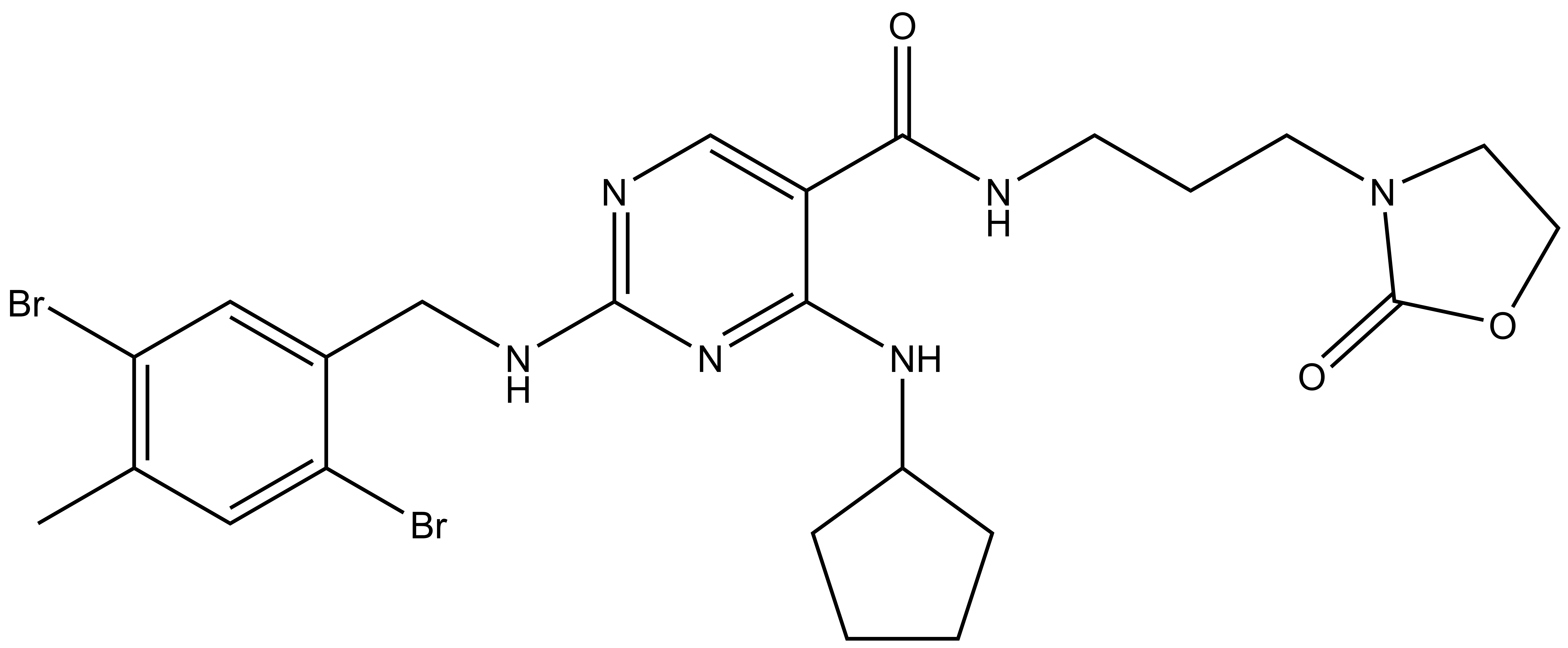
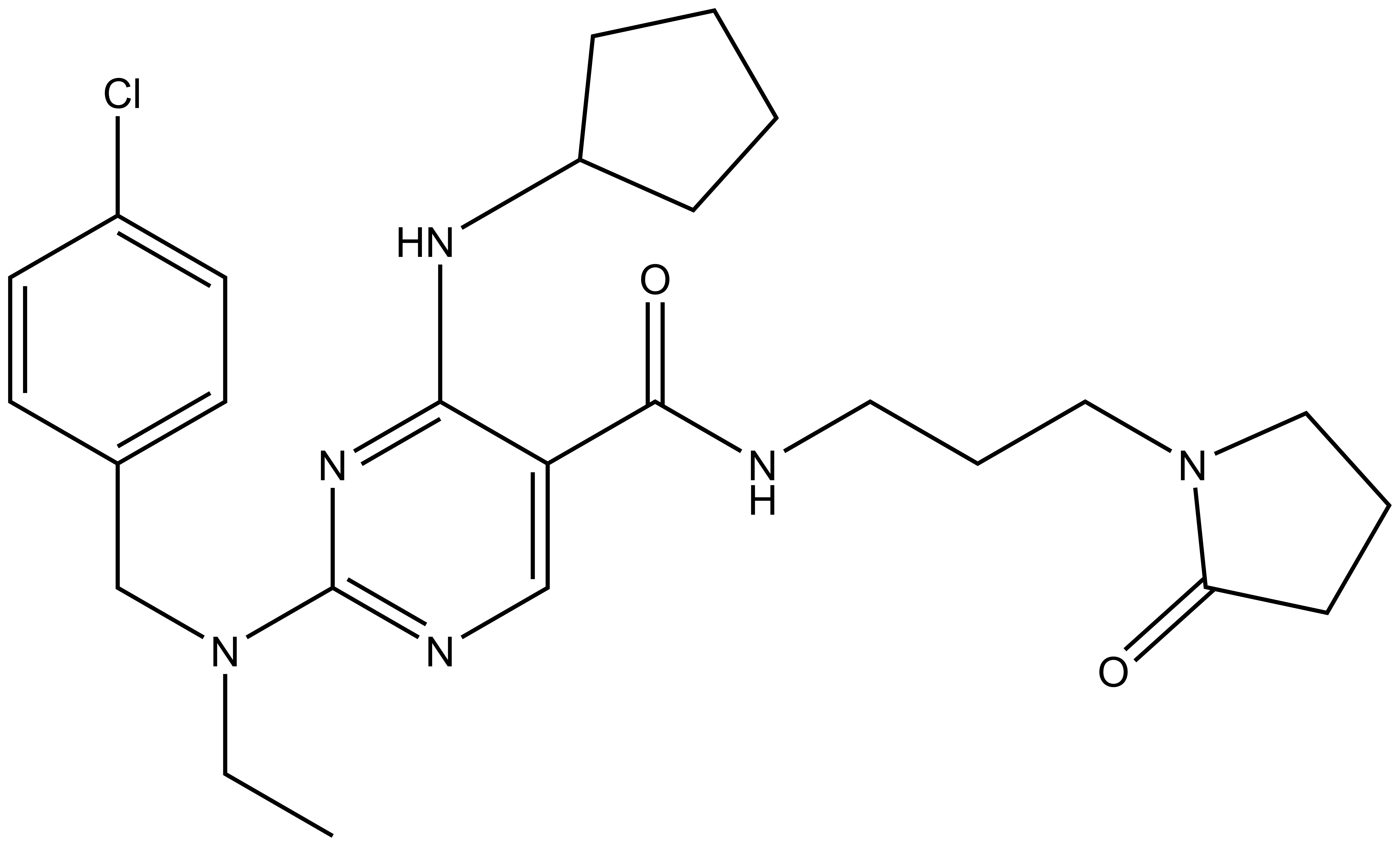
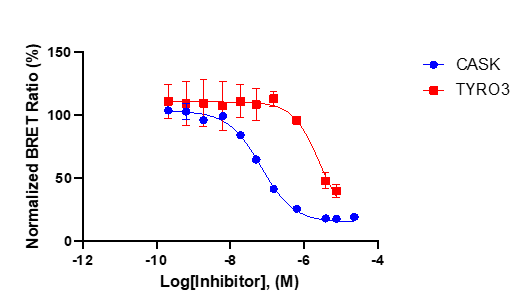
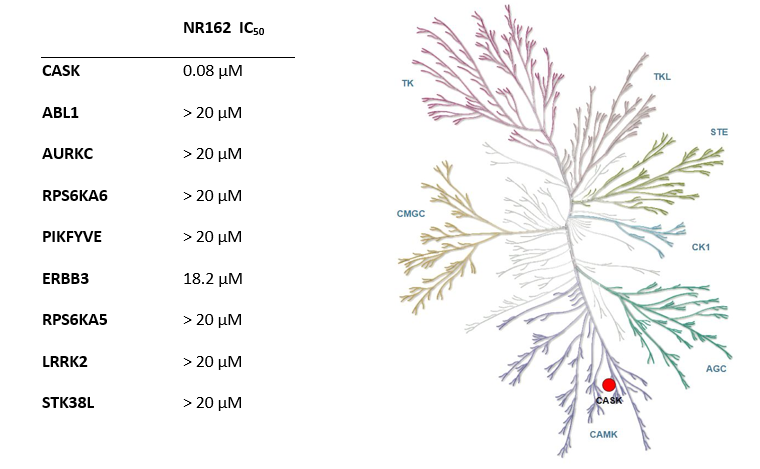
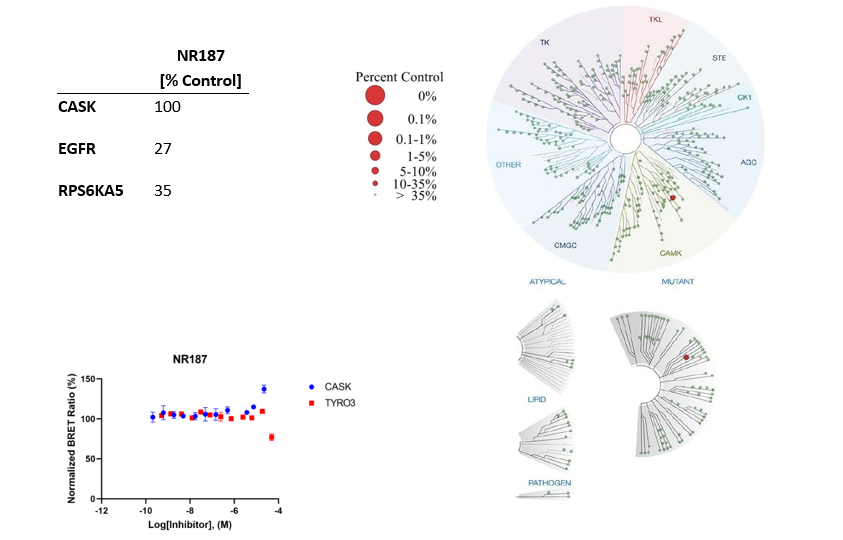
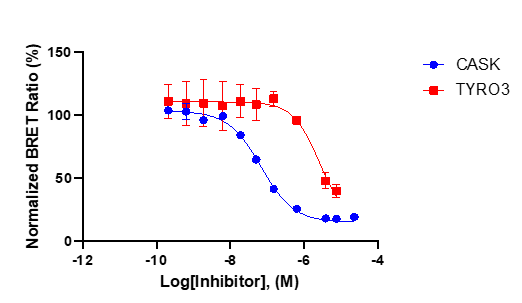
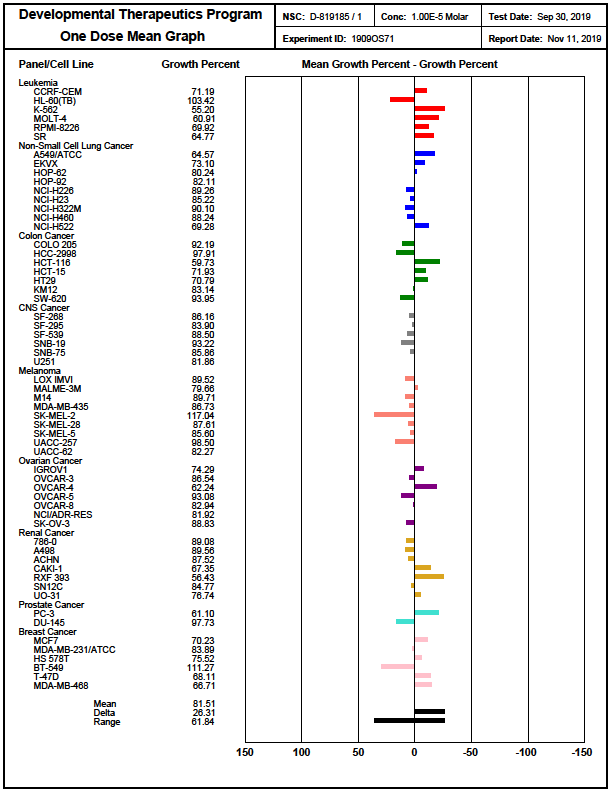
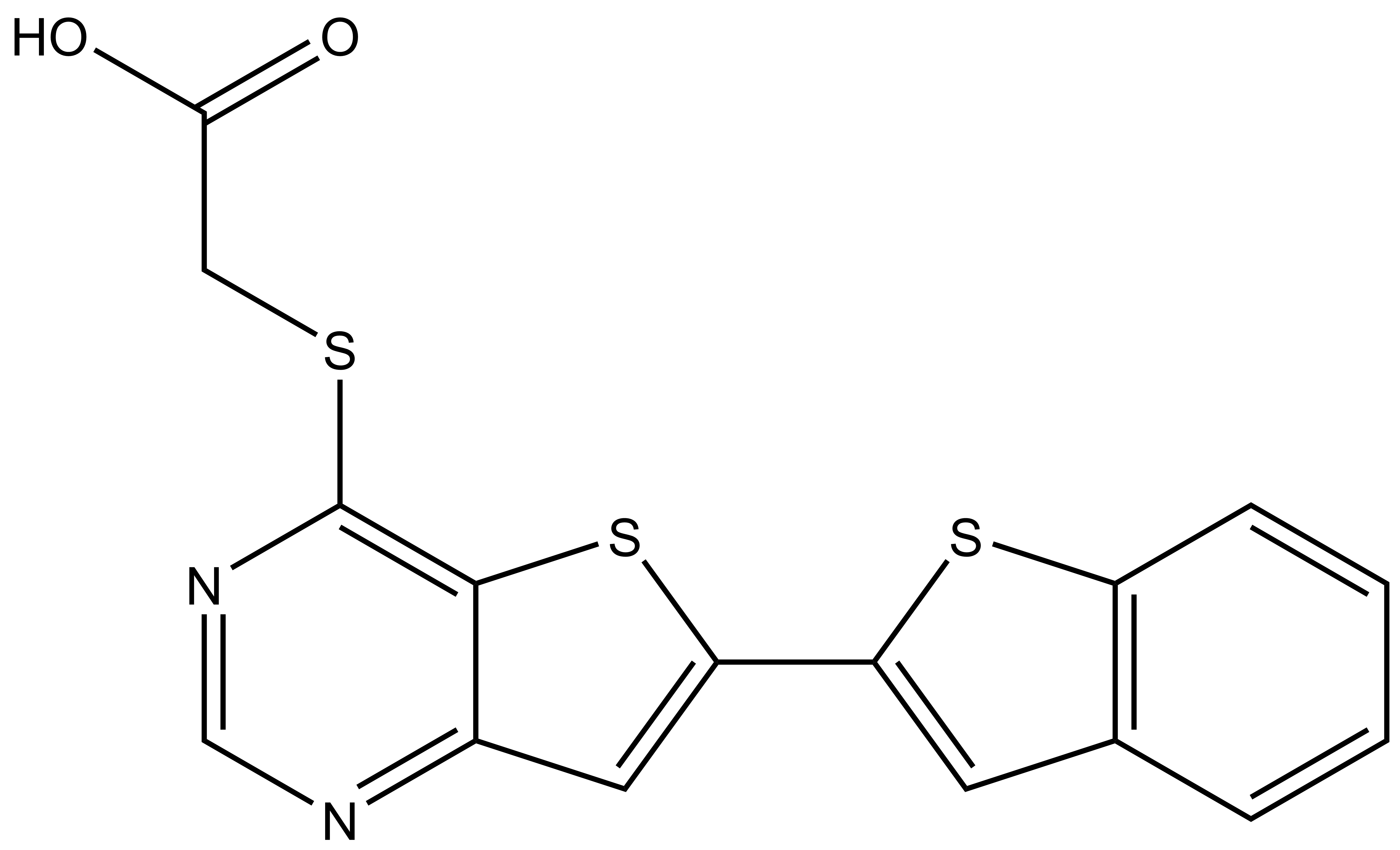
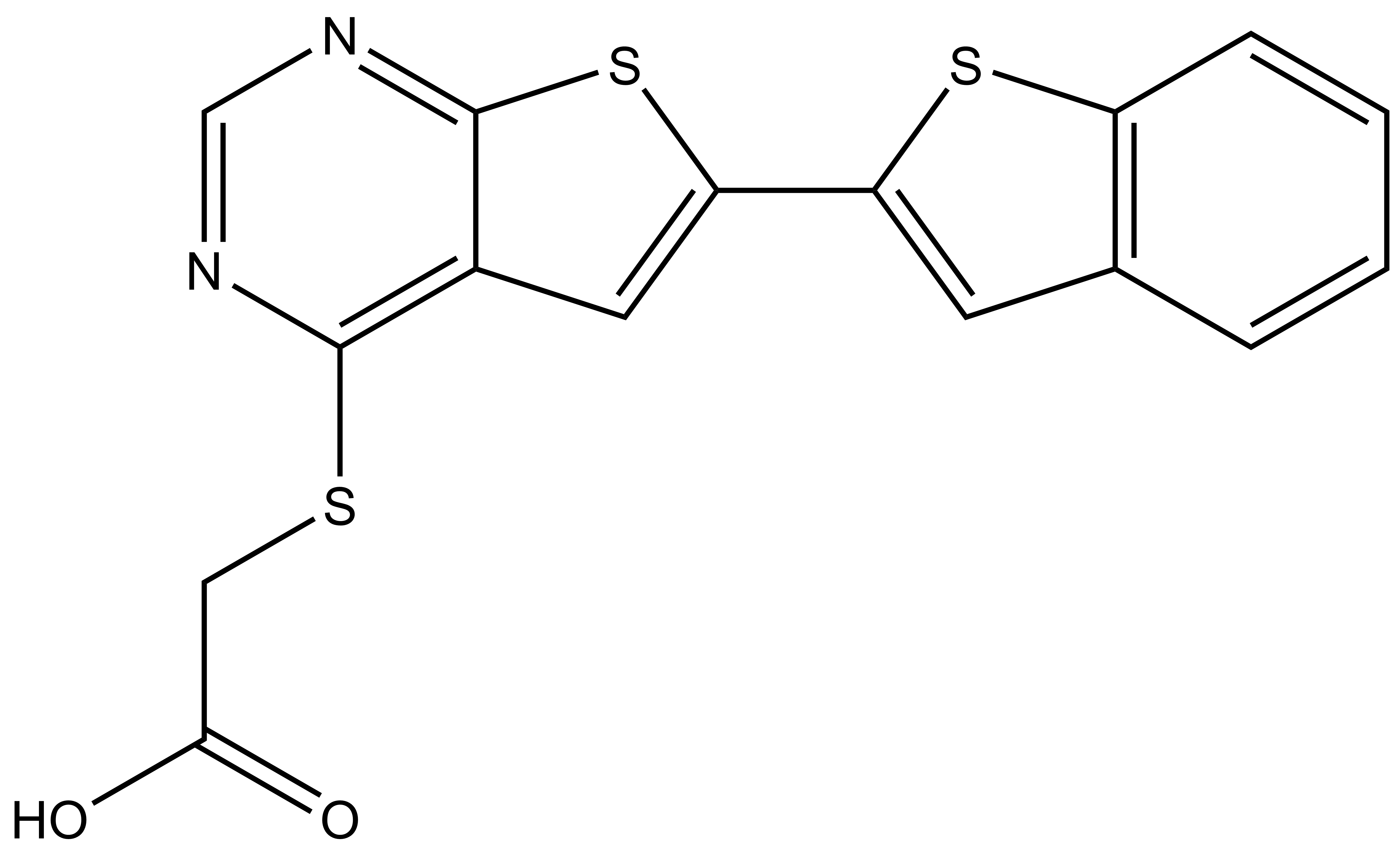
References
1. Doty, R.T., et al., The leukemia-associated gene Mllt1/ENL: characterization of a murine homolog