The field of drug discovery has continuously evolved over time, driven by advancements in scientific understanding and technological innovations. From serendipitous discoveries, such as the discovery of aspirin and penicillin, to targeted pharmacology and high-throughput screenings, the process of identifying new therapeutic agents has undergone significant transformations.
At Structural Genomics Consortium, we are committed to driving advancements in basic and biomedical research that can positively impact the world. We believe that collaborative efforts and innovative solutions are essential for achieving groundbreaking discoveries. Today, we invite researchers from all corners of the globe to stand united in support of renewable antibody resources.
Sign the Petition to Prioritize Renewable Antibody Resources!
Have you ever experienced any of the following research roadblocks?
This probe is available from Sigma and Cayman Chemical.
Its negative control (TH-263) is available for purchase from Cayman Chemical.
| Probe | Negative control | |
 |
|  |
TH-257 |
| TH-263 |
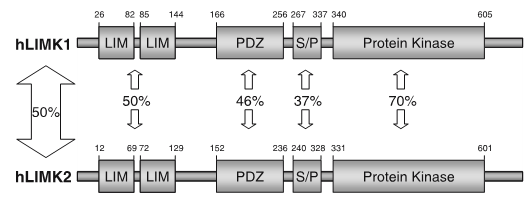
LIM kinases belong to the family of cytoplasmic tyrosine-like kinases with dual specificity (serine/threonine and tyrosine). However, known LIMK substrate are usually phosphorylated at serine and threonine residues LIM kinases comprises LIM kinase 1 (LIMK1) and LIM kinase 2 (LIMK2) which show 50% sequence identity in human. Both LIMK1 and LIMK2 present with a unique domain organization containing two N-terminal LIM domains, a PDZ domain, a proline/serine-rich domain and a C-terminal kinase domain [1].
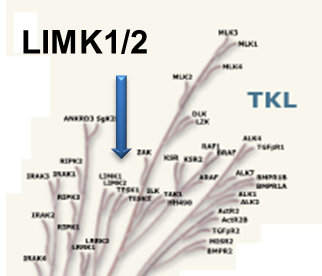
Both proteins are expressed widely in embryonic and adult tissues, but show some cell-type specific expression. Accordingly, the two kinases have overlapping functions, but appear non-redundant. Knockout studies in mice show that LIMK1 is required for development of the central nervous system [2], whereas LIMK2 knockout impairs the activity of testicular germ cells [3].
LIMKs are effectors of cell morphology and motility and apoptosis by regulating the actin cytoskeleton. The LIMKs signal downstream from Rho GTPases and are activated by phosphorylation of the activation loop by upstream kinases, including Rho kinase (ROCK), PAK1/2/4 and MRCKα. The best characterized LIMK substrates are cofilin1 (non-muscle cofilin), cofilin2 (muscle cofilin) and destrin (actin depolymerizing factor, ADF). Phosphorylation of cofilin serine-3 inactivates the actin severing ability promoting F-actin polymerization, stress fibre formation and focal adhesion formation [4].
LIM kinases can shuttle between the cytoplasm and the nuclear compartment of a cell, a process tightly regulated by association with other partners such as p57kip2 and phosphorylation in the activation segment by PAK kinases [1]. Inhibition of LIMK hyper-stabilizes mitotic spindles inducing a G2/M cell cycle block suggesting an important role for these kinases in microtubule dynamics [5].
Increased phosphorylation of LIMK1 has been reported in neurons in areas affected with Alzheimer Disease [6]. LIM kinases play important roles in cancer metastasis like highly invasive prostate and breast cancer, which is reversed by gene silencing [7, 8]. LIMK1 overexpression is also found in malignant melanoma, as well as most tumour cell lines. Other applications for LIMK inhibitors are open-angle glaucoma [9]. In addition, LIMK1 interacts with the long isoform of the type II bonemorphogenetic protein (BMP) receptor contributing to the pathology of Fragile X syndrome, a common inherited form of intellectual disability [10].
