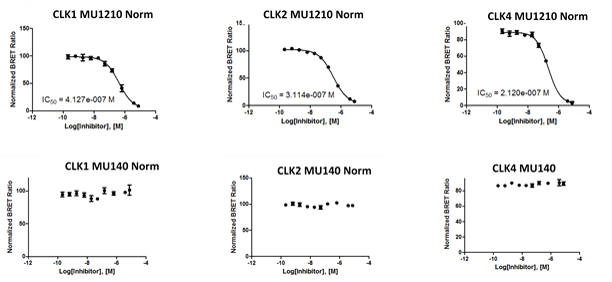
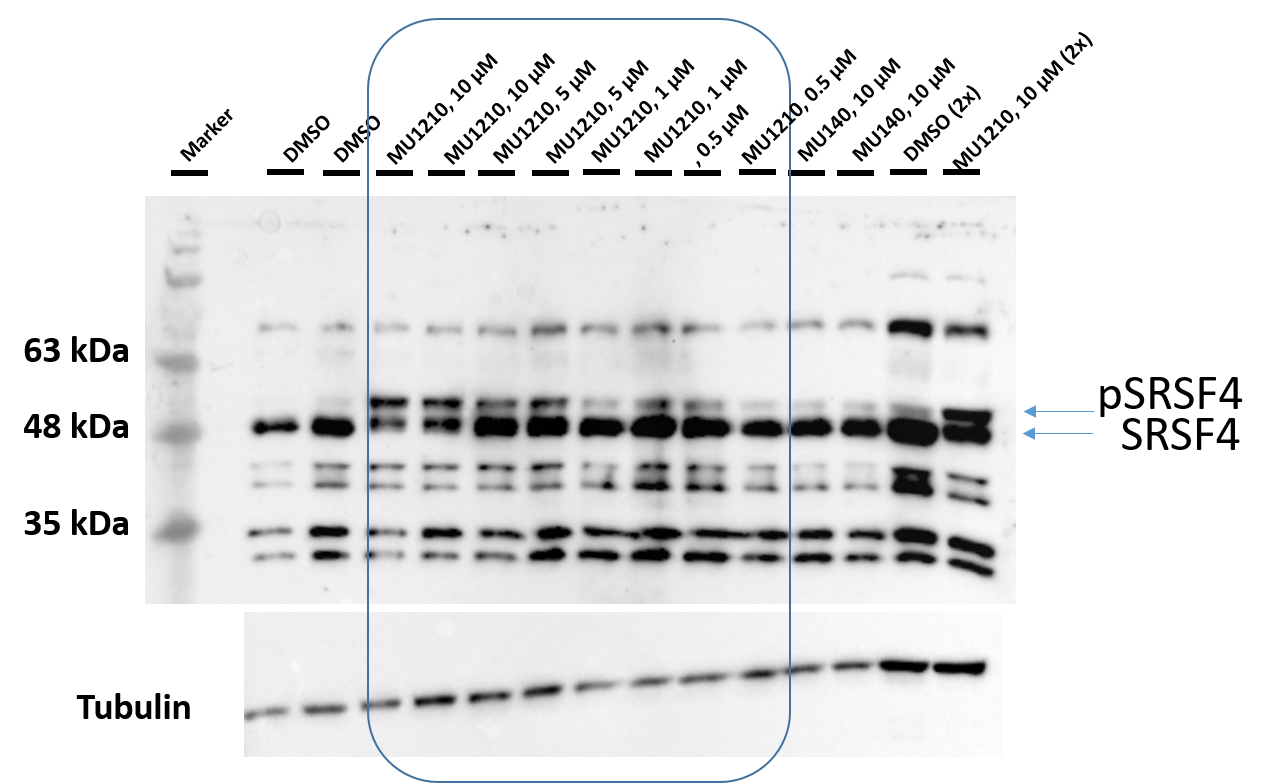
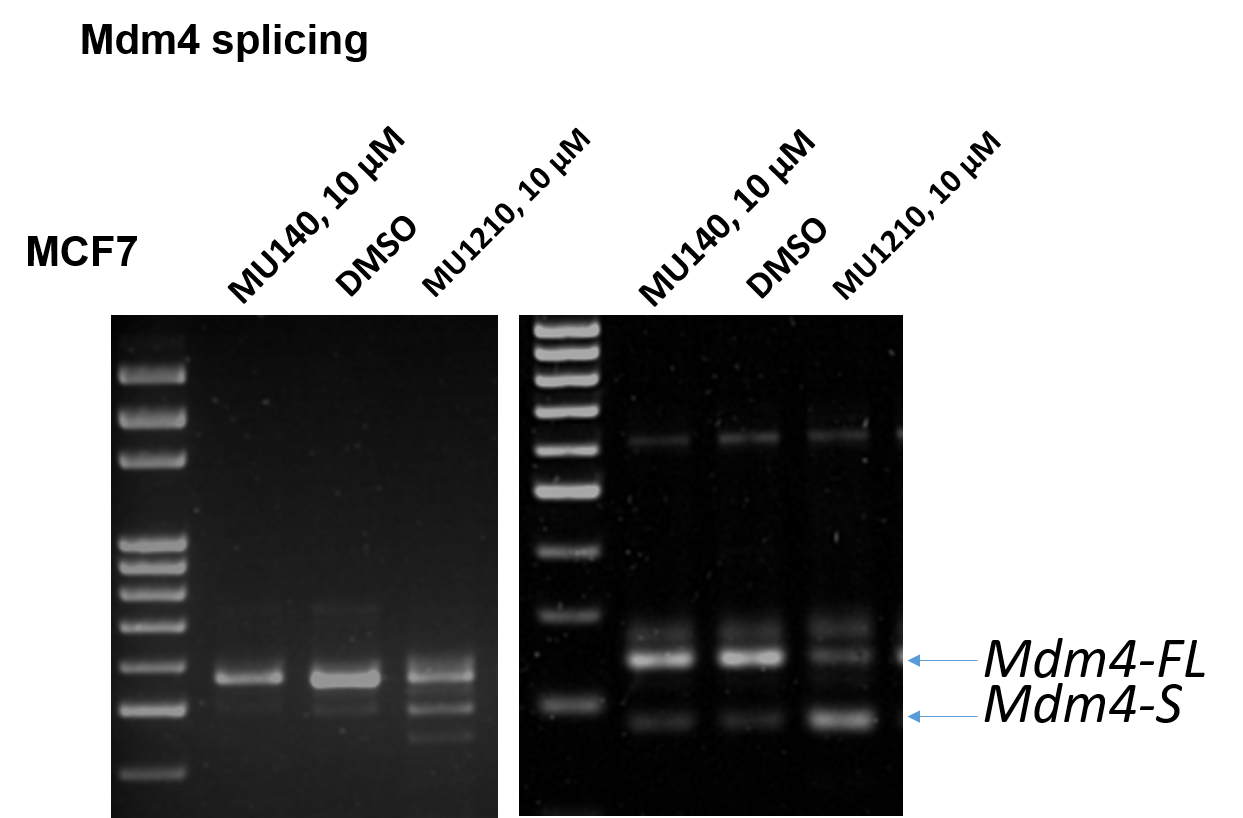
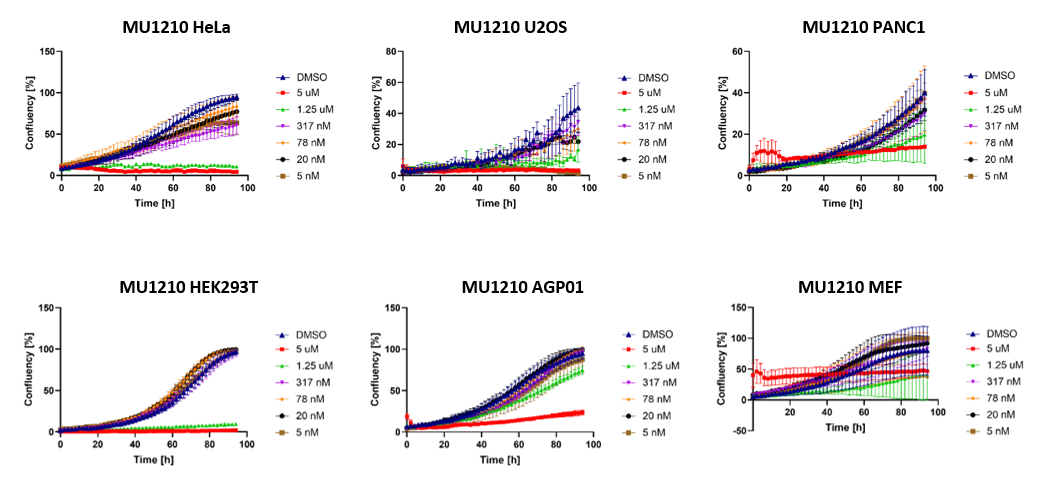
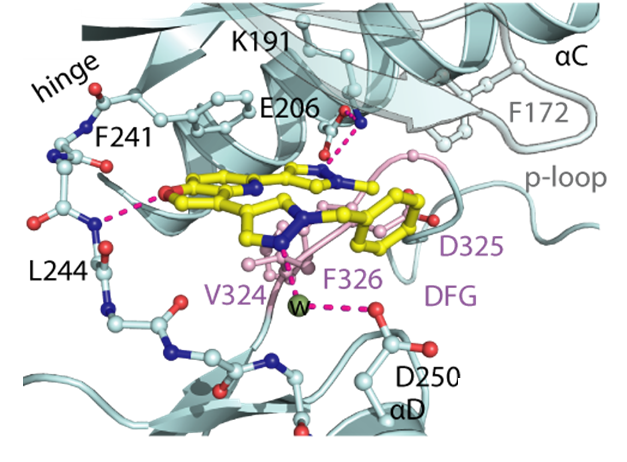
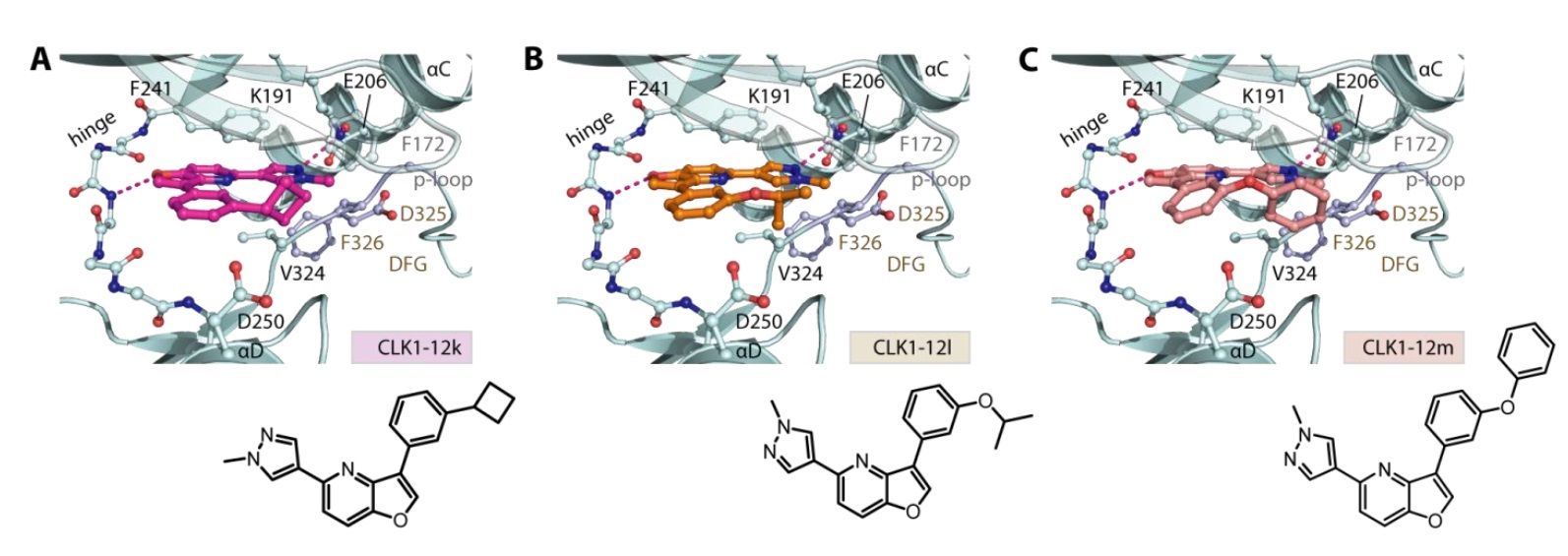
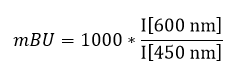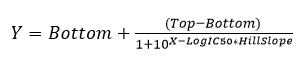1. Wysocka, J., Swigut, T., Xiao, H., Milne, T. A., Kwon, S. Y., Landry, J., Kauer, M., Tackett, A. J., Chait, B. T., Badenhorst, P., Wu, C., and Allis, C. D. (2006) A PHD finger of NURF couples histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation with chromatin remodelling. Nature 442, 86-90
