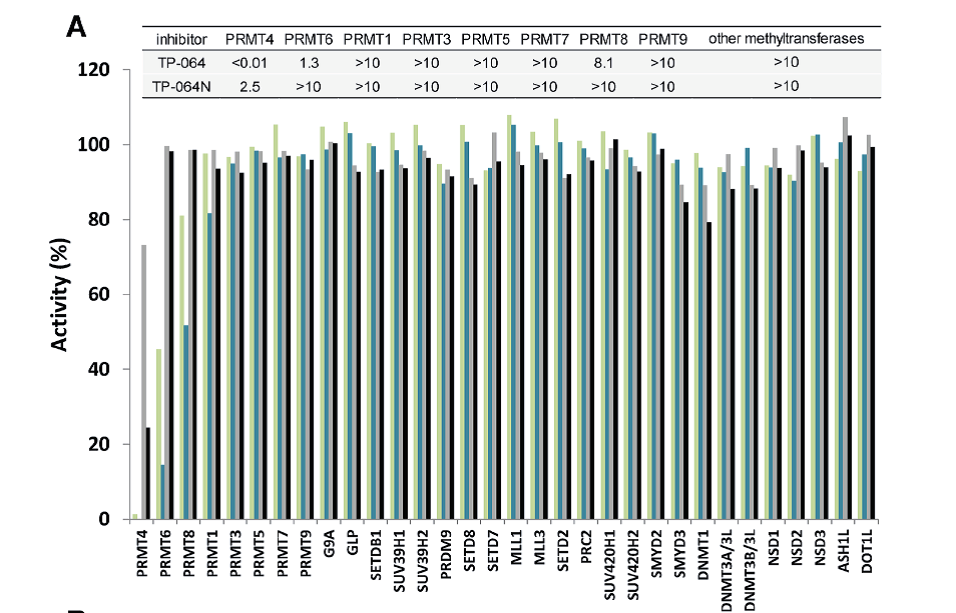
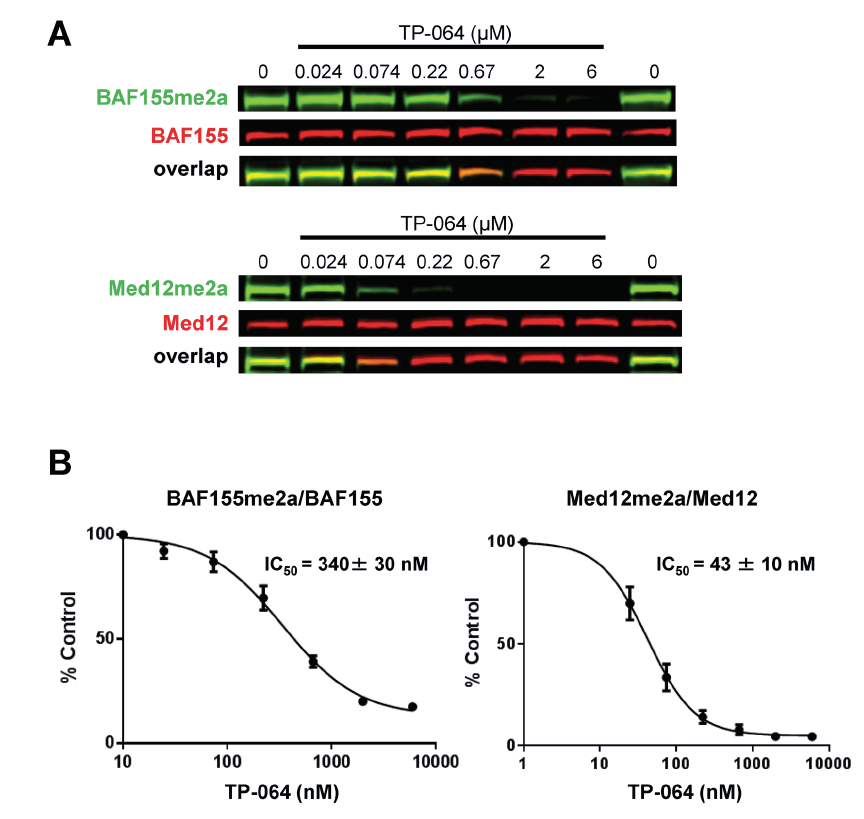
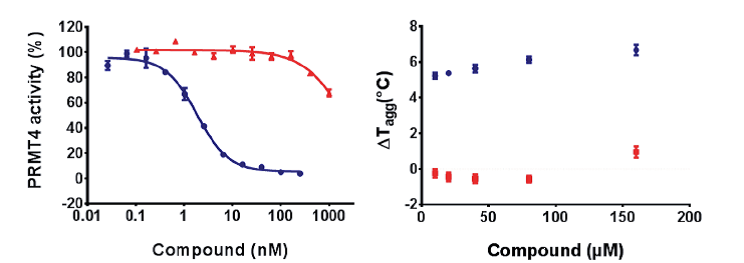
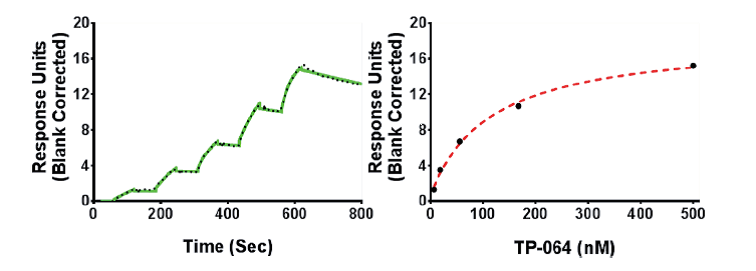
| Probe | | Negative control |
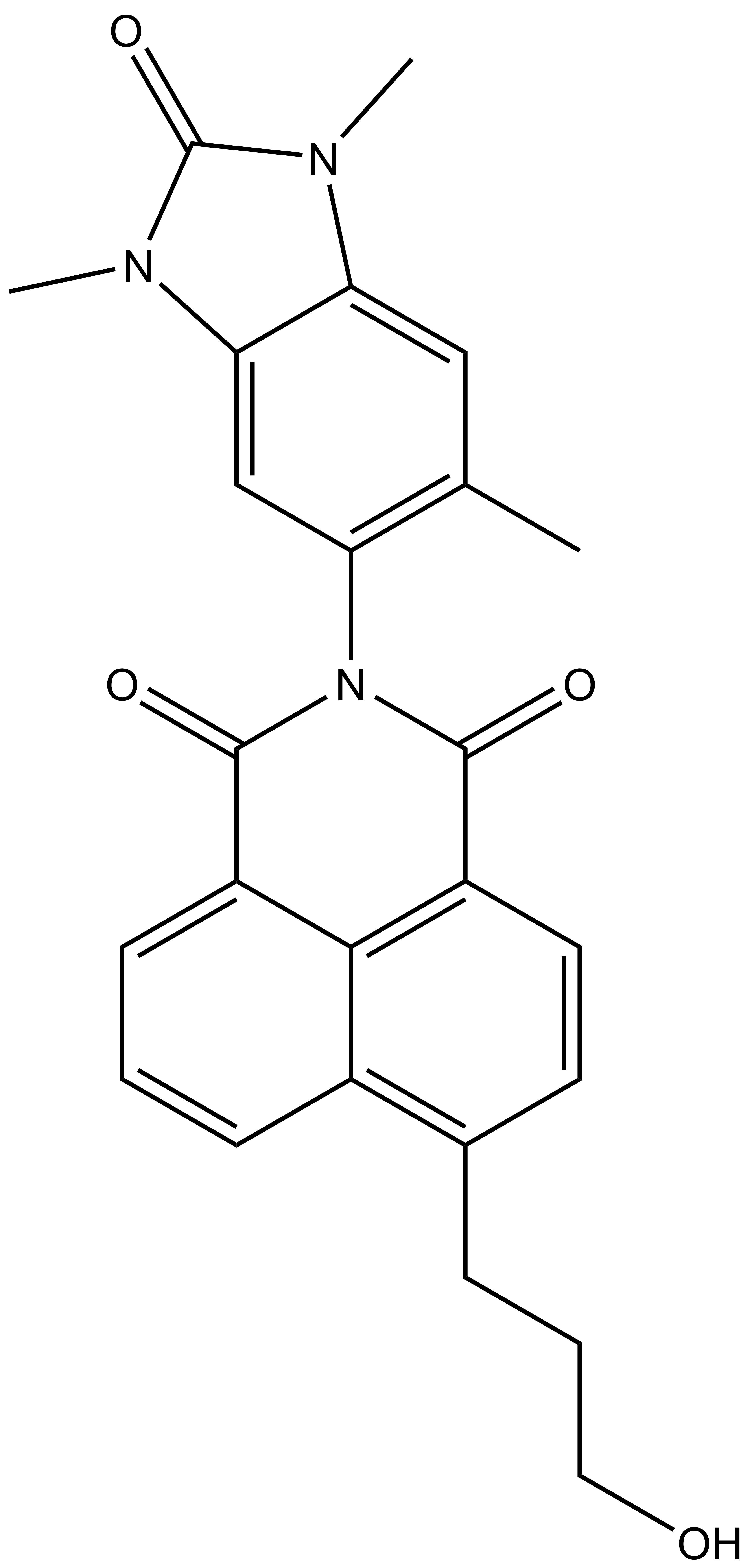 | | 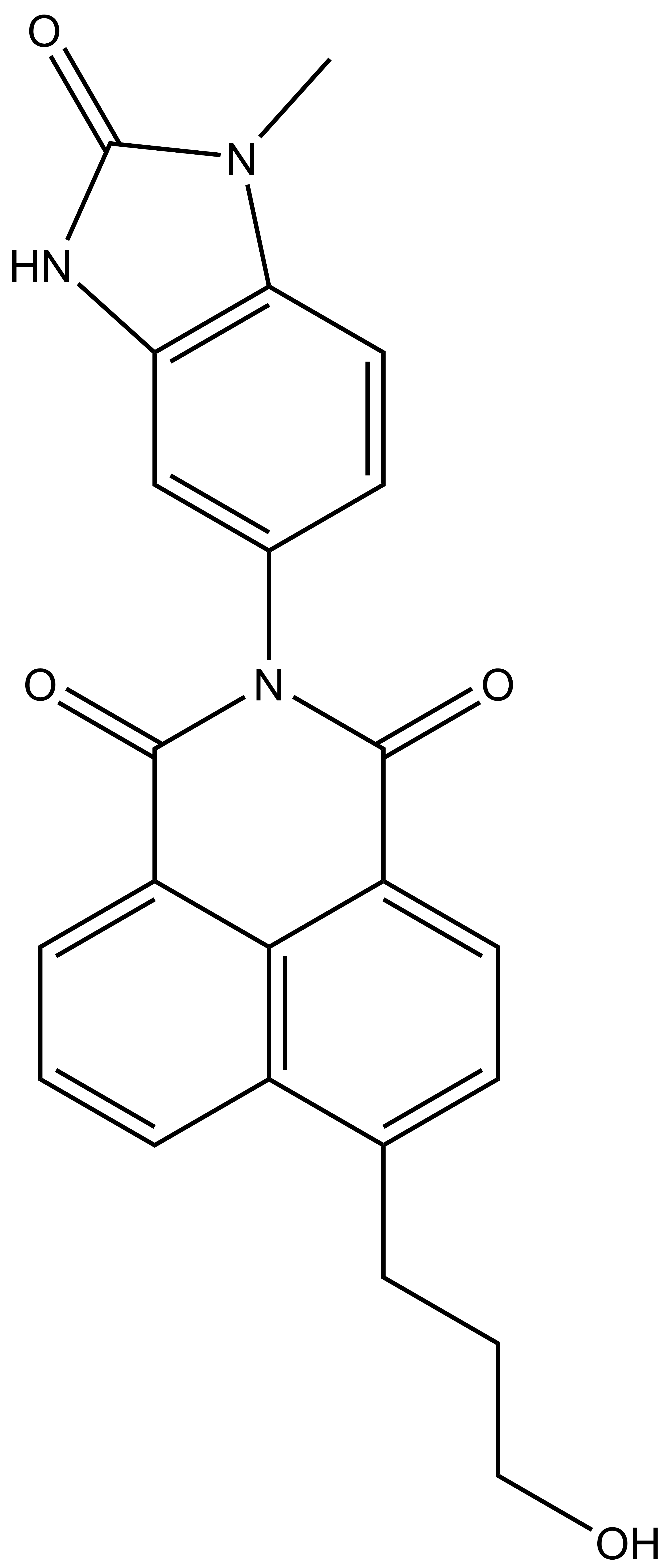 |