and demonstration of an essential role in embryonic development. Blood Cells Mol Dis, 2002. 28(3): p. 407-17.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12367585
2. Mueller, D., et al., A role for the MLL fusion partner ENL in transcriptional elongation and chromatin modification. Blood, 2007. 110(13): p. 4445-54.DOI: 10.1182/blood-2007-05-090514.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17855633
3. Mueller, D., et al., Misguided transcriptional elongation causes mixed lineage leukemia. PLoS Biol, 2009. 7(11): p. e1000249.DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000249.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19956800
4. Yokoyama, A., et al., A higher-order complex containing AF4 and ENL family proteins with P-TEFb facilitates oncogenic and physiologic MLL-dependent transcription. Cancer Cell, 2010. 17(2): p. 198-212.DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2009.12.040.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20153263
5. Biswas, D., et al., Function of leukemogenic mixed lineage leukemia 1 (MLL) fusion proteins through distinct partner protein complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2011. 108(38): p. 15751-6.DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1111498108.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21896721
6. Monroe, S.C., et al., MLL-AF9 and MLL-ENL alter the dynamic association of transcriptional regulators with genes critical for leukemia. Exp Hematol, 2011. 39(1): p. 77-86 e1-5.DOI: 10.1016/j.exphem.2010.09.003.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20854876
7. Erb, M.A., et al., Transcription control by the ENL YEATS domain in acute leukaemia. Nature, 2017. 543(7644): p. 270-274.DOI: 10.1038/nature21688.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28241139
8. Wan, L., et al., ENL links histone acetylation to oncogenic gene expression in acute myeloid leukaemia. Nature, 2017. 