2. Goller, T., Vauti, F., Ramasamy, S., and Arnold, H. H. (2008) Transcriptional regulator BPTF/FAC1 is essential for trophoblast differentiation during early mouse development. Molecular and cellular biology 28, 6819-6827
3. Landry, J., Sharov, A. A., Piao, Y., Sharova, L. V., Xiao, H., Southon, E., Matta, J., Tessarollo, L., Zhang, Y. E., Ko, M. S., Kuehn, M. R., Yamaguchi, T. P., and Wu, C. (2008) Essential role of chromatin remodeling protein Bptf in early mouse embryos and embryonic stem cells. PLoS genetics 4, e1000241
4. Ngeow, K. C., Friedrichsen, H. J., Li, L., Zeng, Z., Andrews, S., Volpon, L., Brunsdon, H., Berridge, G., Picaud, S., Fischer, R., Lisle, R., Knapp, S., Filippakopoulos, P., Knowles, H., Steingrimsson, E., Borden, K. L. B., Patton, E. E., and Goding, C. R. (2018) BRAF/MAPK and GSK3 signaling converges to control MITF nuclear export. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 115, E8668-e8677
5. Dar, A. A.; Majid, S.; Bezrookove, V.; Phan, B.; Ursu, S.; Nosrati, M.; De Semir, D.; Sagebiel, R. W.; Miller, J. R.; Debs, R.; Cleaver, J. E.; Kashani-Sabet, M., BPTF transduces MITF-driven prosurvival signals in melanoma cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2016, 113 (22), 6254–6258.