| Probe | | Negative control |
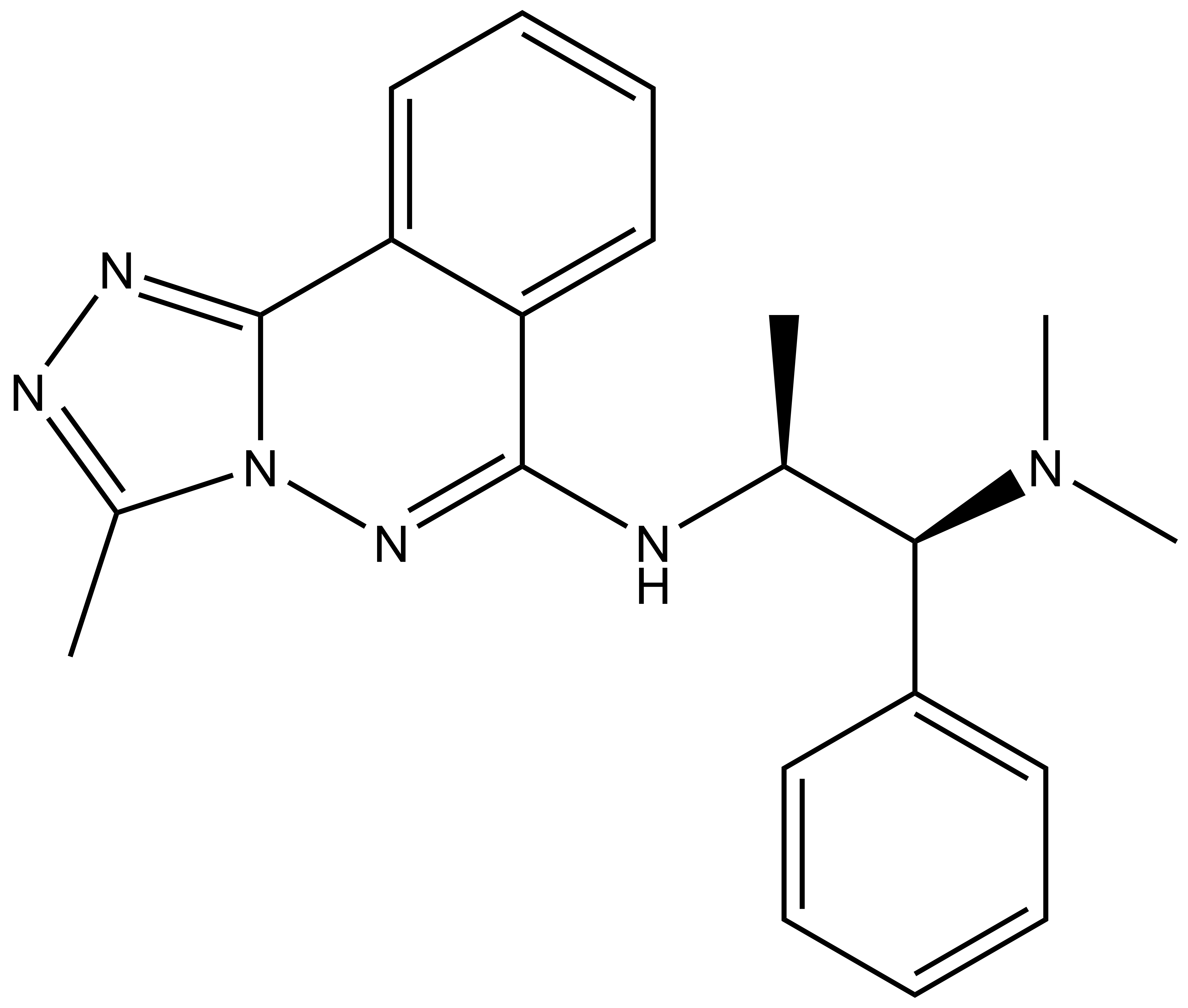 | | 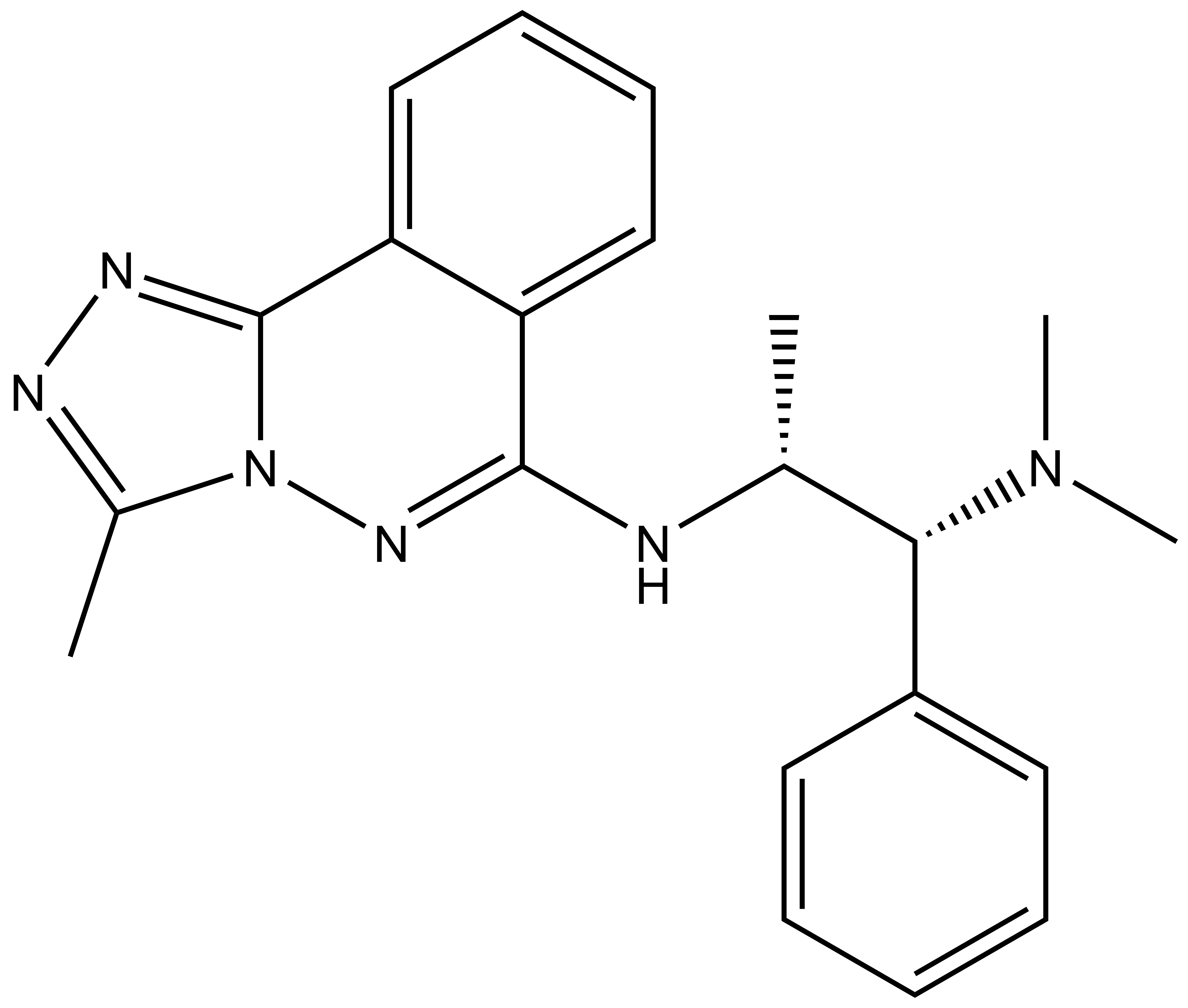 |
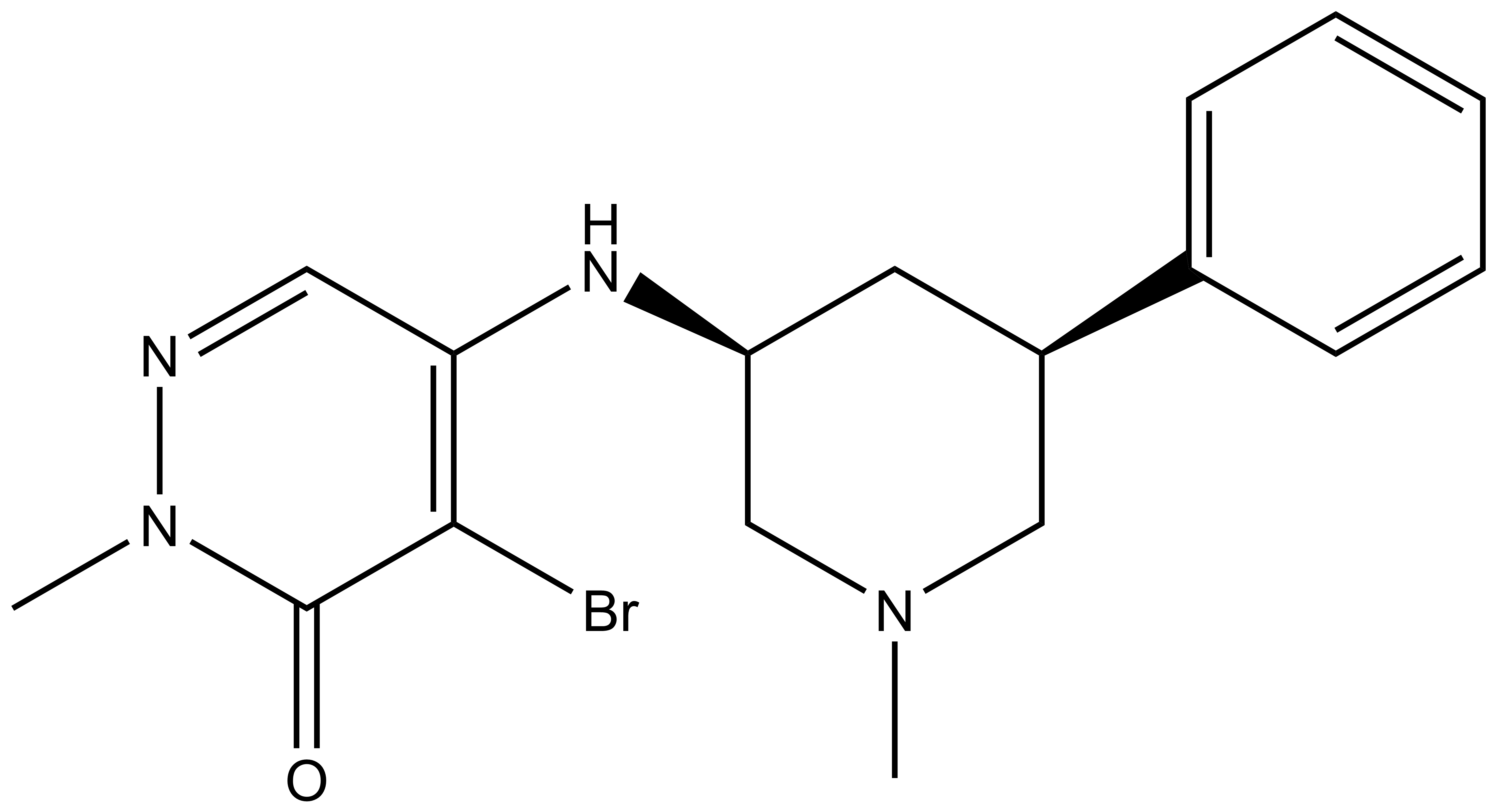
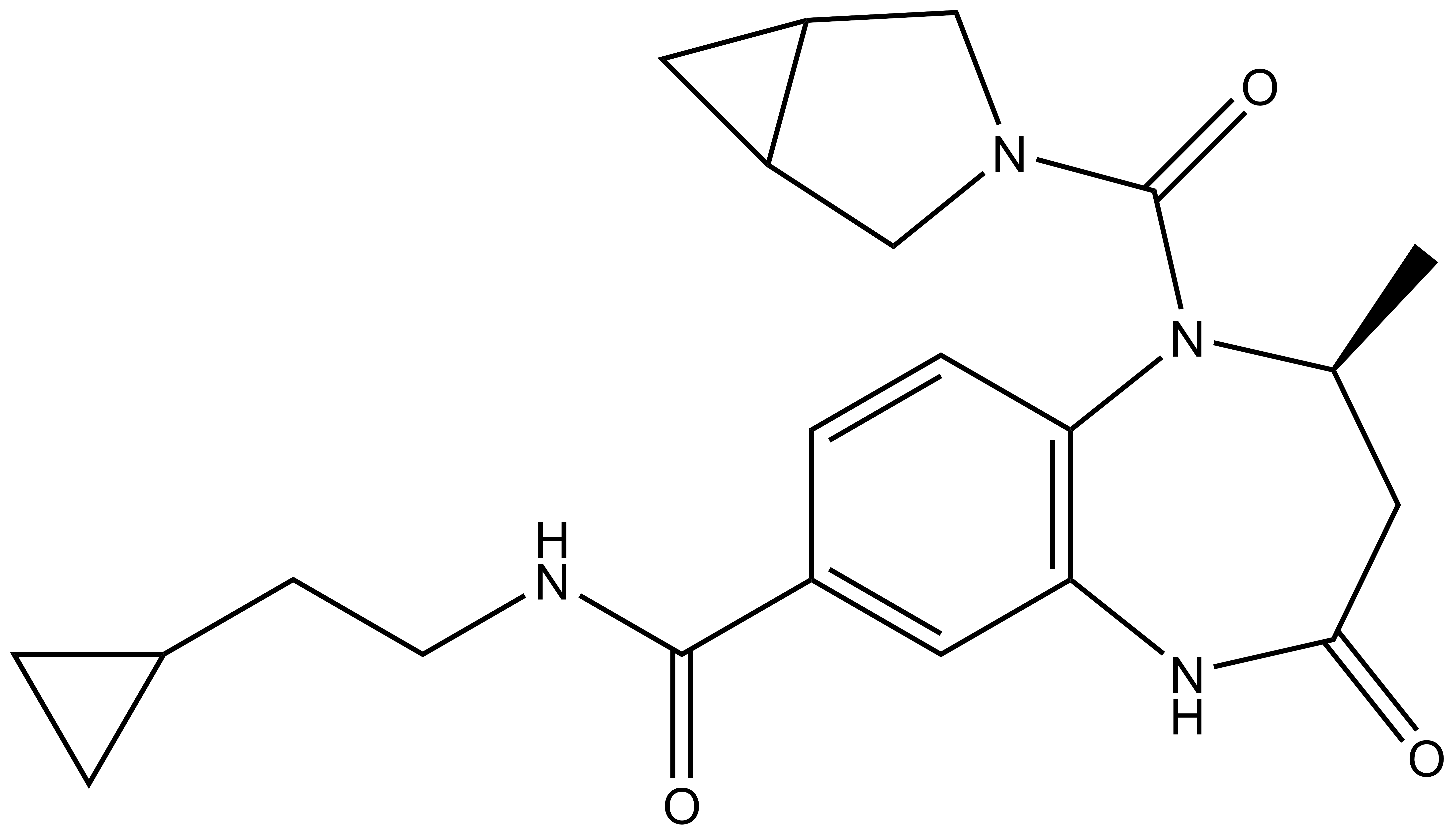
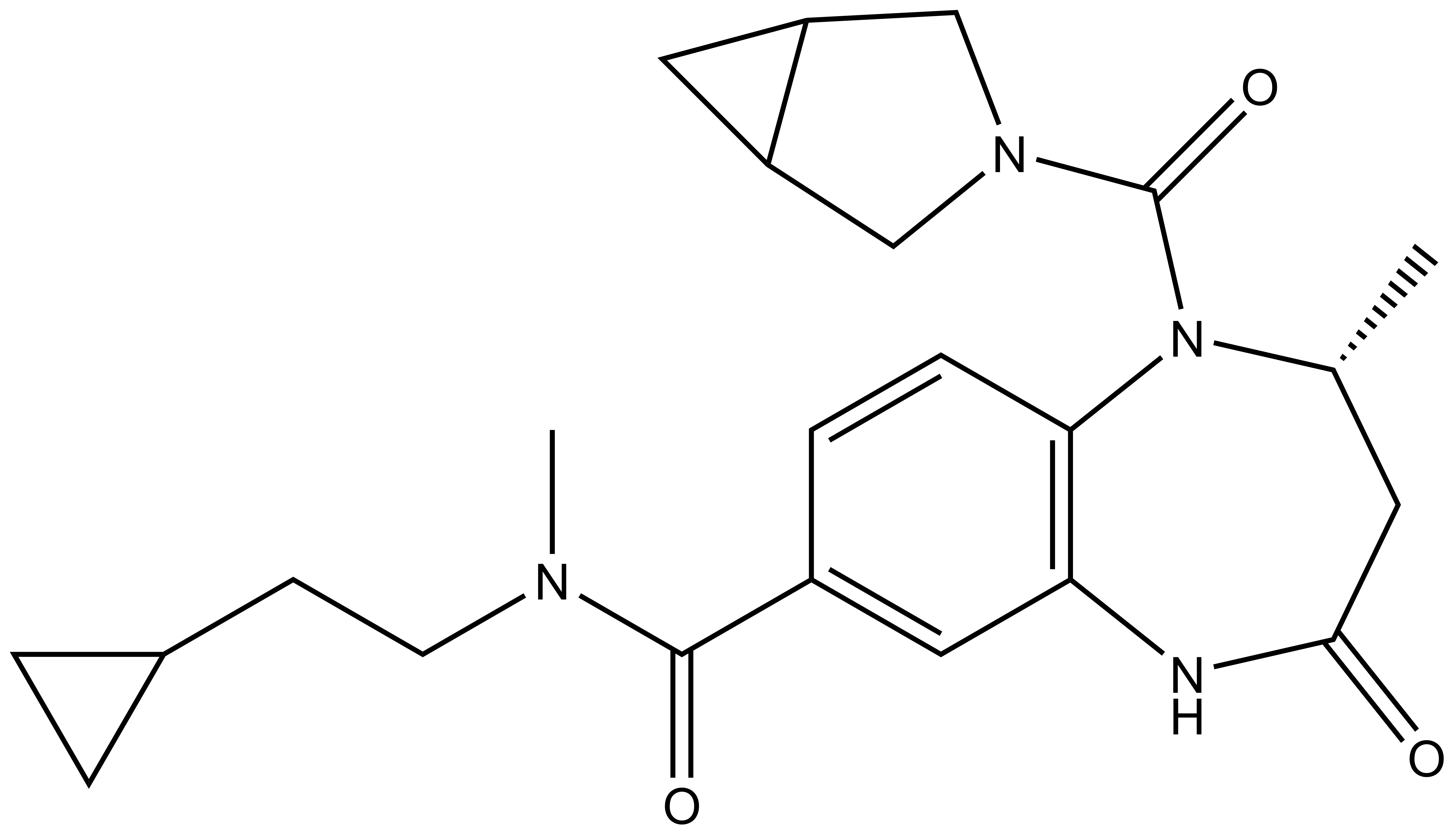
L-Moses | | D-Moses |
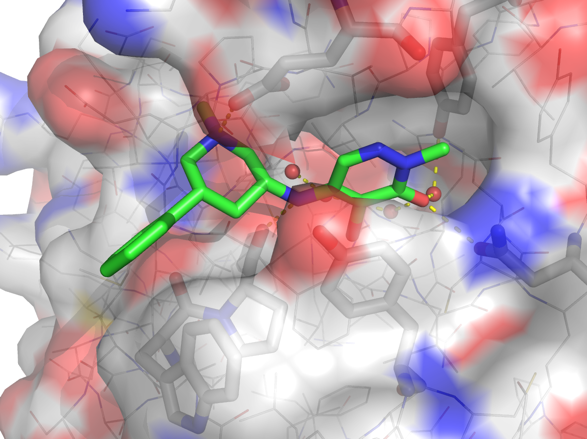
p300/CBP-associated factor (PCAF/KAT2B) and general control non-derepressible 5 (GCN5/KAT2A) are members of subfamily 1 of the bromodomain phylogenetic tree. These multi-domain proteins that have been implicated in retroviral