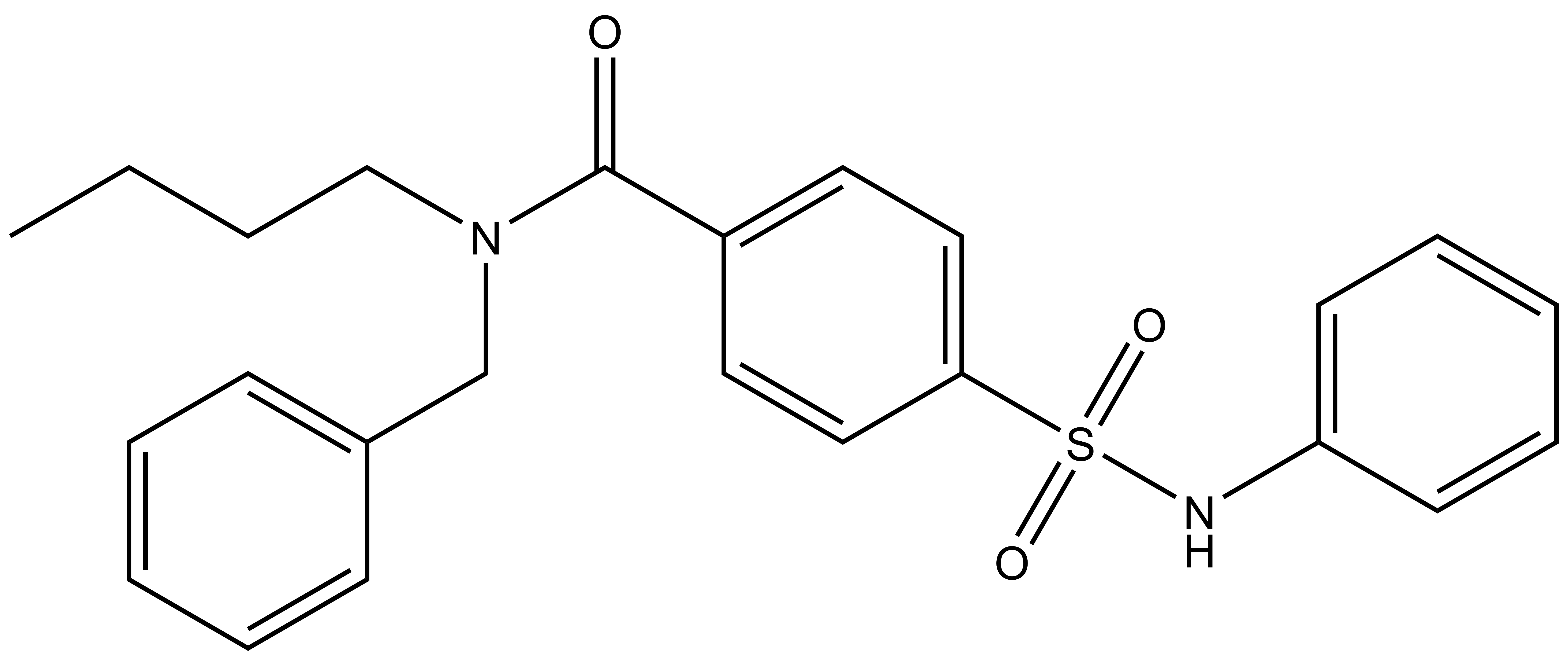
TH-257 is a chemical probe for LIMK1 and LIMK2. TH-257 is an allosteric inhibitor targeting a binding pocket induced by an αC and DFG-out conformation. It potently inhibits cofilin phosphorylation with an IC50 of 84 nM for LIMK1 and 39 nM for LIMK2 in a RapidFire MS assay. TH257 is exquisitely selective and no significant activity against the wider kinome has been observed in the KINOMEscan assay (Dx) at 1 μM (IC50 >> 50 % inhibition). In a life cell NanoBRET assay (Promega) TH257 has an IC50 of 250 nM against ectopically expressed full-length LIMK1 and 150 nM LIMK2, respectively.