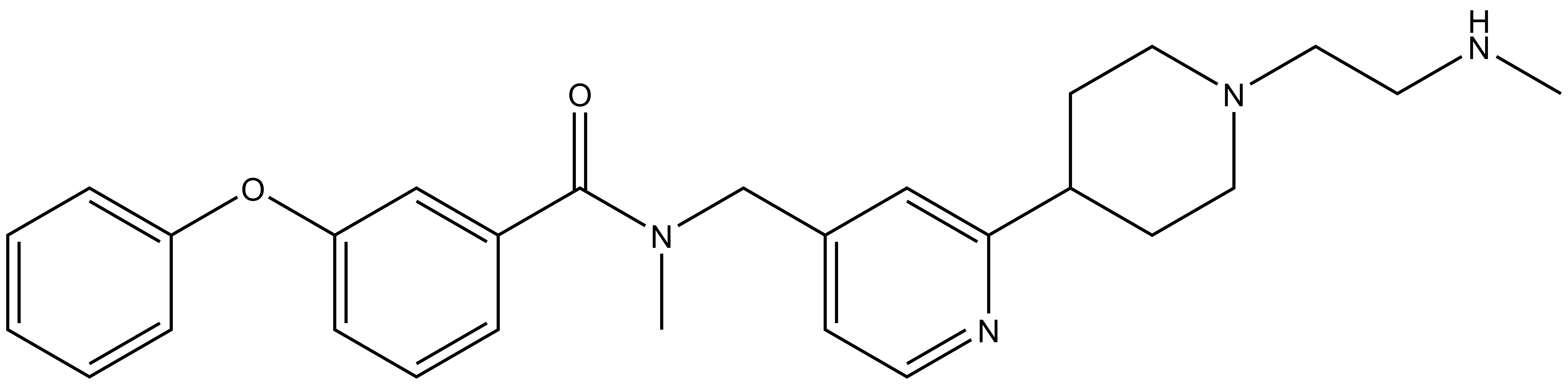
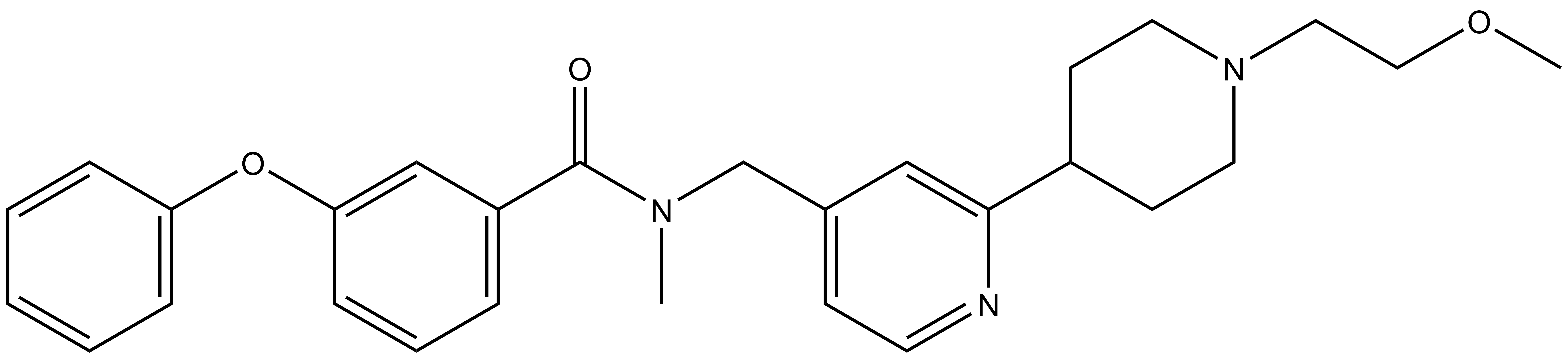
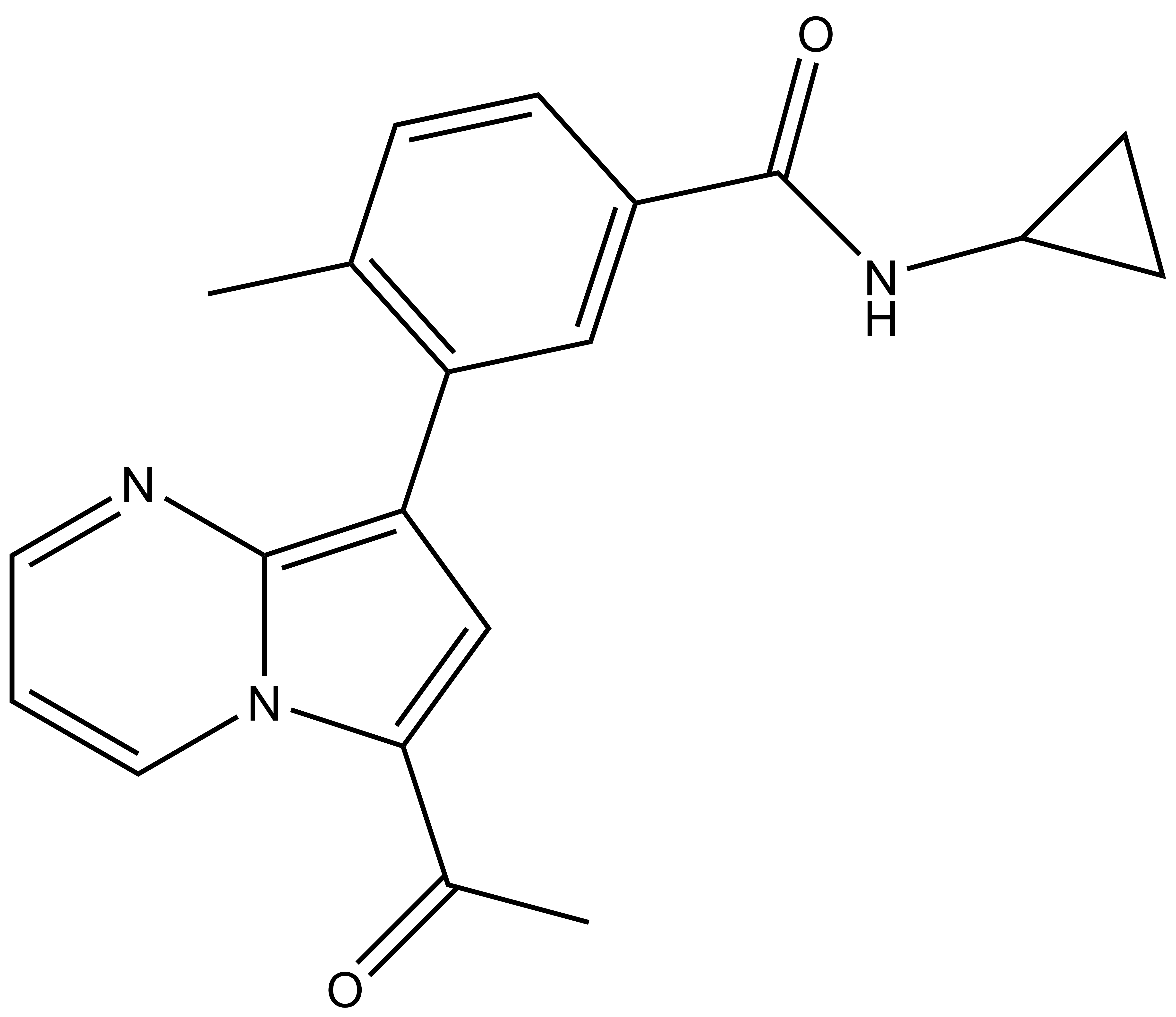
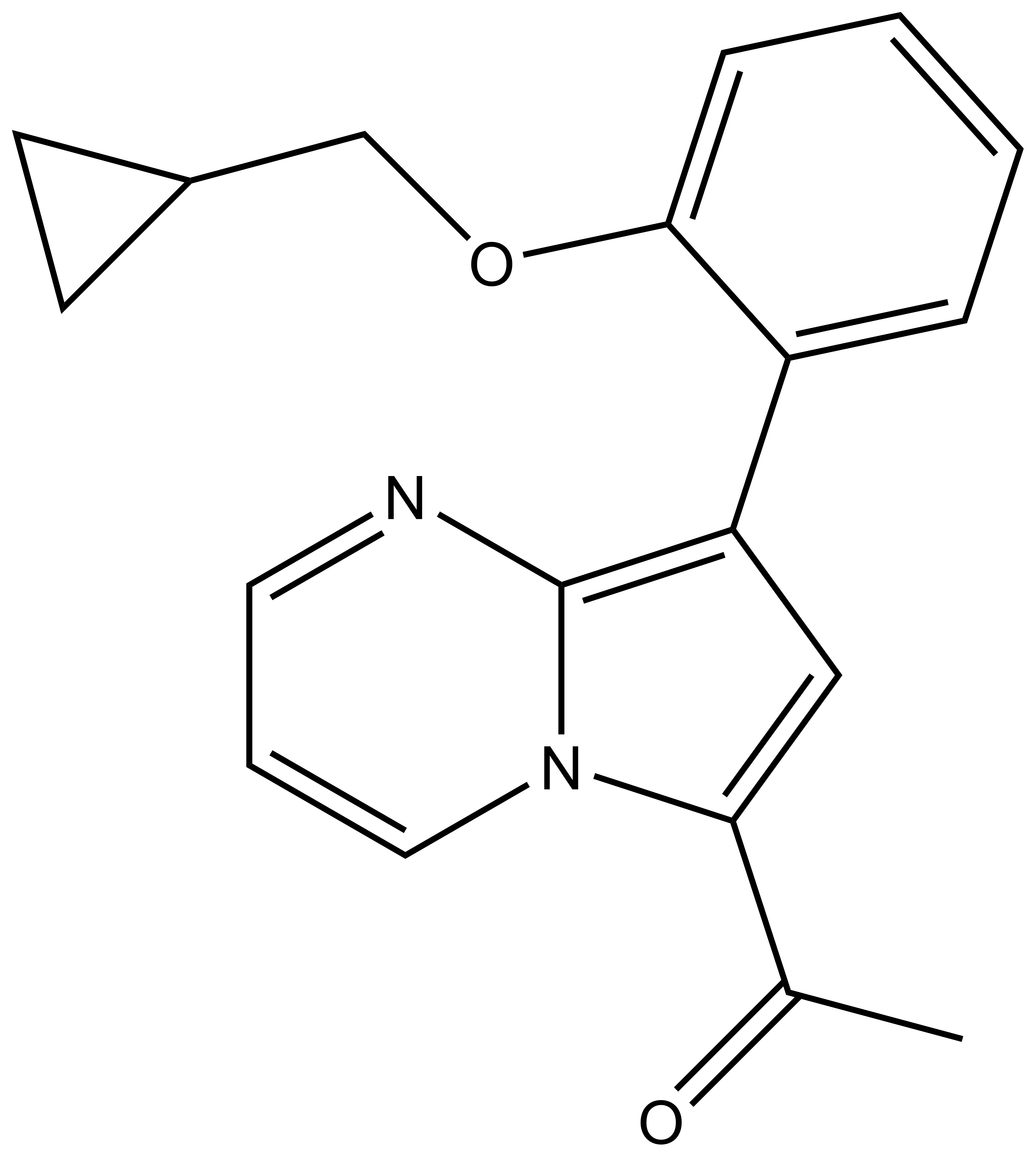
BAY-299 | | BAY-364 |
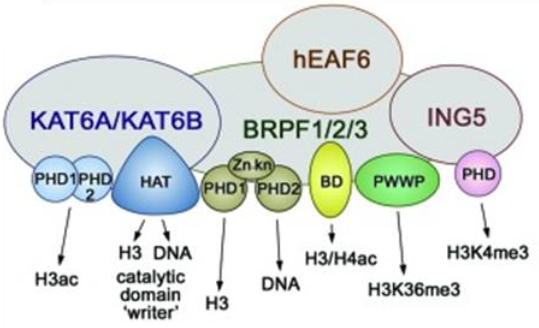
The BRPF (BRomodomain and PHD Finger) family consists of 3 members BRPF1, BRPF2 (also known as BRD1) and BRPF3 that act as scaffolding proteins to assemble HAT complexes of the MOZ/MORF family (MOZ, Ybf2/Sas3, Sas2, and Tip60). These MYST complexes have a tetrameric core containing BRPF, the tumour suppressor ING and Eaf6/EPC (enhancer of polycomb)-related scaffold subunits. MYST complexes play crucial roles in DNA repair, recombination, and replication as well as in transcription activation. MOZ is frequently translocated in acute myeloid leukemia and has an essential role in development and maintenance of hematopoietic stem cells[1].
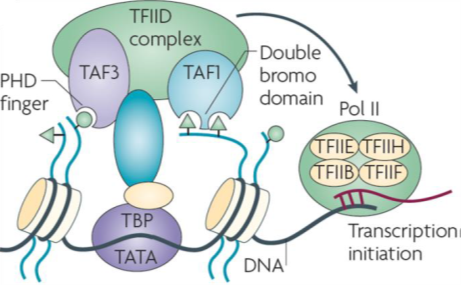
Transcription initiation factor TFIID subunits 1 (TAF1) is a component of the STAGA complex, which contains TRRAP, GCN5, TFIID, CBP/P300, mediator and Sp1, TAF1 is susceptible to oncogenic activation by MYC. Moreover, TAF1 has been shown to block p53 activity and inactivation of TAF1 triggers a DNA damage response. Additionally, the TFIID complex is vital to stem cell reprogramming. There have been few reports of selective inhibitors of TAF1 which are needed to help elucidate its biological role and potentially function to inhibit cancer cell growth and survival.
