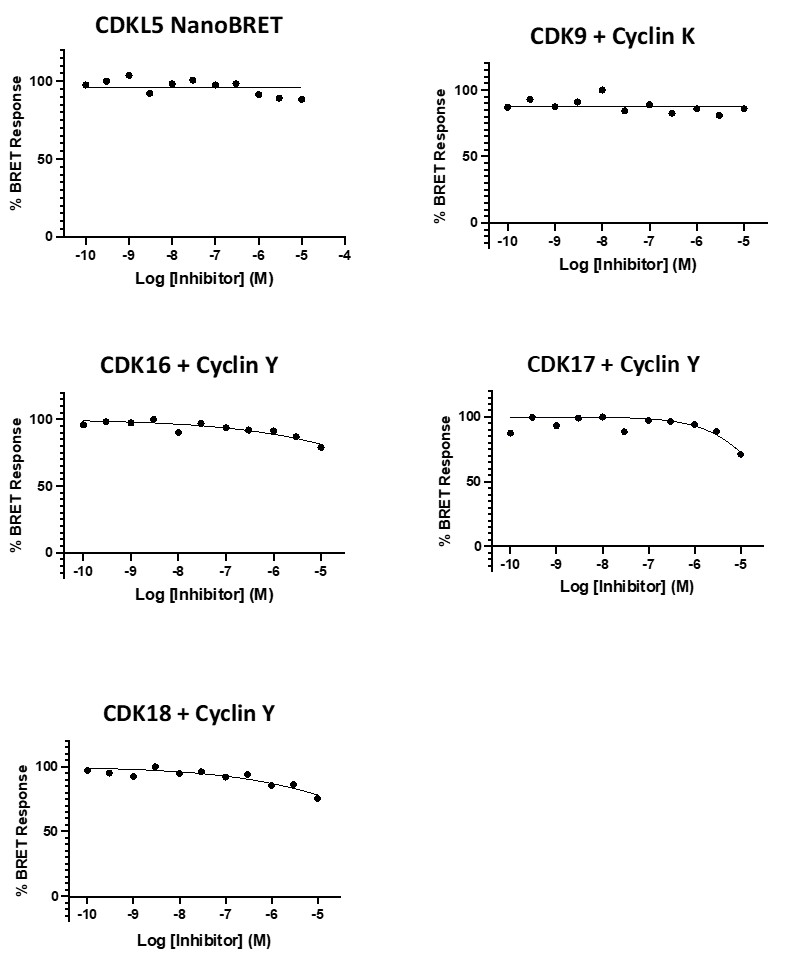
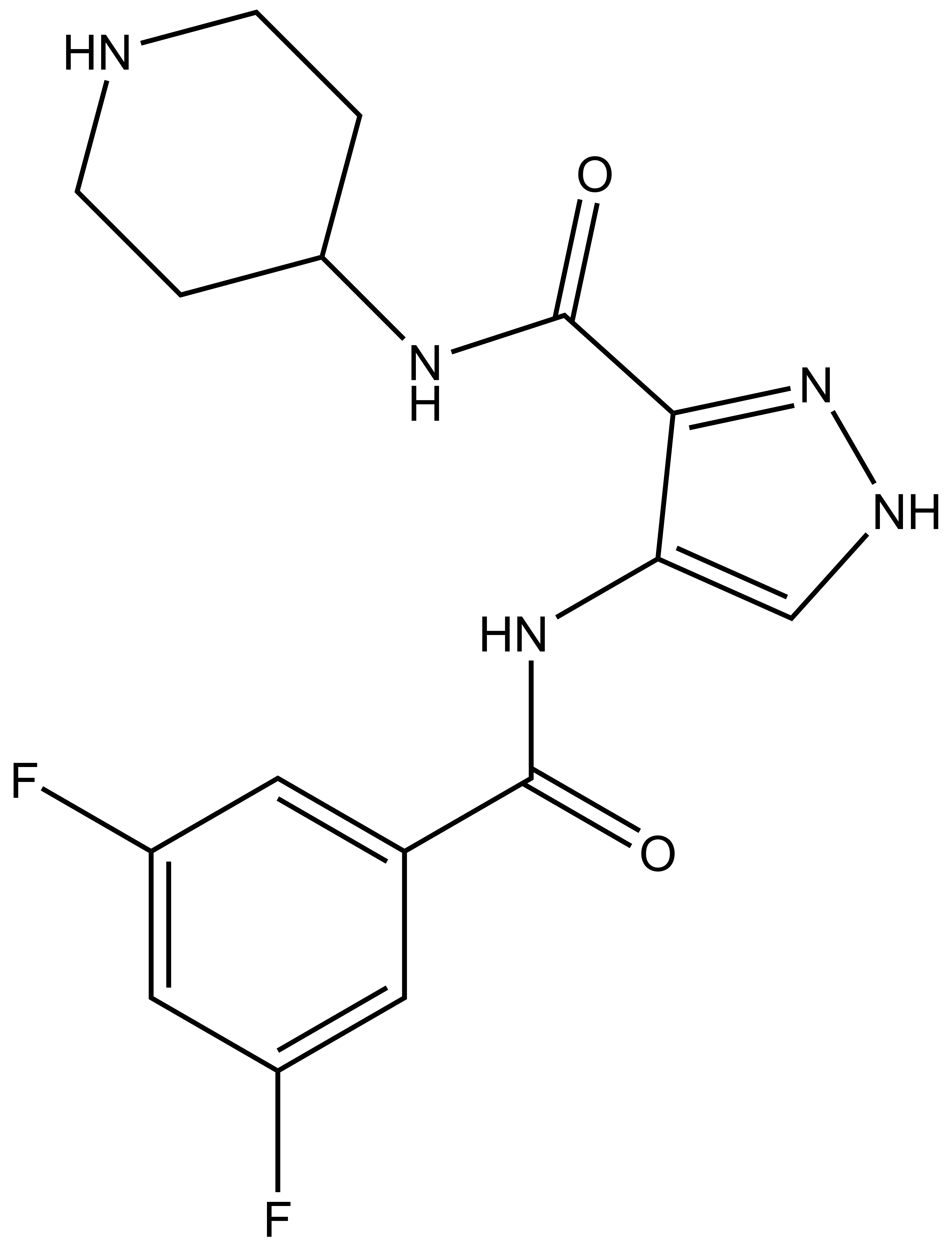
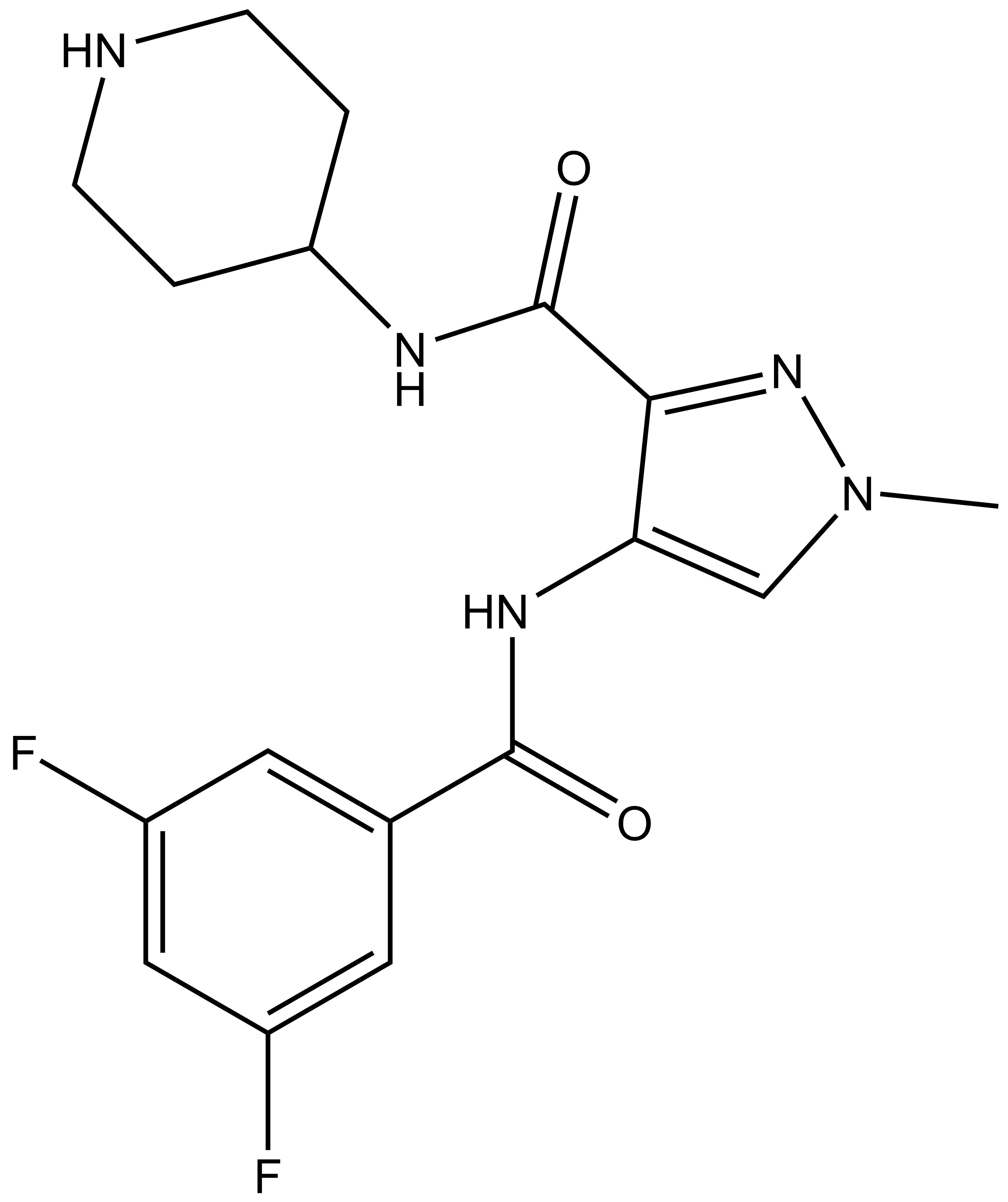
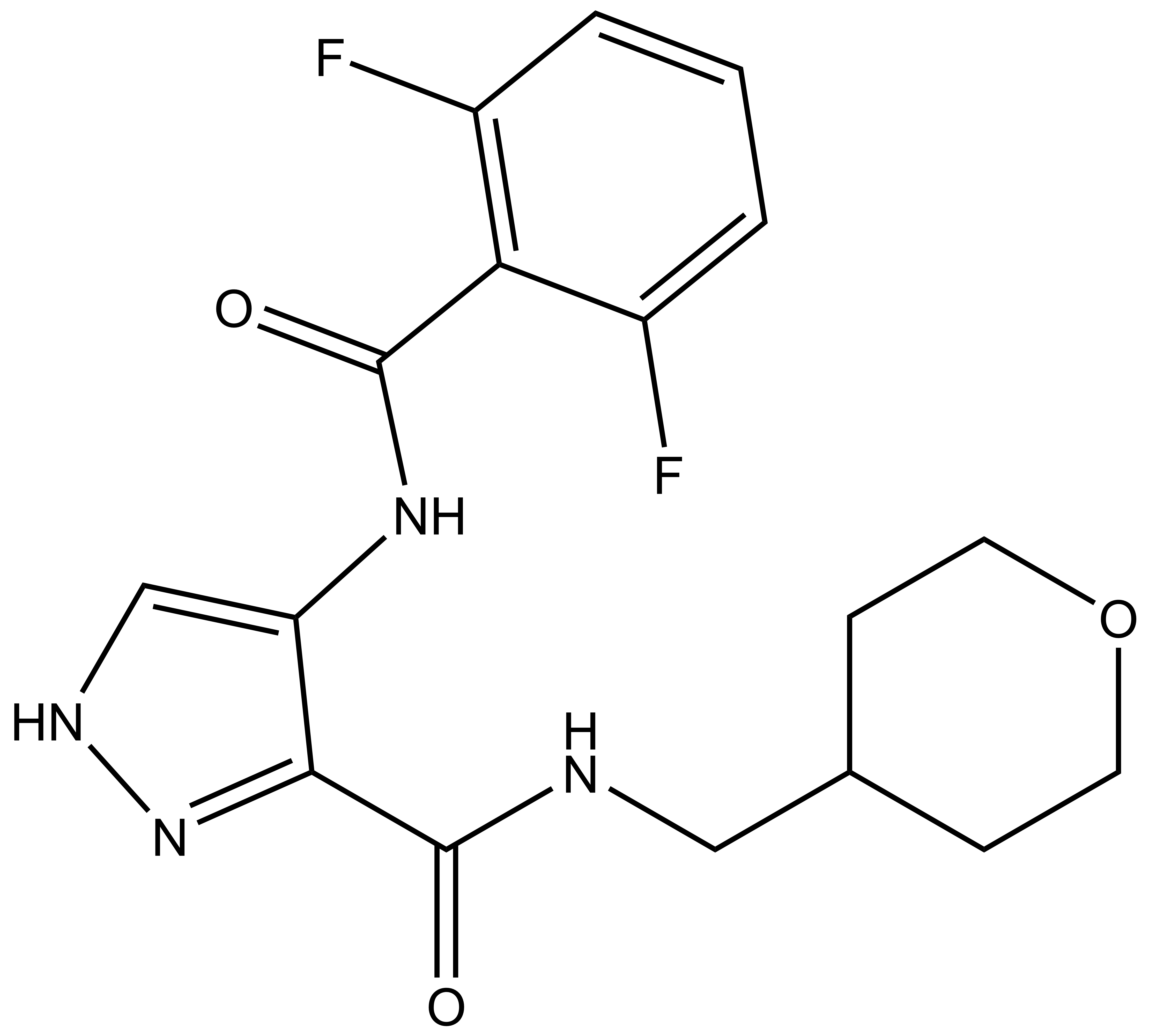
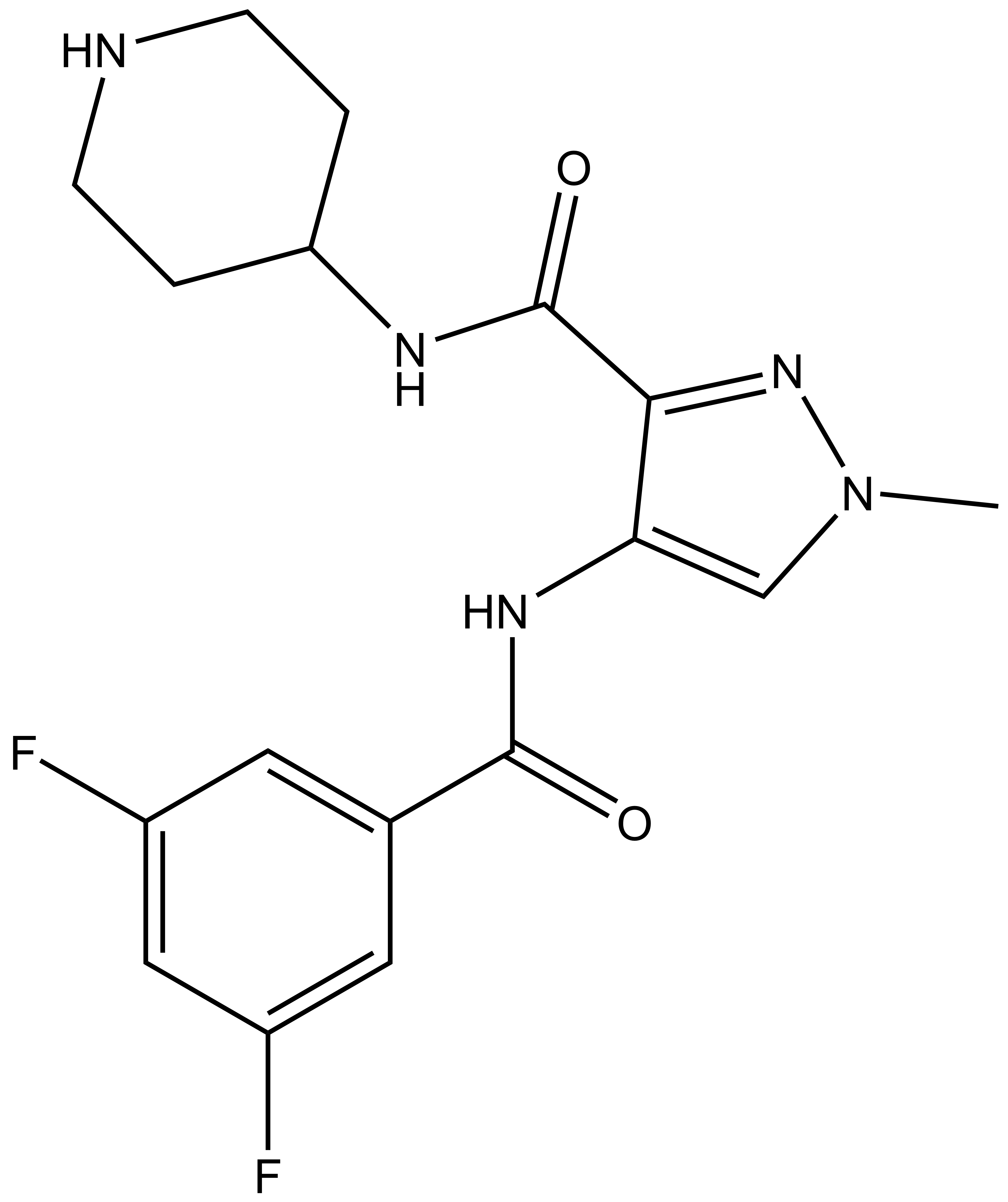