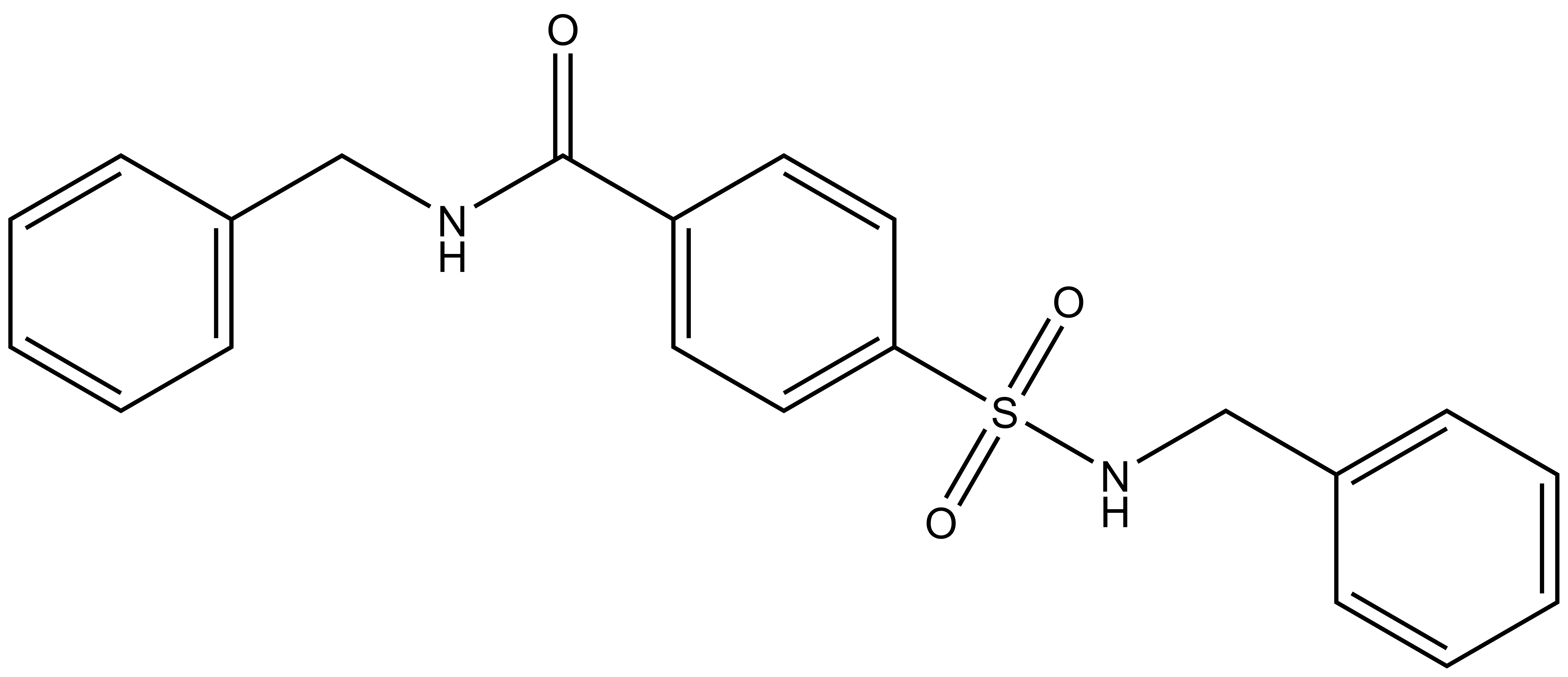
A chemically related negative control compound, TH-263, is provided.