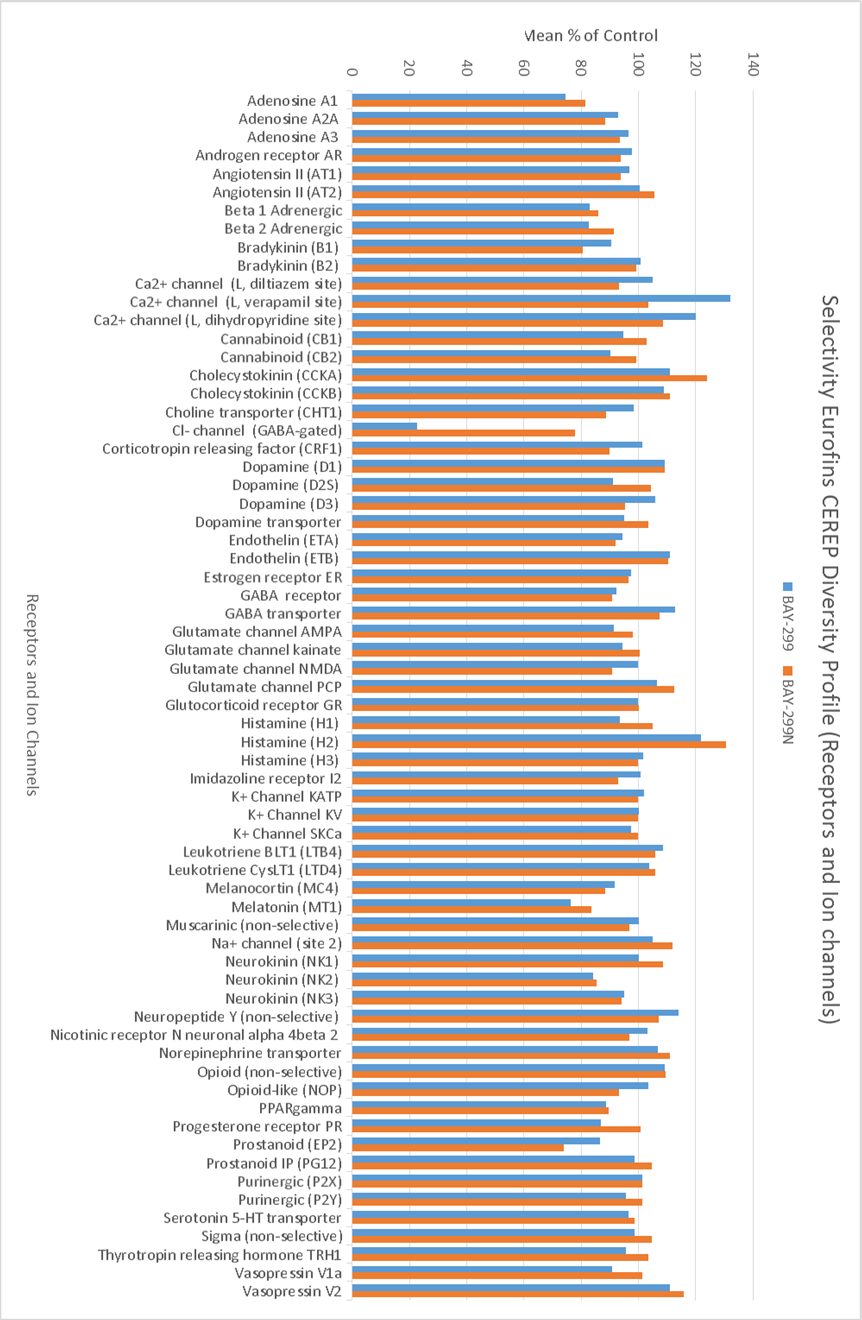
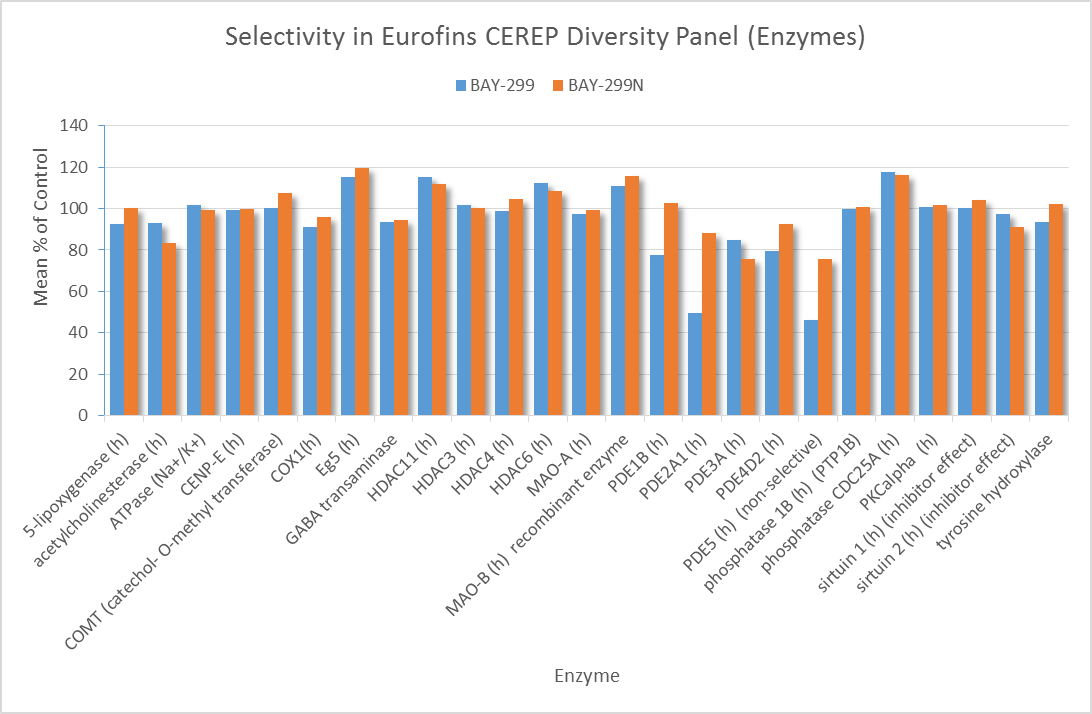
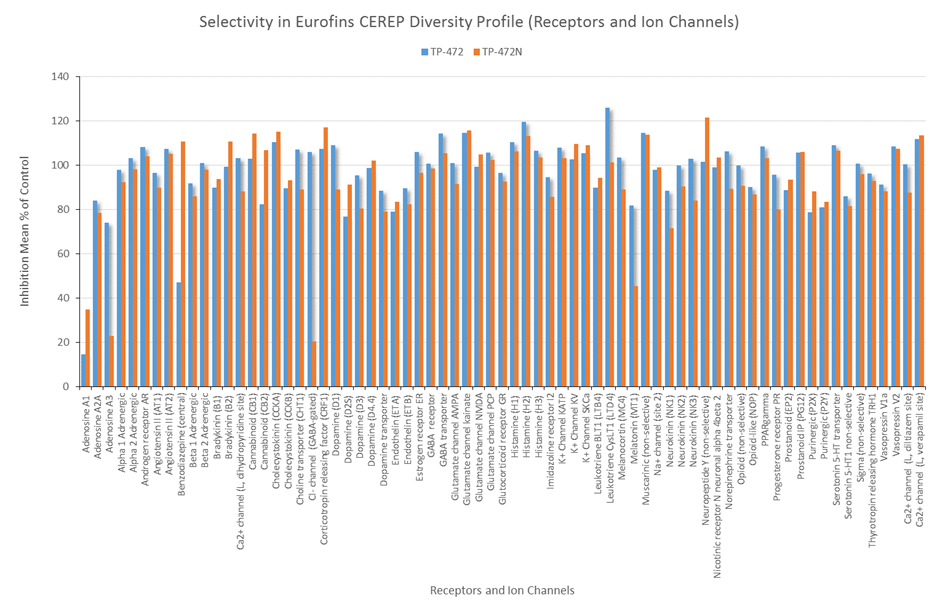
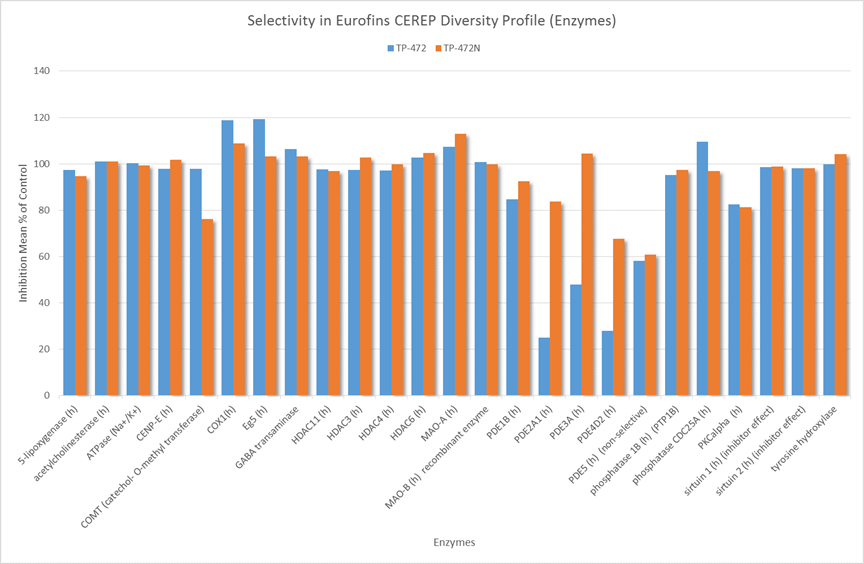
In a collaborative effort Bayer and the SGC have identified and characterised BAY-299 as a potent and selective inhibitor of BRD1 (BROMOscan® [2] IC50 6nM) and the second bromodomain of TAF1 (BROMOscan® [2] IC50 13nM). BAY-299 is selective over other bromodomains; >30-fold selective over the other members of the BRPF family, >30-fold selective over close neighbours BRD9 and ATAD2 and >300-fold selective over BRD4. BAY-299 has <1uM activity in the BRD1 and TAF1 NanoBRET™ cell assays [3]. BAY-299 has a molecular weight of 429.5 and is soluble to 10mg/L in aqueous solutions. The structurally similar BAY-364 (MW 401.4) is inactive against BRD1 (>20uM), has moderate activity against TAF1 (3uM) and is suitable for use as a negative control.