infection, inflammation pathways and cancer development. However, outside of viral replication, little is known about the dependence of these effects on the C-terminal bromodomain. L-Moses is as a chemical probe for the PCAF/GCN5 bromodomain and D-Moses is the enantiomeric negative control. Rational inhibitor design and biophysical characterization led to the discovery of L-Moses. The probe was optimized from the non-selective pan-bromodomain inhibitor, bromosporine to generate a potent, selective (>4500-fold selective over BRD4), permeable and cell-active PCAF/GCN5 bromodomain chemical probe.
Potency
PCAF Ki 47 nM in a HTRF binding competition assay using PCAF bromodomain and a biotin tagged bromodomain ligand.
PCAF KD 48 nM in a BROMOscan assay run at DiscoverX.
GCN5 KD 220 nM in a BROMOscan assay run at DiscoverX.
PCAF KD 126 nM (ITC) using PCAF bromodomain.
GCN5 KD 600 nM (ITC) using GCN5 bromodomain.
Non-family targets
GPCR/Eurofins Panel: In an panel of 130 potential off targets, L-Moses showed no binding (>60% at 10 μM) to all targets except the opioid receptors (mu 100 nM, OPRL1 840 nM, kappa 1,100 nM,) and the 5-HT transporter (220 nM).
Cellular Potency
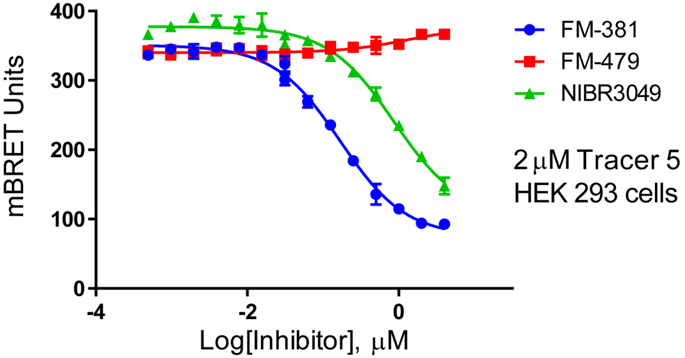
PCAF: IC50 220 nM in Promega NanoBRET assay, measuring displacement of NanoLuc-tagged truncated bromodomain PCAF from Halo-tagged histone H3.3 in HEK293 cells.
IC50 1.2 μM in NanoBRET assay, measuring displacement of NanoLuc-tagged full-length PCAF from Halo-tagged histone H3.3 in HEK293 cells.
IC50 660 nM for competing pull-down of full-length PCAF from cell lysates using immobilized L-Moses
GCN5: IC50 220 nM for competing pull-down of full-length PCAF from cell lysates using immobilized L-Moses.
Cytoxicity assay:
Toxicity of D-Moses and L-Moses was assessed on peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) obtained from 5 healthy donors. PBMC were cultured either with D-Moses or L-Moses at concentrations of 0.1, 1 and 10 μM or with a control (DMSO) for 24 hours. Viability of PBMC were then checked using LIVE/DEAD Fixable Aqua Dead Cell Stain Kit (ThermoFisher Scientific). No observed cytotoxicity was observed at any concentration.