| Probe | Negative control | |
 |
|  |
TH-257 |
| TH-263 |
| Physical and chemical properties for TH-257 | |
| Molecular weight | 422.2 |
| Molecular formula | C24H26N2O3S |
| MollogP | 5.138 |
| PSA | 57.08 |
| No. of chiral centres | 0 |
| No. of rotatable bonds | 10 |
| No. of hydrogen bond acceptors | 6 |
| No. of hydrogen bond donors | 1 |
| Physical and chemical properties for TH-263 (Negative Control) | |
| Molecular weight | 380.1 |
| Molecular formula | C21H20N2O3S |
| MollogP | 3.636 |
| PSA | 66.41 |
| No. of chiral centres | 0 |
| No. of rotatable bonds | 8 |
| No. of hydrogen bond acceptors | 7 |
| No. of hydrogen bond donors | 2 |
SMILES:
TH-257: CCCCN(C(C1=CC=C(S(NC2=CC=CC=C2)(=O)=O)C=C1)=O)CC3=CC=CC=C3
TH-263: O=S(C1=CC=C(C=C1)C(NCC2=CC=CC=C2)=O)(NCC3=CC=CC=C3)=O
InChI:
TH-257: InChI=1S/C24H26N2O3S/c1-2-3-18-26(19-20-10-6-4-7-11-20)24(27)21-14-16-23(17-15-21)30(28,29)25-22-12-8-5-9-13-22/h4-17,25H,2-3,18-19H2,1H3
TH-263: InChI=1S/C21H20N2O3S/c24-21(22-15-17-7-3-1-4-8-17)19-11-13-20(14-12-19)27(25,26)23-16-18-9-5-2-6-10-18/h1-14,23H,15-16H2,(H,22,24)
InChIKey:
TH-257: VNCIWNGCMAKKEO-UHFFFAOYSA-N
TH-263: QDGVJMITKNOVTP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
| Probe | Negative control | |
 |
|  |
JA397 |
| JA314 |
The TAIRE family of protein kinases are the cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK14-18), which are Ser/Thr kinases and belong to the CMGC family. The CDKs are activated by specific cyclins and are known to play an important role in cell cycle regulation (Wood 2018). Therefore, CDKs are now an important protein family that also has therapeutic significance, as demonstrated by the recent FDA-approved drugs for CDK4/6. However, for the TAIRE family little is known. However, the TAIRE family is less well described in the literature. It can be further subdivided into the PFTAIRE family (CDK14-15) and PCTAIRE family (CDK16-18). There is various evidence, for example, that CDK14 is involved in the WNT signalling pathway (Davidson, 2010); CDK15 regulates the beta-catenin/MEK-ERK signalling pathway (Huang, 2015), among others; CDK16 has an effect on cell cycle through phosphorylation of P27 (Yanagi, 2016); CDK17 plays a role in glycerophospholipid metabolism (Liu, 2017); and CDK18 regulates cell motility through the FAK/RhoA/ROCK signalling pathway (Matsuda, 2017).
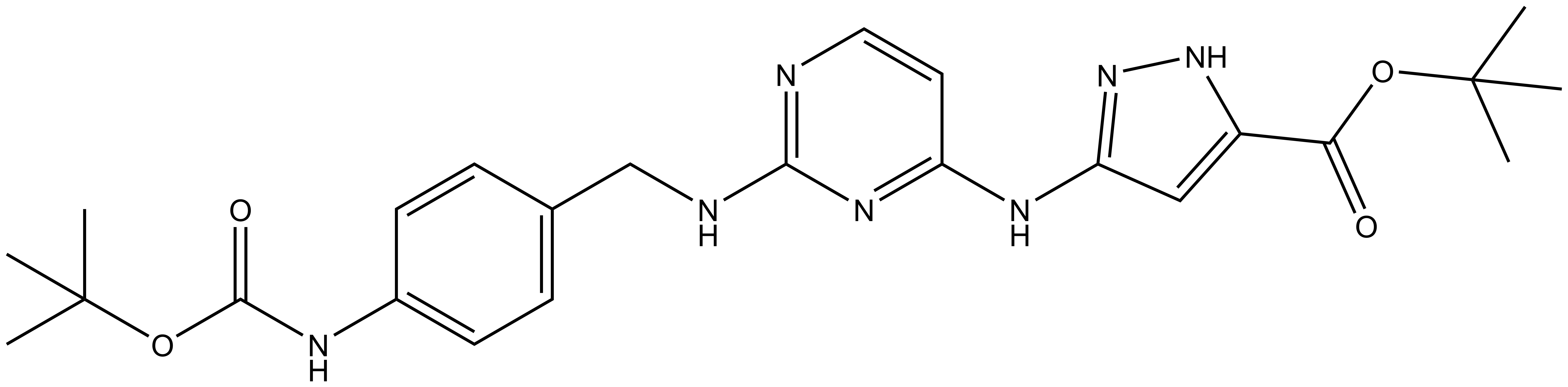
The SGC has developed JA397, a potent and selective inhibitor for the TAIRE family with cellular activity, ranging from IC50 values of 21 nM to 307 nM as determined by NanoBRET.