543(7644): p. 265-269.DOI: 10.1038/nature21687.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28241141
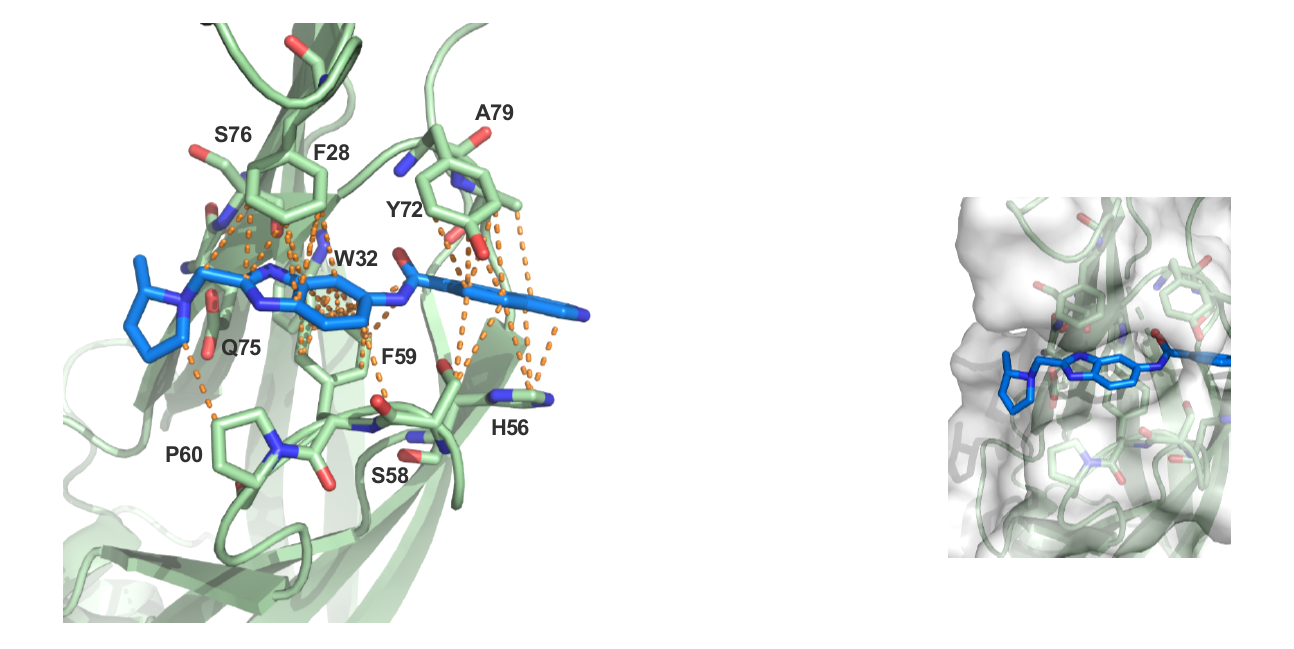
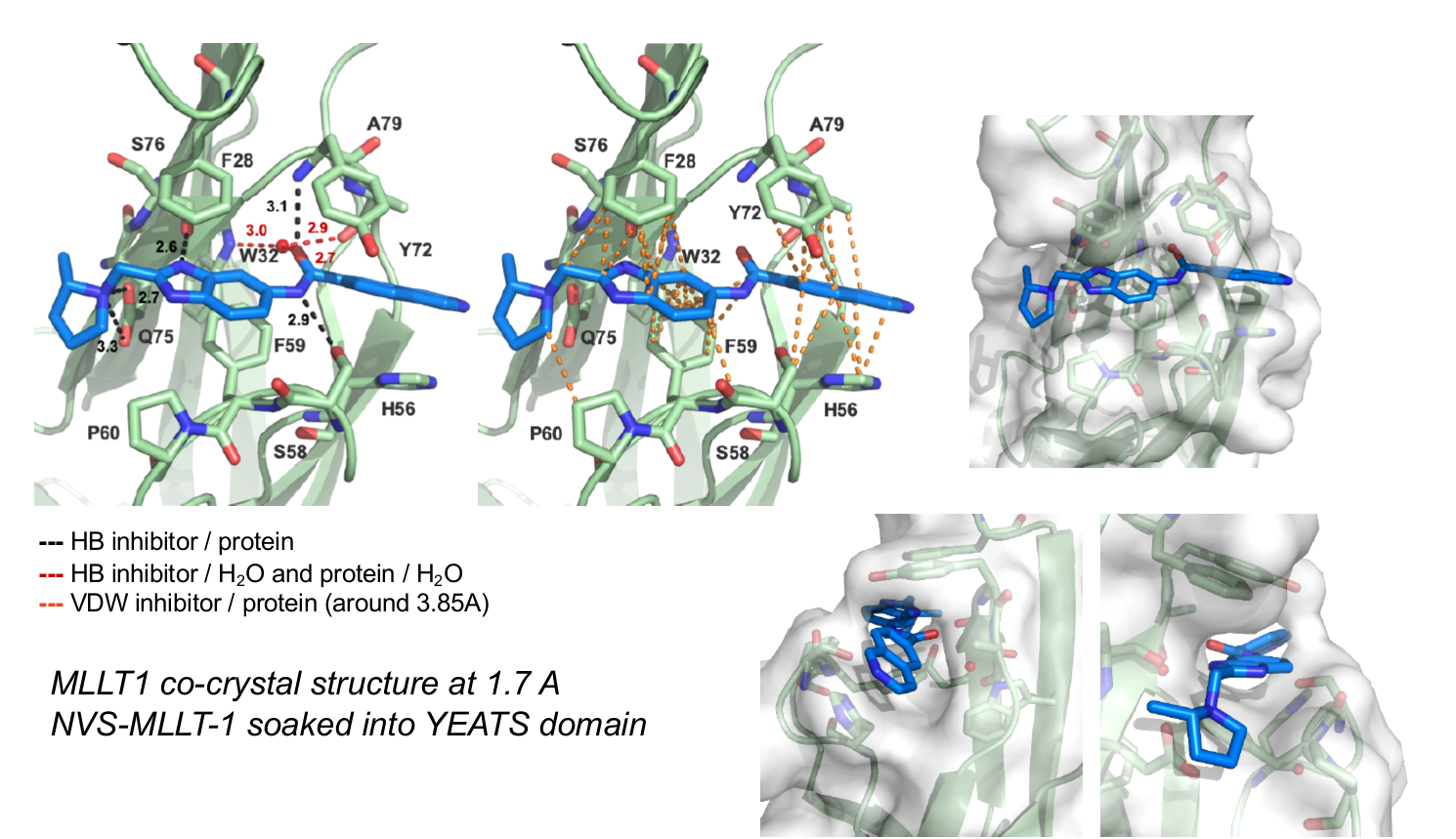
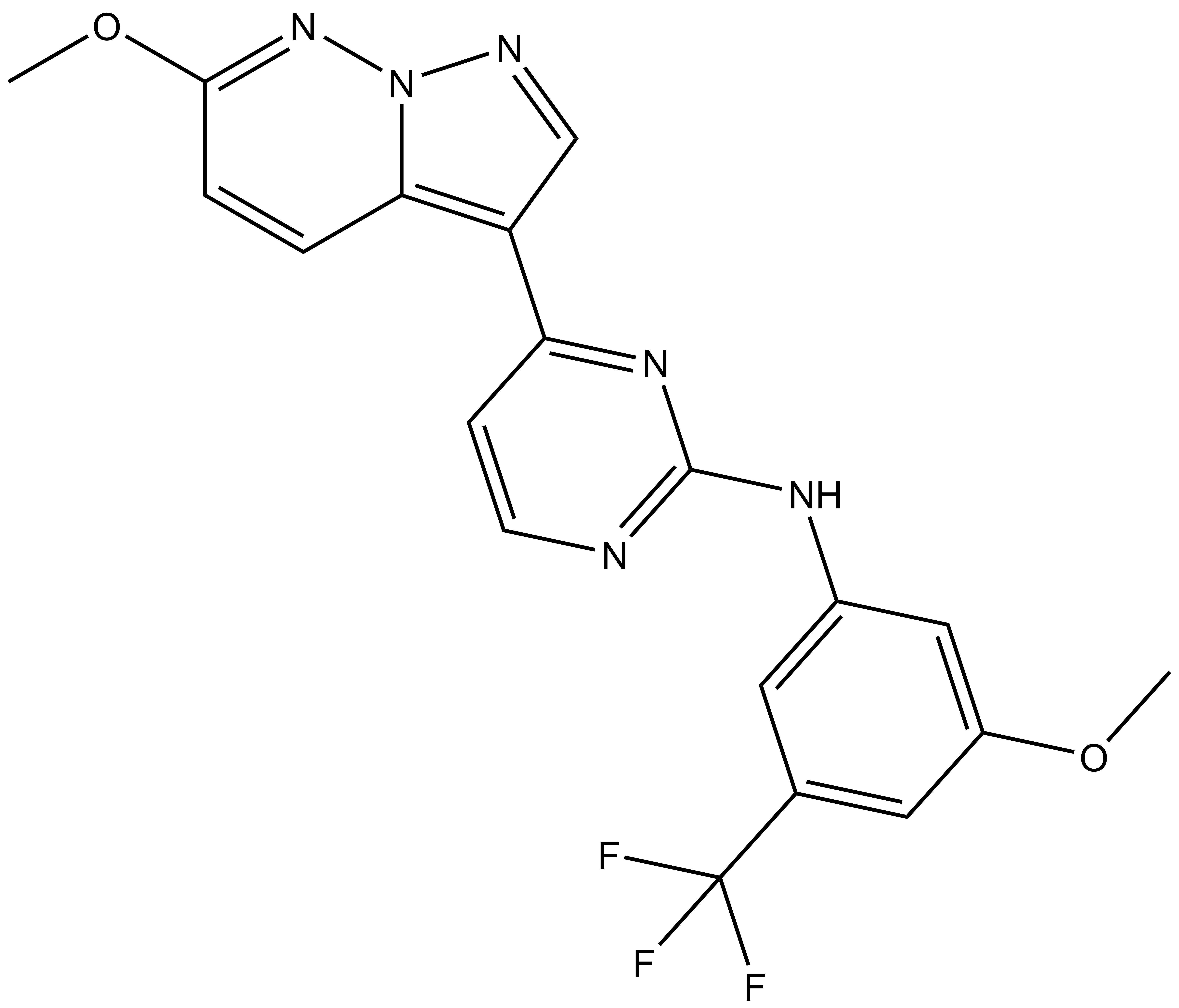
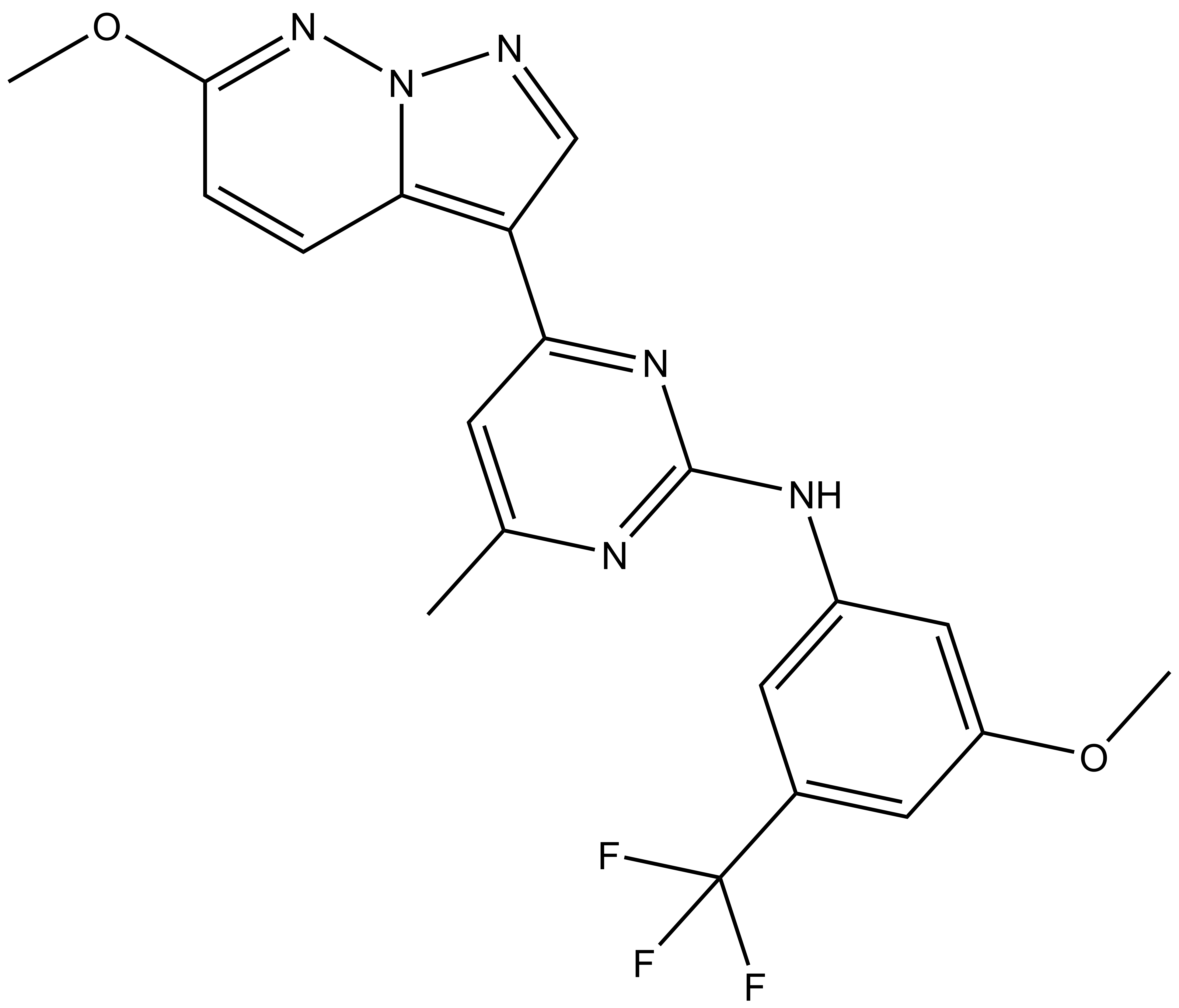
9. Christott, T. et al., Discovery of a selective inhibitor for the YEATS domains of ENL/AF9. SLAS Discov, 2019. 24(2):133-141. DOI: 10.1177/2472555218809904. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30359161
10. Chaikuad, A., S. Knapp, and F. von Delft, Defined PEG smears as an alternative approach to enhance the search for crystallization conditions and crystal-quality improvement in reduced screens. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr, 2015. 71(Pt 8): p. 1627-39.DOI: 10.1107/S1399004715007968.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26249344
11. Moustakim, M., et al., Discovery of an MLLT1/3 YEATS Domain Chemical Probe. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl, 2018. 57(50): p. 16302-16307.DOI: 10.1002/anie.201810617.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30288907
12. Heidenreich, D., et al., Structure-Based Approach toward Identification of Inhibitory Fragments for Eleven-Nineteen-Leukemia Protein (ENL). J Med Chem, 2018. 61(23): p. 10929-10934.DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b01457.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30407816