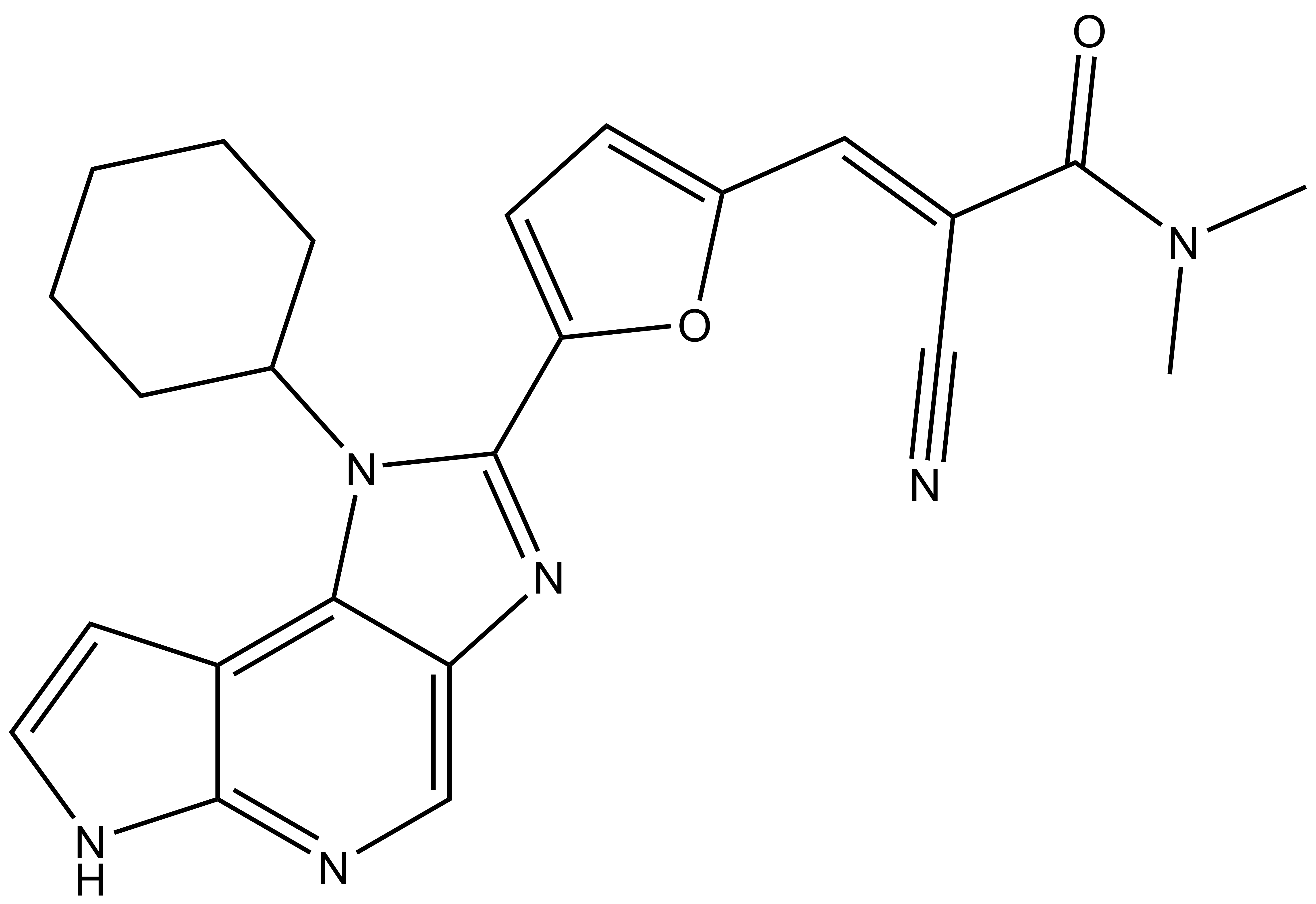
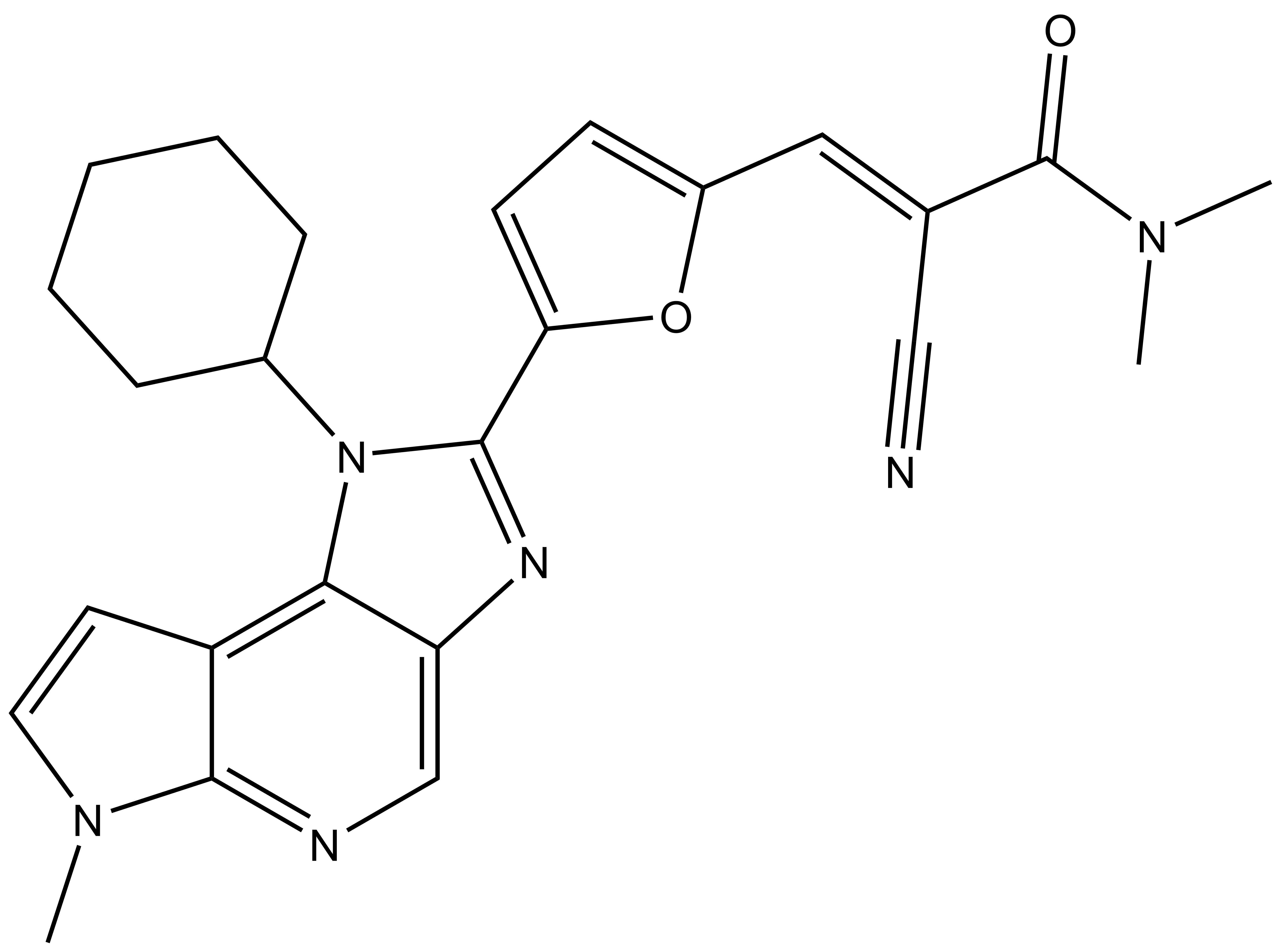
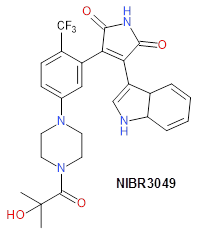
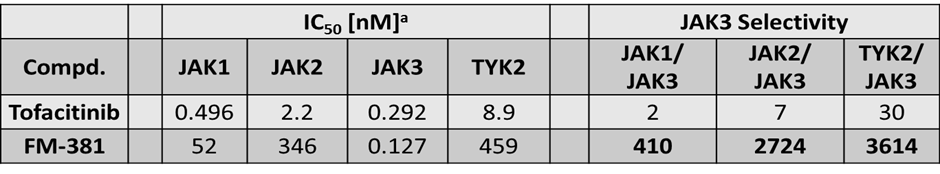
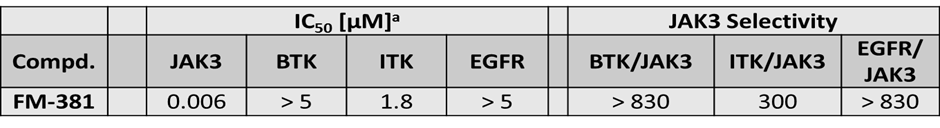
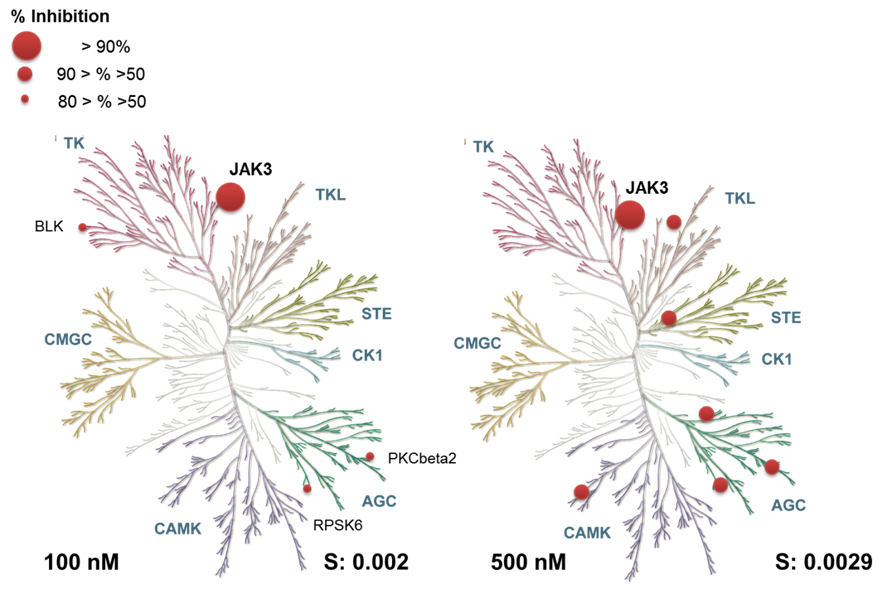
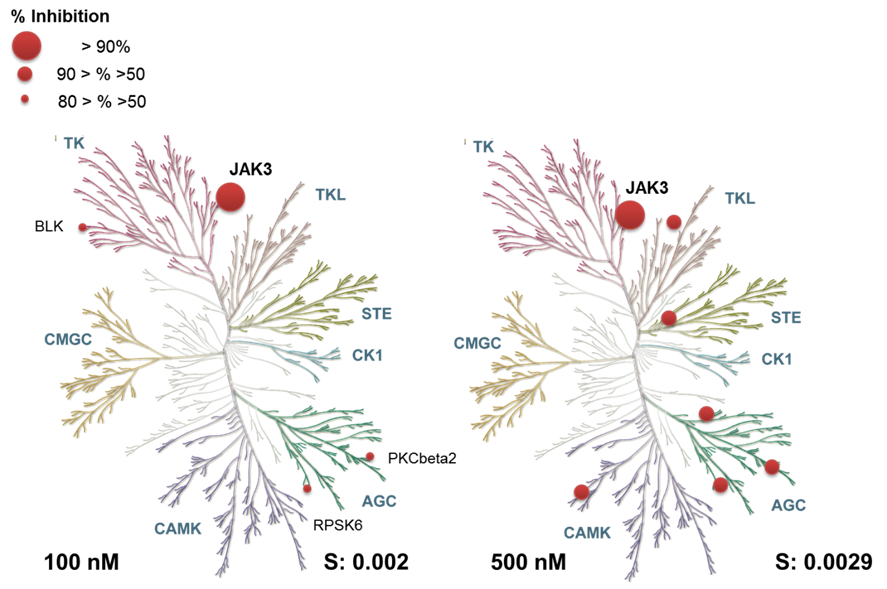
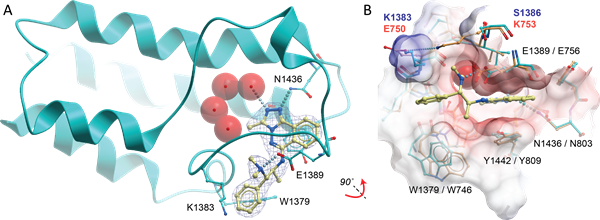