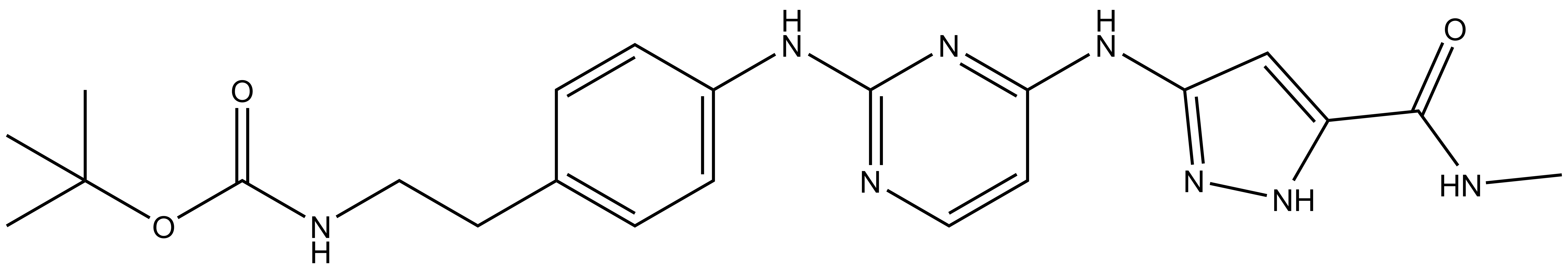
The chemical probe (JA397) is accompanied by a negative control (JA314) that is structurally closely related to the probe molecule.
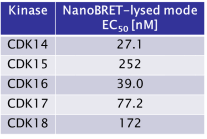 |
JA397 had an EC50 of 27.1 nM, 252 nM, 39.0 nM, 77.2 nM and 172 nM to CDK14, CDK15, CDK16, CDK17 and CDK18, respectively in the NanoBRET-lysed mode assay.
JA397 was selective in an in vitro kinase panel from Reaction Biology at 1 µM against 340 WT Kinases, followed by cellular NanoBRET assays. Selectivity within the CDK family was determined by NanoBRET.
Based on the potency and the selectivity of the chemical probe and to minimize the risk of unspecific cytotoxicity, we recommend a concentration of no higher than 1 µM for cell-based assays.
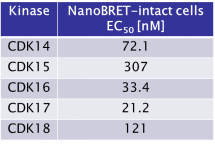
JA397 displayed an EC50 of 72.1 nM, 307 nM, 33.4 nM, 21.2 nM and 121 nM on CDK14, CDK15, CDK16, CDK 17 and CDK18 respectively in intact cells in the NanoBRET assay.
| Probe | Negative control | |
 |
|  |
JA397 |
| JA314 |
| Physical and chemical properties JA397 | |
| Molecular weight | 481.56 |
| Molecular formula | C24H31N7O4 |
| IUPAC name | tert-butyl 3-((2-((4-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)benzyl)amino)pyrimidin-4-yl)amino)-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxylate |
| clogP | 4.86 |
| tPSA | 137.8 |
| No. of chiral centres | 0 |
| No. of rotatable bonds | 11 |
| No. of hydrogen bond acceptors | 10 |
| No. of hydrogen bond donors | 4 |
| Storage | r. t. |
SMILES: O=C(C1=CC(NC2=NC(NCC3=CC=C(C=C3)NC(OC(C)(C)C)=O)=NC=C2)=NN1)OC(C)(C)C
InChI: InChI=1S/C24H31N7O4/c1-23(2,3)34-20(32)17-13-19(31-30-17)28-18-11-12-25-21(29-18)26-14-15-7-9-16(10-8-15)27-22(33)35-24(4,5)6/h7-13H,14H2,1-6H3,(H,27,33)(H3,25,26,28,29,30,31)
InChIKey: JQLMEZBHIJSVKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N
| Physical and chemical properties JA314 | |
| Molecular weight | 452,52 |
| Molecular formula | C22H28N8O3 |
| IUPAC name | tert-butyl (4-((4-((5-(methylcarbamoyl)-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)amino)pyrimidin-2-yl)amino)phenethyl)carbamate |
| clogP | 3.55 |
| tPSA | 140.6 |
| No. of chiral centres | 0 |
| No. of rotatable bonds | 10 |
| No. of hydrogen bond acceptors | 9 |
| No. of hydrogen bond donors | 5 |
| Storage | r. t. |
SMILES: O=C(C1=CC(NC2=NC(NC3=CC=C(C=C3)CCNC(OC(C)(C)C)=O)=NC=C2)=NN1)NC
InChI: InChI=1S/C22H28N8O3/c1-22(2,3)33-21(32)25-11-9-14-5-7-15(8-6-14)26-20-24-12-10-17(28-20)27-18-13-16(29-30-18)19(31)23-4/h5-8,10,12-13H,9,11H2,1-4H3,(H,23,31)(H,25,32)(H3,24,26,27,28,29,30)
InChIKey: VJWCJKXRULCPCJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Kinome-wide selectivity profile of JA397 was determined in our in-house kinase DSF-panel comprising 105 kinases and at Reaction Biology at 1 µM comprising 340 WT kinases.