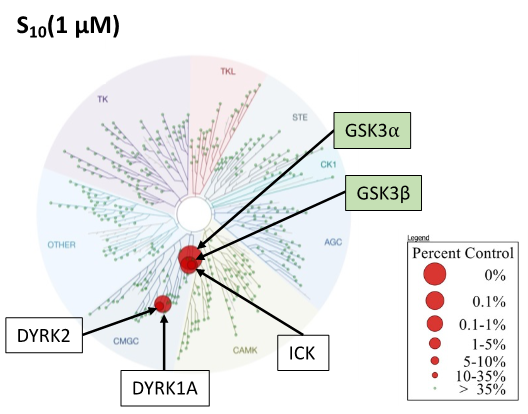
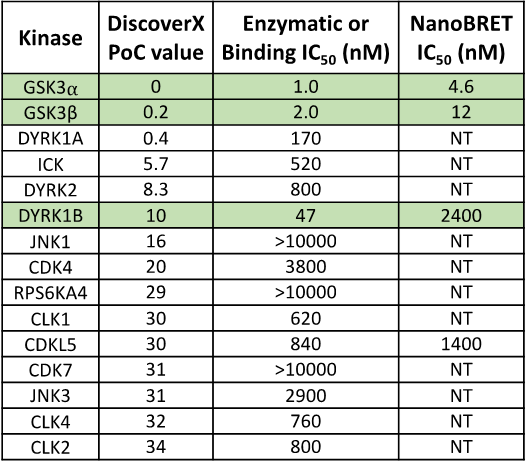
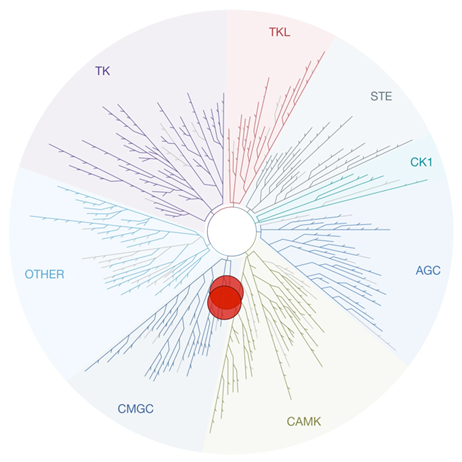
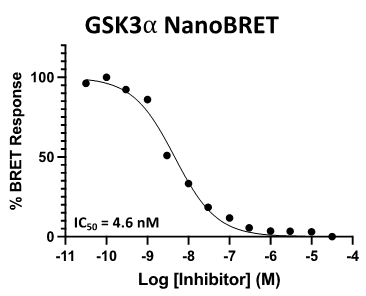
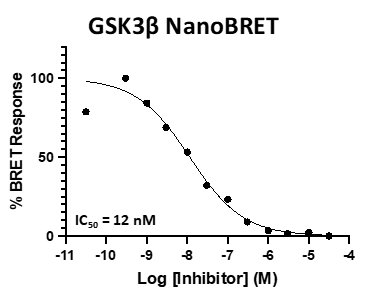
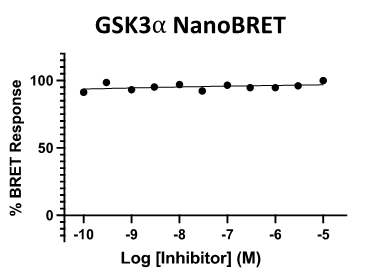
SGC 20th Anniversary Symposium Europe RECAP: From protein structures to probing biology
Twenty years have now passed since the inception of the Structural Genomics Consortium (SGC), marking a remarkable journey dedicated to advancing knowledge through open science and collaboration.
On Wednesday, September 6th, the SGC Karolinska hosted the 20th Anniversary Symposium Europe in Stockholm. This symposium served as a continuation of the celebration that began in Toronto earlier in March, commemorating past achievements and charting the course for what lies ahead.