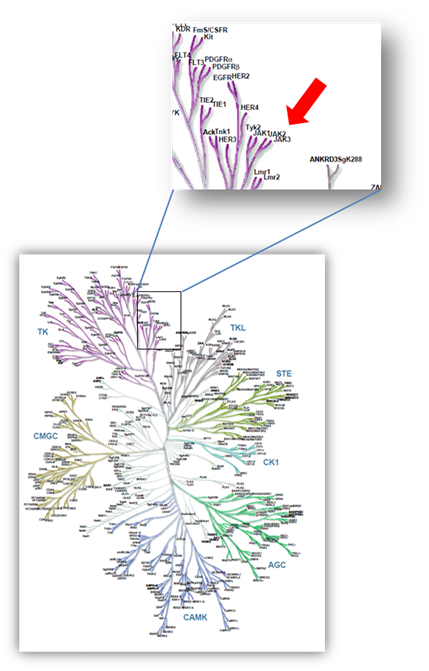 Janus kinases (JAKs) belong to the family of cytoplasmic tyrosine kinases. In human, the JAK family itself consist of 4 members (JAK1, JAK2, JAK3 and TYK). JAK family members are multi-domain proteins of about 130 kDa, which are highly homologous with respect to their domain structure and residue conservation within their structured domains.
Janus kinases (JAKs) belong to the family of cytoplasmic tyrosine kinases. In human, the JAK family itself consist of 4 members (JAK1, JAK2, JAK3 and TYK). JAK family members are multi-domain proteins of about 130 kDa, which are highly homologous with respect to their domain structure and residue conservation within their structured domains.