The selectivity against a CDK family was determined by NanoBRET.
DSF-Panel against 105 kinases:
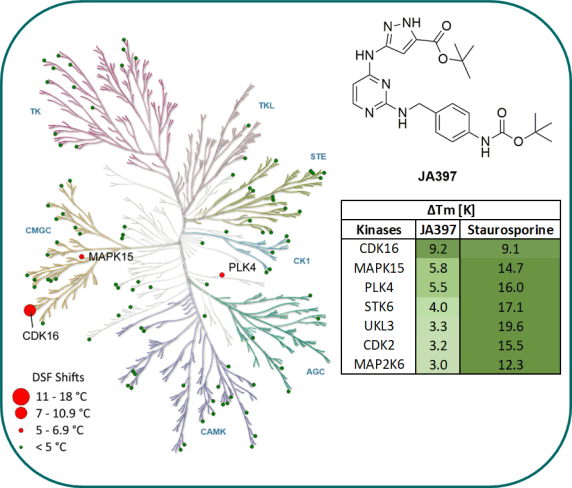 |
Reaction Biology (340 WT kinases) @ 1µM:
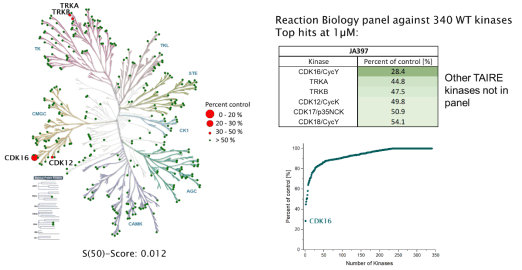 |
Selectivity within the CDK-Family:
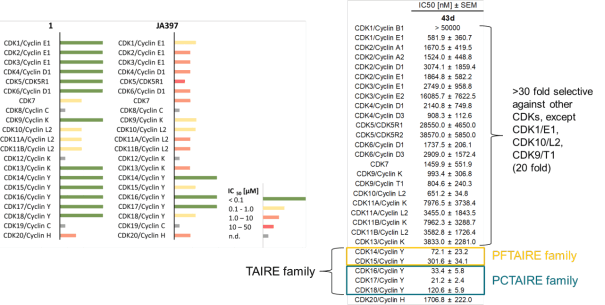 |
The negative control JA314 showed no stabilization against 105 kinases screened in our in-house DSF-Panel.
DSF-Panel against 105 kinases:
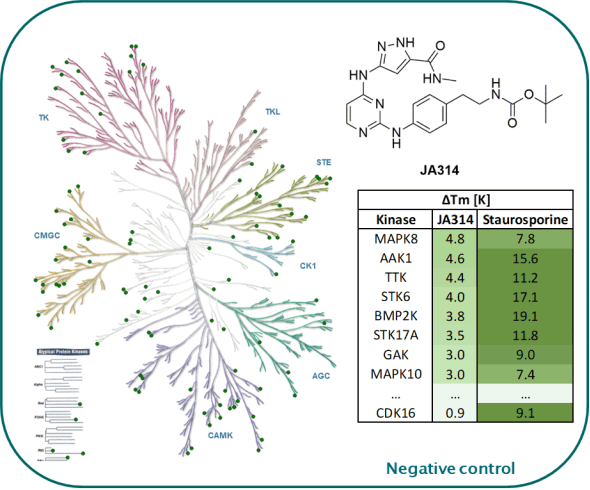 |
JA397 displayed an EC50 values ranging from 21 nM to 307 nM against the TAIRE family, determined by NanoBRETTM assay.
 |
The negative control compound 314 displayed a EC50 value of 4165 nM against CDK16, determined by NanoBRETTM assay.
Amrhein JA, Berger LM, Tjaden A, Krämer A, Elson L, Tolvanen T, Martinez-Molina D, Kaiser A, Schubert-Zsilavecz M, Müller S, Knapp S, Hanke T. Discovery of 3-Amino-1H-pyrazole-Based Kinase Inhibitors to Illuminate the Understudied PCTAIRE Family. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 27;23(23):14834. doi: 10.3390/ijms232314834. PMID: 36499165; PMCID: PMC9736855.
Davidson G, Niehrs C. Emerging links between CDK cell cycle regulators and Wnt signaling. Trends Cell Biol. 2010 Aug;20(8):453-60. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2010.05.002. Epub 2010 Jun 4. PMID: 20627573.
Huang C, Du R, Jia X, Liu K, Qiao Y, Wu Q, Yao N, Yang L, Zhou L, Liu X, Xiang P, Xin M, Wang Y, Chen X, Kim DJ, Dong Z, Li X. CDK15 promotes colorectal cancer progression via phosphorylating PAK4 and regulating β-catenin/ MEK-ERK signaling pathway. Cell Death Differ. 2022 Jan;29(1):14-27. doi: 10.1038/s41418-021-00828-6. Epub 2021 Jul 14. PMID: 34262144; PMCID: PMC8738751.
Liu M, Xu Z, Du Z, Wu B, Jin T, Xu K, Xu L, Li E, Xu H. The Identification of Key Genes and Pathways in Glioma by Bioinformatics Analysis. J Immunol Res. 2017;2017:1278081. doi: 10.1155/2017/1278081. Epub 2017 Dec 6. PMID: 29362722; PMCID: PMC5736927.
Matsuda S, Kawamoto K, Miyamoto K, Tsuji A, Yuasa K. PCTK3/CDK18 regulates cell migration and adhesion by negatively modulating FAK activity. Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 31;7:45545. doi: 10.1038/srep45545. PMID: 28361970; PMCID: PMC5374530.
Wood DJ, Endicott JA. Structural insights into the functional diversity of the CDK-cyclin family. Open Biol. 2018 Sep;8(9):180112. doi: 10.1098/rsob.180112. PMID: 30185601; PMCID: PMC6170502.
Yanagi T, Matsuzawa S. PCTAIRE1/PCTK1/CDK16: a new oncotarget? Cell Cycle. 2015;14(4):463-4. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2015.1006539. PMID: 25590439; PMCID: PMC4347670.
Alzheimer’s Disease and brain awareness month in June provides a significant opportunity to recognize the critical importance of brain research and its profound impact on global health. Through an open science model, SGC is dedicated to unravelling the complexities of neurological disorders that affect over 1 billion people worldwide – diseases that include Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), and rare neurodegenerative diseases like Huntington’s disease.
Tweet your story or post it on LinkedIn using: #20yearsSGC
In the pursuit of understanding the function of all human proteins, it is essential to employ various tools, including the use of potent, selective, and broadly characterized small molecule modulators, known as chemical probes. These chemical probes are often described as one of the most versatile tools to explore the role of a specific protein in complex biological systems and advance existing knowledge about the protein and its relevance for therapeutic development. In this dynamic realm of drug discovery, breakthroughs often stem from collaborative efforts and innovative resources.
Trainees are an integral part of the 20 years SGC global network of over 250 scientists. Since 2015, we've proudly partnered with Mitacs, offering over 550 internship units to trainees across 25+ unique projects, totaling $8.4M. This direct support funds trainee stipends and research costs.
North Carolina, May 10, 2023 – The Structural Genomics Consortium (SGC) at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill has been awarded a $1.5 million grant from the U.S Department of Defense to support drug discovery efforts aimed at the investigation of small molecules that could potentially serve as new treatment options for patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS), also known as Lou Gehrig’s Disease.